![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Organic Compound
|
Always contain carbon, usually hydrogen & oxygen too.
Originally coined to refer to compounds made from living things, but now much can be made in lab. |
|
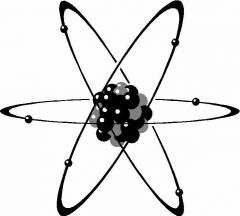
Atoms
|
Smallest unit of an element that retains characteristics of that element.
|
|
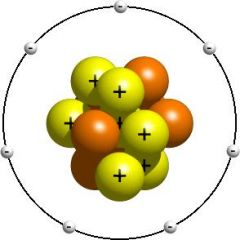
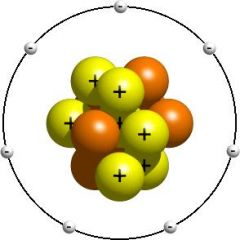
Atom Nucleus
|
Positively charged central portion of an atom.
|
|
|
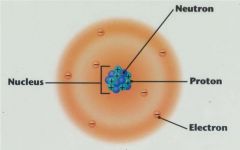
Proton
|
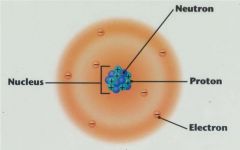
In Atom Nucleus, contribute to positive charge.
A subatomic particle. |
|
|
Neutrons
|
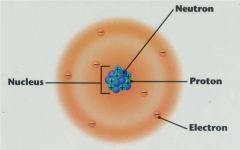
In Atom Nucleus, contribute mass, but no charge.
A subatomic particle. |
|
|
Electrons
|
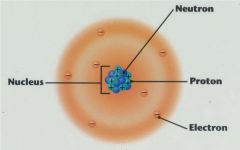
Outside of Atom Nucleus, negatively charged.
|
|
|
Synthesis
|
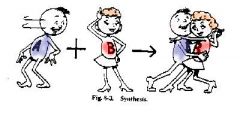
Requires energy, building up, putting together.
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
Releases energy, breaking down, taking apart.
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
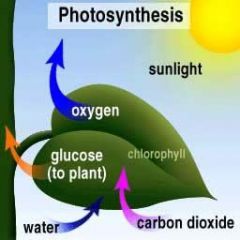
Autotrophs converting light energy into chemical energy.
|
|
|
Cellular Respiration
|
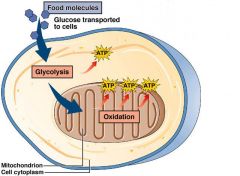
Breaking down food (sugars).
|
|
|
Macromolecules
|
Carbohydrates; Lipids;
Proteins; Nucleic Acids. 4 most important classes of molecules in living cells. |
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
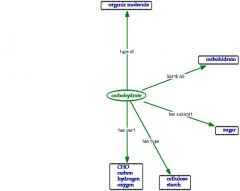
Contained in all living cells.
Carbon with Oxygen & Hydrogen in 2:1 ratio. |
|
|
Monosaccharides
|
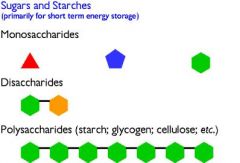
Simple sugars
Glucose |
|
|
Polysaccharides
|
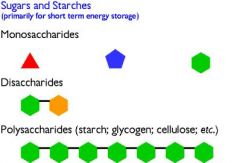
“Many sugars”
|
|
|
Plant Polysaccharides
|

Structure is cellulose.
Energy is stored in starch. |
|
|
Animal Polysaccharides
|
Structure is Chitin.
Energy is stored in Glycogen. |
|
|
Chitin
|
In animals, simple sugars made into complex molecules.
|
|
|
Glycogen
|

In animals, stored in muscles.
|

