![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
name the foramina in roof of the medulla that connect the ventricles with the subarachnoidal space
|
Luschka x 2
Magendie x 1 |
|
|
what foramina drains the fourth ventricle laterally into the subarachnoidal space
|
the 2 foramen of Luschka
|
|
|
what drains the fourth ventricle posteroinferiorly into cerebellomedullary cistern
|
Magendie's foramen
|
|
|
ventricle circulation starts from the 2 ... that are found in the ... then through the ... to the ... to the ... then off to the ...
|
lateral ventricles
cerebral hemispheres interventricular foramina (right & left) Third ventricle (midline; thalamus) cerebral aqueduct (midbrain) fourth ventricle (pons & medulla) |
|
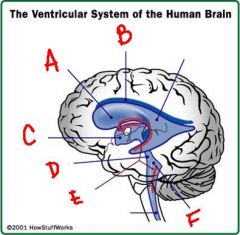
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. e. f. |
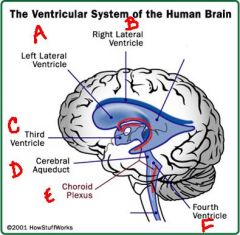
a. lateral ventricle
b. lateral ventricle c. third ventricle d. cerebral aqueduct e. choroid plexus f. fourth ventricle |
|
|
hydrocephalus is ...
|
is an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid
|
|
|
what are the 3 ways you can get a hydrocephalus condition:
1. 2. 3. |
1. increase in production of cerebrospinal fluid
2. blockage in system 3. impaired absorption of cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
describe the obstructive classification of hydrocephalus:
|
obstruction within the ventricular system
|
|
|
describe the communicating classification of hydrocephalus:
|
obstruction in the subarachnoid space or venous sinuses
|
|
|
a. abnormal
b. normal |
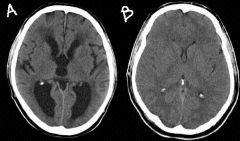
identify the normal and abnormal brains:
a. b. |
|
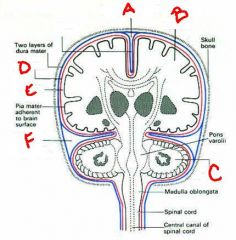
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. e. f. |
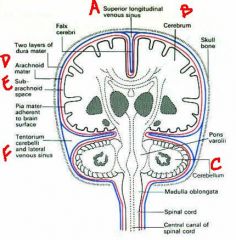
a. superior longitudinal venous sinus (superior sagittal)
b. cerebrum c. cerebellum d. arachnoid mater e. subarachnoid space f. lateral venous sinus (bonus question: so where is the inferior sagittal sinus) |
|
|
a. cavernous sinus
b. superior sagittal c. inferior sagittal d. straight e. sigmoid f. transverse g. confluens |
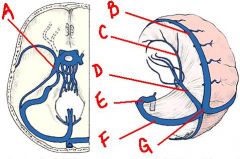
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. |
|
|
a. superior sagittal
b. great cerebral vein c. opthalmic vein d. facial vein e. cavernous sinus f. inferior petrosal g. internal jugular v. h. sigmoid i. superior petrosal j. transverse k. straight l. inferior sagittal m. confluens |
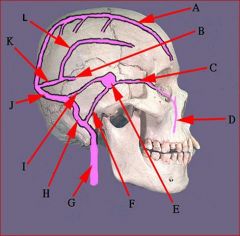
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. |
|
|
c. sigmoid
e. confluens g. transverse h. superior petrosal i. inferior petrosal j. cavernous k. superior sagittal |
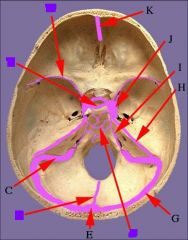
identify the labeled structures:
c. e. g. h. i. j. k. |
|
|
the medial angle of the eye, the nose and the lips is known as the ... this area usually drains through the ... but due to ... venous blood may go, via the ophthalmic vein, to the ... this can lead to damage of the ... running through the cavernous sinus.
|
danger triangle of the face
facial vein anastomoses cavernous sinus nerves |
|
|
arteries at the base of the brain supply all parts of the brain. there are 2 sources:
1. 2. |
1. Vertebral aa.
2. Internal carotid aa. |
|
|
the vertebral arteries originate from the ... then they travel through the ... of C1-... but not ... they then join to form the ... artery at the ... and the ... artery ends and bifurcates into the 2 ... arteries
|
subclavian artery
transverse foramina c6 c7 basilar artery pons basilar artery 2 posterior cerebral arteries |
|
|
the internal carotid arteries originate from ... and run up through the ... and partially through ... it branches into ... and ... and continues laterally as ...
|
common carotid artery
carotid canal Foramen lacerum anterior cerebral posterior communicating middle cerebral artery |
|
|
a. anterior communicating artery
b. cn2 c. middle cerebral artery d. cn3 e. basilar artery f. internal carotid artery g. posterior communicating artery h. posterior cerebral artery i. superior cerebellar artery |
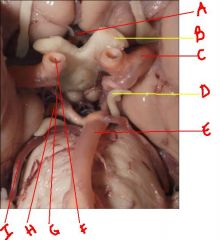
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. |
|
|
berry
anterior circle of willis anterior communicating posterior communicating middle cerebral |
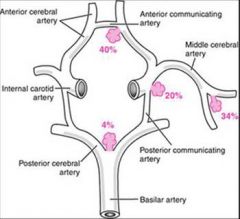
... aneurysms occur mostly in the ... part of the ... at branch points of ... and ... and ...
|
|
|
a. vertebral artery
b. anterior spinal artery c. posterior spinal artery d. posterior inferior cerebellar artery |
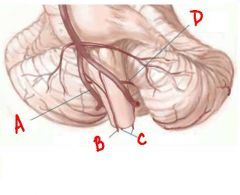
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. |
|
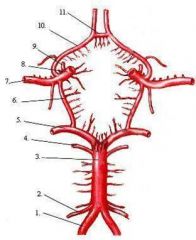
identify the labeled structures:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. |
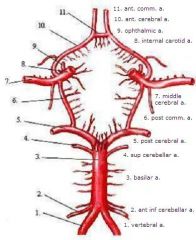
1. vertebral a.
2. ant inf cerebellar a. 3. basilar a. 4. sup cerebellar a. 5. post cerebral a. 6. post comm. a. 7. middle cerebral a. 8. internal carotid a. 9. ophthalmic a. 10. ant. cerebral a. 11. ant. comm. a. |

