![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the of the clinical lab is to provide you with information, the information you need from the lab is:
1. 2. |
1. identify the presence or absence of suspected pathogen
2. antibiotic sensitivity profile of suspected pathogen |
|
|
from where does sputum come:
|
the lungs
|
|
|
what types of collected specimens for the clinical lab should be sterile but are usually contaminated:
1. 2. |
urine
sputum |
|
|
..., ... and ... are all normally sterile and any bacteria found in these samples are potential pathogens
|
Blood
CSF tissue samples |
|
|
what is the major drawback to identifying bacteria by culture:
|
takes 2 to 3 days to get results
|
|
|
what is specificity:
|
measure of how often the test or method gives false positive results
|
|
|
what is sensitivity:
|
measure of how often the test or method gives false negative results
|
|
|
acid fast stains what organism discussed in class:
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
if a sample of urethral discharge from a male patient shows Gram-negative diplococci, ... is the most likely pathogen
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
a patient with a persistent cough, night sweats, fever and shows an acid-fast bacillus in their sputum, the organism is most likely ...
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
... staining is a very specific method of identifying an organism
|
Fluorescent antibody
|
|
|
what would you use to check for Helicobacter pylori in a stool sample:
|
enzyme immunoassay (EIA) test
|
|
|
the following describes what organism:
This organism causes ulcers and can be grown in culture, however it requires a gastric biopsy to get a tissue sample. An alternative is to use antibodies made against it to detect the presence of the organism in stool samples |
Helicobacter pylori
|
|
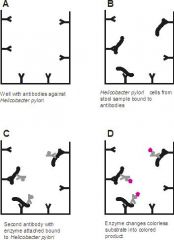
what does the above picture depict:
|
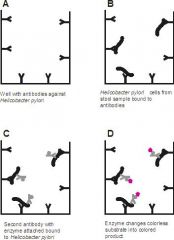
enzyme immunoassay (EIA) test
|
|
|
Chlamydia trachomatis must be grown in tissue culture, but since it has a specific DNA sequence, what kind of kit has been developed to detect it:
|
PCR
|
|
|
what is an indirect method of determining if a person has an infection with a given pathogen
|
serological tests to see if the patient has antibodies
|
|
|
what is the organism that causes Rocky Mountain spotted fever:
|
Rickettsia rickettsii
|
|
|
what is the problem with serology:
|
it takes several days to weeks for antibodies titers to rise high enough to be sure an active infection is taking place
|
|
|
the following describes what organism:
this organism is part of the normal intestinal flora and if a person that carries this strain is given antibiotics that wipe out a large portion of the bacteria, it will overgrow and produce toxin |
Clostridium difficile
|
|
|
how would you test to see if Clostridium difficile was producing toxin:
|
test fecal specimen with antibodies against the toxin
|
|
|
The Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy provides recommendations for antibiotics to use until the ... report comes back.
|
sensitivity
|
|
|
resistance to the antibiotic vancomycin evolved in ... then the genes for vancomycin resistance spread to ...
|
Enterococcus
Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
are all strains of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to vancomycin:
|
no
|
|
|
what is the name of the organism that causes tuberculosis:
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
what does the following describe:
specimen is plated on agar and grown overnight then tests are performed to identify the likely pathogen. a suspension is spread on an agar plate and paper disks containing different antibiotics are placed on the agar surface then incubated overnight. |
Antibiotic Disk Diffusion Tests
|
|
|
the lowest concentration of an antibiotic that will prevent growth of the bacterium:
|
minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
|
|
|
what would be a faster method to determine the presence of antibiotic resistance other than antibiotic disk diffusion tests:
|
PCR
|

