![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
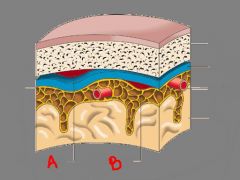
that tissue thats lying outside of the skull is called ...
|
scalp
|
|
|
the scalp is composed of:
s. c. a. l. p. |
skin
connective tissue aponeurosis (connects 2 muscles: frontalis & ccipitalis) loose connective tissue periosteum |
|
|
aponeurosis is ...
|
specialized tendon that attaches muscles to bones
|
|
|
a. temporalis
b. frontalis c. occipitalis d. masseter |
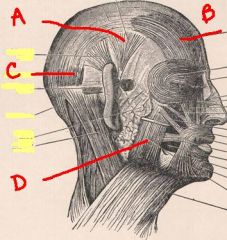
identify the labeled muscles in the head:
a. b. c. d. |
|
|
blood supply to the scalp is primarily from ... and the frontal area is supplied by ...
|
external carotid a.
branches of internal carotid a. |
|
|
the occipitalis and the frontalis are connected by ...
|
aponeurosis (epicranial)
|
|
|
from a scalp laceration, profuse bleeding is due to ... and ...
|
abundant anastomoses of arteries
Surrounding connective tissue attached to arteries prevents contraction |
|
|
scalp lacerations can be ... if large enough
|
fatal
|
|
|
what are meninges
|
connective tissue
|
|
|
meninges surround the ... and ...
|
brain
spinal cord |
|
|
the brain and spinal cord together form the ...
|
central nervous system (cns)
|
|
|
the three layers of the meninges are:
1. 2. 3. |
1. dura
2. arachnoid 3. pia |
|
|
the thickest of the meninges is the ... and it is the outermost layer
|
dura
|
|
|
this meninges layer is attached intimately with the brain and cannot be pealed away.
|
pia
|
|
|
this meninges layer is thin and spider-like and lies just beneath the dura.
|
arachnoid
|
|
|
this benign tumor of the brain is typically encapsulated and grows on the underside of the dura and does not invade the brain
|
meningioma
|
|
|
there are/is ... layer(s) of dura around the spinal cord and ... layer(s) of dura around the brain
|
one
two |
|
|
... is the dura layer that surrounds the brain but lies closest to the bone
|
periosteal
|
|
|
... is the dura layer that is closest to the brain
|
meningeal
|
|
|
... is the dura that surrounds the brain but does not surround the spinal cord
|
periosteal
|
|
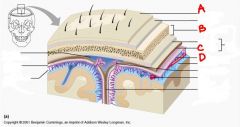
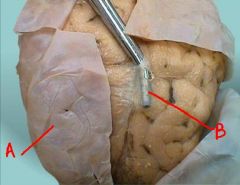
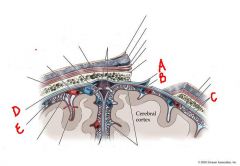
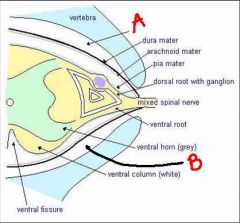
identify the labeled structures in the figure:
a. b. c. d. |
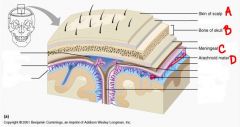
a. scalp
b. skull c. meningeal d. arachnoid |
|
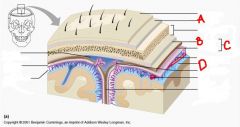
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. |
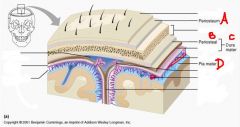
a. periosteum
b. periosteal c. dura mater d. pia mater |
|
|
a. dura mater
b. arachnoid membrane |
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. |
|
|
a. pia mater
b. arachnoid c. dura mater |
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. |
|
|
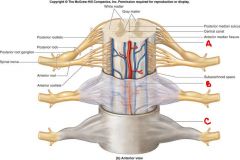
a. anterior cranial fossa (V)
b. middle cranial fossa (V) c. posterior cranial fossa (C2,3) d. foramen magnum |
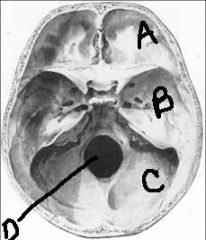
identify the labeled structures and their innervations:
a. b. c. identify the labeled structure: d. |
|
|
there are ... in-foldings of meningeal layer in the skull
|
3
|
|
|
the meningeal folding ... lies mid-sagittal between cerebral hemispheres
|
falx cerebri
|
|
|
the meningeal folding ... lies mid-sagittal between cerebellar hemispheres
|
falx cerebelli (small)
|
|
|
the meningeal folding ... lies horizontal between occipital lobes and cerebellum
|
tentorium cerebelli
|
|
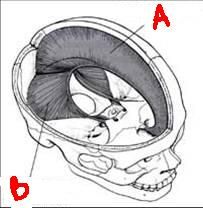
name the labeled structures:
a. b. |
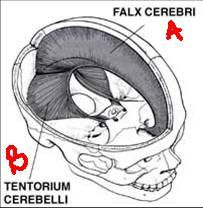
a. falx cerebri
b. tentorium cerebelli |
|
|
is the epidural space in the brain real or potential?
|
potential - blood can get in here and create a real space
|
|
|
is the epidural space in the spinal cord real or potential?
|
real - contains fat & veins; here is where you do epidural
anesthesia |
|
|
is the subdural space real or potential?
|
potential
|
|
|
where is the subdural space located?
|
below the dura and on top of the arachnoid
|
|
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. e. |
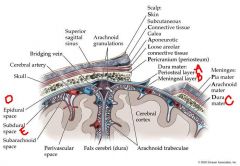
a. periosteal layer
b. meningeal layer c. dura mater d. epidural space e. subdural space |
|
|
a. extradural (epidural)
b. subdural |
identify where the hemorrhage is:
a. b. |
|
|
a. epidural space
b. epidural space |
identify the area labeled:
a. b. |
|
|
epidural
subdural intracerebral |
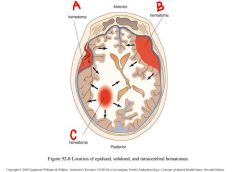
identify the labeled hematomas:
a. b. c. |
|
|
pterion
-weakest part of the skull -middle meningeal artery runs beneath it -bone very thin/fragile -a blow to the pterion may rupture the artery causing an extradural haematoma. |
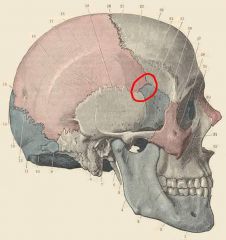
name the circled area and what is it's significance?
|
|
|
is the subarachnoid space real or potential?
|
real
|
|
|
what do you find in the subarachnoid space?
|
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
|
|
|
where is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) produced?
|
choroid plexus (in ventricles)
|
|
|
what is the function of the arachnoid granulations?
|
“transfer” CSF to superior sagittal sinus (venous blood)
|
|
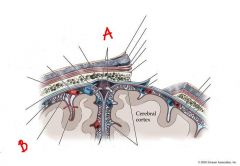
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. |
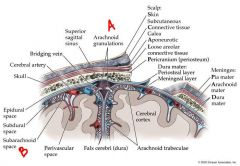
a. arachnoid granulations
b. subarachnoid space |
|
|
what does the subarachnoid space contain?
|
cerebral arteries and veins and csf
|
|
|
what is significant about the pia attachment?
|
intimately attached to brain = no sub-pial space
|
|
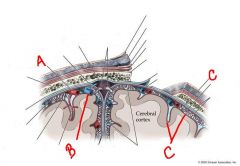
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. |
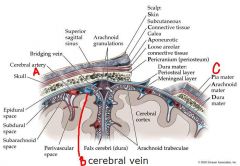
a. cerebral artery
b. cerebral vein c. pia mater |
|
|
... are structures in the brain that are filled with ... that has been produced by the choroid plexus
|
ventricles
cerebrospinal fluid-CSF |
|
|
where does one find the "choroid plexus"
|
in all ventricles of the brain
|
|
|
the ... are a system of four communicating cavities within the brain that are continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord
|
ventricles
|

