![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
all cells have what 3 basic components:
1. 2. 3. |
1. cell envelope (barrier)
2. genetic material 3. cytoplasm |
|
|
what types of cells have cell walls:
|
plant and most prokaryotic cells
|
|
|
viruses are considered particles and not cells and have 2 of the basic components common to all cells, they are:
1. 2. |
cell envelope
genetic material |
|
|
All organisms have been divided into two categories:
1. 2. |
prokaryotes
eukaryotes |
|
|
prokaryotes have organelles:
(true/false) |
false
|
|
|
prokaryotes do not have a nucleus but instead have a ... which is ...
|
nucleoid
a region in the cell where the chromosomes are located |
|
|
prokaryotic ribosomes are ...
Eukaryotic ribosomes are ... |
70s
80s |
|
|
where would you find 70s ribosomes:
|
mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
|
|
|
what are the 3 microbial domains:
1. 2. 3. |
bacteria
archaea eukarya |
|
|
classification of organisms on the basis of the evolutionary relatedness is called ...
|
phylogeny
|
|
|
Mitochondria appear to be related to the ...
|
modern purple bacteria
|
|
|
Many antibiotics that interfere with protein synthesis in bacteria will also affect what:
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
what are the names of the following bacterial shapes:
1. single cells 2. chains of two cells |
cocci
diplococci |
|
|
what are the names of the following bacterial shapes:
1. irregular clusters of cells 2. long chains of cells 3. rod shaped cells |
1. staphylococci
2. streptococci 3. bacilli (singular-bacillus) |
|
|
what are the names of the following bacterial shapes:
1. curved or spiral shaped rods 2. tightly coiled |
1. called spirilla (singular-spirillum)
2. spirochetes |
|
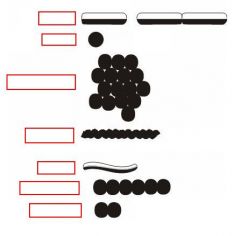
identify the bacterial shapes:
|
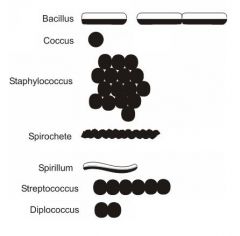
(see figure)
|
|
|
what are the cocci shaped microorganisms:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. |
1. Chlamydia
2. Chlamydophila 3. Enterococcus 4. Moraxella 5. Neisseria 6. Staphylococcus 7. Streptococcus |
|
|
what are the curved or spiral shaped microorganisms:
1. 2. |
1. Campylobacter
2. Helicobacter |
|
|
what are the spirochete shaped microorganisms:
1. 2. 3. |
1. Borrelia
2. Leptospira 3. Treponema |
|
|
what are the filamentous shaped microorganisms:
1. 2. |
1. Actinomyces
2. Mycoplasma |
|
|
what is the diameter of a typical
coccus: rod: red blood cell: |
1. 2μm
2. 1μm 3. 6μm |
|
|
how many layers is the cell envelope in most bacteria:
identify the layer(s) |
at least 2
cytoplasmic membrane and cell wall |
|
|
gram positive bacteria stain ... and grand negative bacteria stain ...
|
purple/blue
pink/red |
|
|
what is the difference between gram positive and gram negative cell walls:
|
gram positive: cell wall has thick layer of peptidoglycan
gram negative: cell wall has thin layer of peptidoglycan and surrounded by second membrane called outer membrane |

