![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DOC for atrial flutter
|
Propranolol*
Verapamil* digoxin Starred- used first |
|
|
DOC for atrial fibrillation
|
Propranolol*
Amiodarone* anticoagulant therapy* dofetilide starred- used first |
|
|
DOC for AV nodal reentry
|
Propranolol*
Verapamil* digoxin starred- used first |
|
|
DOC for acute supraventricular tachycardia
|
Adenosine*
Verapamil starred- used first |
|
|
DOC for acute ventricular tachycardia
|
Lidocaine*
Amiodarone* |
|
|
DOC for ventricular fibrillation
|
Amiodarone*
Epinephrine* Lidocaine starred-used first |
|
|
Class IA drugs
|
Quinidine
Procainamide Disopyramide |
|
|
Class IB drugs
|
Lidocaine
Mexiletine tocainide |
|
|
Class IC drugs
|
Flecainide
Propafenone |
|
|
Class II drugs
|
Propranolol
metoprolol esmolol |
|
|
Class II MOA
|
inhibits phase 4 depolarization in SA and AV node.
B-adrenoreceptor blocker |
|
|
Class III drugs
|
Amiodarone
Sotalol dofelitide |
|
|
Class IV drugs
|
Verapamil
Diltiazem |
|
|
Class IV MOA
|
inhibits action potential in SA and AV node.
Ca 2+ channel blocker |
|
|
Other anti-arrhythmics not mentioned in the classes
|
digoxin and adenosine
|
|
|
Pt: reversible lupus erythematosus-like syndrome
|
procainamide
|
|
|
Negative ionotrophic effects and Vasoconstriction
|
Disopyramide
|
|
|
tx: ventricular arrhythmias arising during myocardial ischemia (IE MI)
|
Lidocaine
|
|
|
Tx: chronic tx of ventricular arrhthmias associated with previous MI
|
Mexiletine
|
|
|
Tx: ventricular tachyarrhythmias, pulmonary toxicity
|
Tocainide
|
|
|
Tx: refractory ventricular arrhythmias; useful in suppressing premature ventricular contraction
|
Flecainide
|
|
|
tx: reduces incidence of sudden arrhythmic death after myocardial infarction
|
Propranolol
|
|
|
Tx: wide spectrum cardiac anti-arrhythmatic; reduces the risk of bronchospasm
|
Metoprolol
|
|
|
tx: used for in acute arrhthmias that occur during surgery or ER situations
|
esmolol
|
|
|
SE: hyper-, Hypo-thydroidism, photosensitivity, etc
|
amiodarone
|
|
|
Long term therapy to decrease rate of sudden death following an acute MI.
|
sotalol
|
|
|
1st line agent in pts with persistent atrial fibrillation and HF or in those with CAD w/ impaired left ventricular function
|
dofelitide
|
|
|
tx: better for atrial arrhythmias. Also to treat reentrant supraventricular tachycardia.
|
Verapamil and dilitiazen
|
|
|
tx: control ventricular response rate in atrial fibrillation and flutter
|
Digoxin
|
|
|
DOC for abolishing acute supraventricular hypotension
|
adenosine
|
|
|
Reserved for life threatening Vent Arrhyth and to resuscitate pts in V-Fib
|
Bretylium
|
|
|
Rapid conversions of Atrial fib or flutter to normal sinus rhythm
|
Ibutilide
|
|
|
Which drugs can cause torsades?
|
Sotalol, procainamide, Quinidine
|
|
|
WHat are the side effects of amiodarone?
|
-thyroid abnormailies (hypo- and hyper-connected w high iodine content) (die to amiodaron’s structural relatedness to thyroxin
-photosensitive skin rashes -slate grey/blue discoloration of skin (smurfism) -pulmonary fibrosis -corneal micro deposits GI SE and elevated LFTs |
|
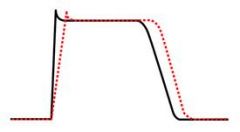
what class is this?
|
IA
|
|
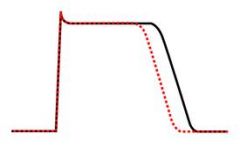
what class is this?
|
IB
|
|
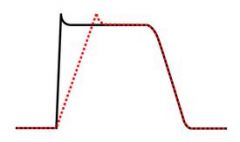
what class is this?
|
IC
|
|
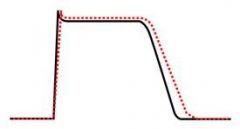
What class is this?
|
Class III
|

