![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the cell membrane is also called the ... or ...
|
plasma membrane
plasmalemma |
|
|
the cell membrane is composed of a ... bilayer and ...
|
phospholipid
proteins |
|
|
the cytoplasmic side is the ...
|
interior
|
|
|
the extracellular environment of the cell is the ...
|
outside
|
|
|
what are 2 functions of the cell membrane:
1. 2. |
1. communication with the extracellular environment and other cells
2. selectively controls entry and exit of ions and other substances into/out of cell. |
|
|
plasma membrane is ... nm thick and only visible by ...
|
8-10
transmission electron microscopy |
|
|
amphipathic phospholipids have a ... portion and a ... portion
|
hydrophobic
hydrophilic |
|
|
... membrane proteins transverse the membrane while ... membranes are only attached to the membrane
|
integral
peripheral |
|
|
membrane surface also contains a variety of carbohydrate moieties
such as ... and ... |
glycoproteins
glycolipids |
|
|
glycolipids and glycoproteins function:
1. 2. 3. |
1. Cell-to-cell recognition
2. Receptor function 3. Repel other cells (RBCs) |
|
|
what happens when you remove the sugar groups for cell surfaces?
|
sometimes the cells don’t function properly
|
|
|
Cell coat or ... is a sticky coat made up of ... groups
|
glycocalyx
carbohydrate |
|
|
carbohydrate components are exclusively located on the ... surfaces of cell membranes
|
extracellular
|
|
|
the cell membrane is said to be ... because integral membrane proteins can move laterally within the plane of the lipid bilayer.
|
fluid
|
|
|
lateral movement of membrane proteins may be important in the mediation of ...
|
hormone response
|
|
|
Movement of these proteins are restricted by their interaction with cytoskeletal proteins located in the cells cytoplasm or with other proteins located in the extracellular matrix or adjacent cells (e.g., junctions). briefly describe this mechanism:
|
proteins can only go so far up in the membrane before they are stopped by the tight junction
|
|
|
... allow cells to respond to specific chemical signals
|
cell receptors
|
|
|
cell receptors are (integral/peripheral) membrane proteins that convey their signal to various ...
|
integral
internal messengers |
|
|
water molecules like to form complex cage-like structures known as ...
|
clathrates
|
|
|
the 4 major membrane phospholipids are:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
phosphatidylcholine (PC)
phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) phosphatidylserine (PS) spingomyelin (SM) |
|
|
why do membrane phospholipids usually contain C16 saturated fatty acids?
|
longer saturated fatty acids would be solids at physiologic temperatures
|
|
|
membrane phospholipids also contain longer-chain (>c16) ... fatty acids
|
unsaturated
|
|
|
3 common saturated fatty acids found within membrane phospholipids are:
1. 2. 3. |
Myristate (C14)
Palmitate (C16) Stearate (C18) |
|
|
5 common unsaturated fatty acids found within membrane phospholipids are:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
Palmitoleate (C16:1)
Oleate (C18:1) Linoleate (C18:2) Linolenate (C18:3) Arachidonate (C20:4) |
|
|
what are the 2 other major type of membrane lipids besides phospholipids:
1. 2. |
cholesterol
glycolipids |
|
|
cholesterol makes up makes up as much as ... of the plasma membrane
|
1/2
|
|
|
a. polar
b. nonpolar cholesterol |
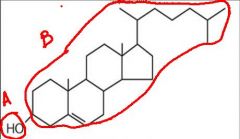
identify which part of this molecule is polar and which is non polar and what is this molecule?
|
|
|
what is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
1. 2. |
control membrane fluidity
provides a more solid bed for membrane proteins to stick to at the cell surface |
|
|
lipid rafts are ...
|
regions that are highly enriched in cholesterol and sphingolipid
|
|
|
invaginated lipid rafts domains are called ...
|
caveolae
|
|
|
the cell membrane is said to be ... because (1,2,3) are mostly found on the outer leaflet of the membrane and ... charged phospholipid head groups (PE, PS, PI) are more abundant on inner leaflet of the membrane
|
asymmetrical
Glycolipids, PC, sphingomyelin negatively |
|
|
membranes may differ in two regards:
1. 2. |
from different cell types
different organelles within the same cell |
|
|
the following describes what:
biological membranes can be considered as a two-dimensional liquid where all lipid and protein molecules diffuse more or less freely into their respective positions within the membrane |
fluid mosaic model
|
|
|
Ion channels, pumps, G protein-coupled receptors are examples of what type of membrane protein?
|
integral
|
|
|
G proteins, enzymes, receptors are examples of what type of membrane proteins?
|
peripheral
|
|
|
... membrane proteins require a detergent (such as SDS or Triton X-100) or some other nonpolar solvent to be displaced.
|
integral
|
|
|
... is most common structural motif found in integral proteins
|
alpha-helix
|
|
|
... motif is found in some prokaryotic membranes (called porins)
|
ß-barrel
|
|
|
integral membrane proteins must be must be ... having hydrophobic amino acid R-groups contact the membrane, while more polar R-groups are found at the intra- and extracytoplasmic ends
|
amphipathic
|
|
|
several transmembrane ... can collectively form a channel in the membrane that allows for movement of ... or ... substances across the nonpolar membrane
|
alpha-helices
ionic polar |

