![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lipids are generally (hydrophobic/hydrophilic), soluble in ... and largely insoluble in ...
|
hydrophobic
organic solvents water |
|
|
name 7 functions of lipids:
|
membranes
energy reserves cushion vital organs insulation vitamins hormones chemical messengers |
|
|
how much fat is in the average american diet?
|
38%
|
|
|
what pathological conditions are related to lipids:
|
Obesity
Cardiovascular disease Atherosclerosis Diabetes Cancer Metabolic syndromes Lipid Storage Diseases alzheimer's disease |
|
|
what are the 5 classes of lipids?
|
Triglycerides
Phospholipids Sphingolipids (spingophospholipids and glycolipids) Eicosanoids Cholesterol |
|
|
what are the building blocks of lipids?
|
fatty acids
|
|
|
Chemically, fatty acids can be described as long-chain ... acids
|
monocarboxylic
|
|
|
length of the fatty acid chain usually ranges from ... to ...
|
12
24 |
|
|
why do fatty acids have an even number of carbon atoms?
|
all derived from acetyl CoA precursor, the 2-carbon building block
|
|
|
a. alpha
b. omega |
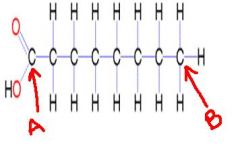
identify the labeled carbons:
a. b. |
|
|
In ... nomenclature fatty acids have an “-oic acid” suffix.
|
IUPAC
|
|
|
In common nomenclature, the suffix is usually ...
|
“-ic”
|
|
|
Fatty acids can also be abbreviated using the number of carbons in the fatty acid chain, followed by a colon and the number of ... present, while ... or ... indicate positions of double bonds
|
unsaturated bonds or double
Δ ω |
|
|
identify the type of nomenclature of the following fatty acid:
octadecanoic acid = stearic acid = C18:0 |
systemic name = common name = symbol
|
|
|
fatty acids without any double bonds are said to be ...
|
saturated
|
|
|
animal fats are solid because the saturated fatty acid molecules are ...
|
packed together very tightly
|
|
|
... fatty acids have ... bonds that form "kinks" or bends that cause the fatty acid molecules to pack loosely
|
unsaturated
double |
|
|
mono- and polyunsaturated fats are in the form of a ...
|
liquid
|
|
|
a. saturated
b. unsaturated |
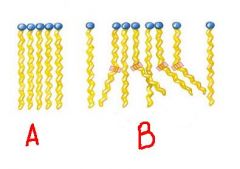
what kind of fatty acid is a. and what kind of fatty acid is b.
|
|
|
Unsaturated fatty acids can occur either in cis or trans geometric isomers. In naturally occurring fatty acids, the double bonds are in the ...-configuration. ...-fats are found in fried and processed foods and contribute to coronary artery disease and can be carcinogenic.
|
cis
trans |
|
|
Free fatty acids are an important fuel source and are preferred by ... and ... to glucose).
|
heart
skeletal muscle |
|
|
triglyceride structure: glycerol is esterified with ...
|
three fatty acids
|
|
|
triglyceride
|
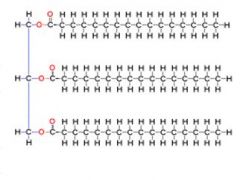
identify this molecule:
|
|
|
main function of triglycerides is ...
|
energy storage
|
|
|
any extra calories consumed will be stored as ...
|
triglycerides
|
|
|
glycerol
|
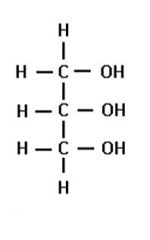
identify this molecule:
|
|
|
Triglyceride Levels (mg/dL):
Normal: < ... Borderline High: ... High: ... Very High: ... |
150
150-199 200-499 500 or above |
|
|
High triglyceride levels may be due to …
|
Cirrhosis, alcoholism
Diet low in protein, high in carbohydrates Hypothyroidism Pancreatitis Poorly controlled diabetes Nephrotic syndrome Familial hyperlipoproteinemia |
|
|
in ... the carboxyl group of each fatty acid is esterified to the hydroxyl groups on carbon-1 and carbon-2 of the glycerol molecule. The phosphate group is attached to carbon-3 by an ester link.
|
phospholipids
|
|
|
how many fatty acids are attached to a phospholipid?
|
2
|
|
|
Phospholipids are ... molecules, meaning they have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties.
|
amphipathic
|
|
|
phospholipid
|
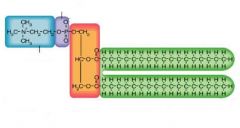
identify this molecule:
|
|
|
One of the primary functions of phospholipids is to serve as the main constituent of ...
|
cell membranes
|
|
|
in phospholipids, one of the fatty acids replaced with a phosphoric acid esterified to a functional group:
c... e... s... g... i... |
choline
ethanolamine serine glycerol inositol |
|
|
... are fats that resemble phoshatidylcholine, except the fatty acid at C1 of glycerol contains either an O-alkyl (-O-CH2-) or O-alkenyl ether (-O-CH=CH-) species.
|
plasmalogens
|
|
|
... are highly enriched in neuronal membranes and may act as endogenous antioxidants within cells
|
plasmalogens
|
|
|
a. glycerol
b. choline plasmalogen |
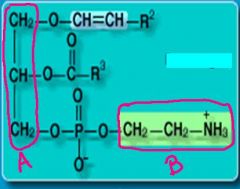
identify the part of the molecule labeled:
a. b. and identify the type of fatty acid it is .. |
|
|
An example of a plasmalogen is ... which is an important mediator of hypersensitivity and inflammation.
|
platelet activating factor (PAF)
|
|
|
in sphingolipids, the backbone is ... derived from ... rather than glycerol
|
sphingosine
serine |
|
|
examples of sphingolipids include:
a. b. c. |
a. ceramides
b. sphingomyelin b. glycolipids |
|
|
sphingosine
|
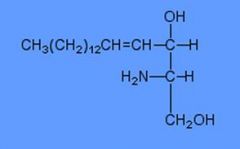
identify this molecule:
|
|
|
what type of lipid helps to form the myelin sheath surrounding axons and functions in cell recognition and cell signaling.
|
sphingolipids
|
|
|
what type of lipid helps to form a mechanically stable and chemically resistant barrier within plasma membranes?
|
sphingolipids
|
|
|
... are oxygenated derivatives of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids
|
eicosanoids
|
|
|
what enzymes are used to form eicosanoids?
|
cyclooxygenase (COX) lipoxygenase
|
|
|
ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids are named for where there ... bond occurs.
|
double
|
|
|
cyclooxygenase (COX) is blocked by ...
|
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
|
|
|
the 4 main groups of eicosanoids are:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. leukotrienes
2. prostaglandins 3. prostacyclins 4. thromboxanes |
|
|
... are major players in inflammatory response
|
eicosanoids
|
|
|
cholesterol
|
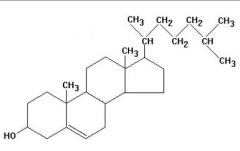
identify this molecule:
|
|
|
... is a cell membrane component and precursor to steroid hormones and ...
|
cholesterol
vitamin D |
|
|
central core consisting of ... fused rings is shared by all steroids
|
four
|
|
|
liver synthesizes ... grams of cholesterol a day (... of blood cholesterol)
... of blood cholesterol comes from dietary sources (meat and dairy) |
2
85% 15% |
|
|
... (good cholesterol) carry ... (bad cholesterol) away from arteries
|
HDLs
LDLs |
|
|
a. sphingolipid
b. plasmalogen c. triglyceride d. sphingolipid (glycolipid) e. phospholipid |
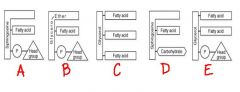
identify the types of lipids labeled:
a. b. c. d. e. |

