![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
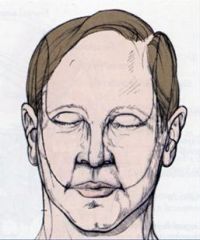
identify the dermatome distribution of trigeminal nerve:
|
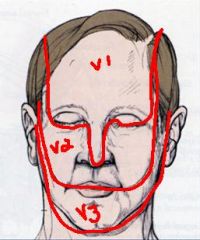
(see diagram)
|
|
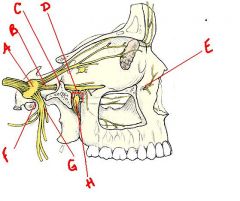
identify the following structures:
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. |
a. trigeminal ganglion
b. maxillary nerve v2 c. foramen rotundum d. pterygopalatine fossa e. infraorbital foramen f. foramen ovale g. mandibular nerve v3 h. pterygopalatine ganlion |
|
|
infratemporal fossa
|
identify this space:
|
|
|
what are the contents of the infratemporal fossa:
a. b. c. d. e. |
a. Temporalis
b. Medial Pterygoid c. Lateral Pterygoid d. V3 Mandibular Nerve e. Maxillary Artery |
|
|
what are the 4 major sensory branches of v3 (mandibular branch of trigeminal):
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. Auriculotemporal
2. Buccal 3. Inferior Alveolar 4. Lingual |
|
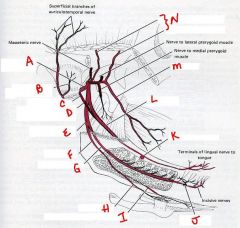
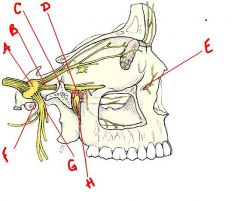
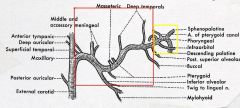
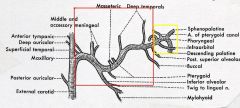
identify the labeled nerves:
|
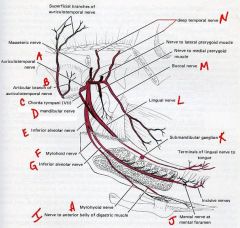
(see figure)
|
|
|
what does auriculotemporal innervate:
|
Skin around the ear
|
|
|
what does lingual innervate:
|
anterior 2/3rds of tongue for general sense
|
|
|
what does chorda tympani innervate:
|
taste to ant. 2/3rds of tongue, and secretomotor to sublingual and submandibular glands.
|
|
|
what does inferior alveolar innervate:
|
sensory innervation to the lower teeth
|
|
|
what does mylohyoid innervate:
|
motor fibers to the mylohyoid and anterior belly of the digastric
|
|
identify the labeled structures:
|
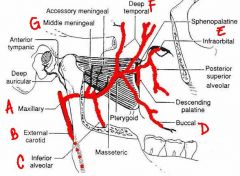
(see figure)
|
|
identify the anatomical area in the red box and in the yellow box:
|
red=infratemporal fossa
yellow=pterygomaxillary fissure (leads to pterygopalatine fossa) |
|
|
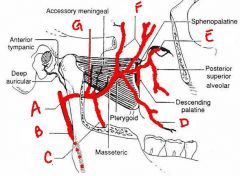
nerve supply to parotid gland comes from ... that hitch a ride with a branch of ...
|
parasympathetics from CN9
V3 |
|
|
Preganglionic parasympathetics leave CN 9 distal to the jugular foramen as the tympanic branch. Re-enters skull through jugular foramen forms a plexus in the middle ear, reappears in the middle cranial fossa as the ... that
lies lateral to the ... and exits thru foramen ovale. the preganglionics synapse in the ... |
lesser petrossal nerve
greater petrossal nerve otic ganglion |
|
|
... nerve originates from trunk of V3 splits around middle meningeal artery and contains postganglionics fibers from ... ganglion and distributes these fibers to parotid gland.
|
auriculotemporic
otic |

