![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the first law of thermodynamics:
|
energy can neither be created or destroyed
|
|
|
an endergonic reaction ...
|
nonspontaneous reaction and absorbs energy from bonds, do not occur spontaneously
|
|
|
enthalpy
|
the internal energy or chemical bond energy in the form of heat
ΔH ~ ΔE |
|
|
what is the second law of thermodynamics:
|
all systems tend toward equilibrium - the lowest energy
|
|
|
the greater the disorder or randomness in a system, the larger the ...
|
entropy
|
|
|
the third law of thermodynamics states that:
|
the entropy content of a system can only be zero at 0 degrees Kelvin
|
|
|
in this equation below:
ΔH - TΔS = 0 the 0 represents what? |
free energy
|
|
|
ΔH represents
|
change in enthalpy
|
|
|
TΔS represents
|
change in entropy
|
|
|
at equilibrium what is going on in terms of energy?
|
there is energy in the system, but none to do work
|
|
|
a spontaneous reaction is said to be ...
|
exergonic
|
|
|
an enthalpically favored reaction is said to be ...
|
exothermic
|
|
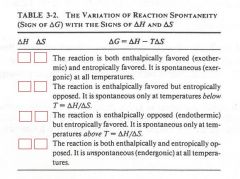
fill in the boxes with either a plus or minus sign:
|
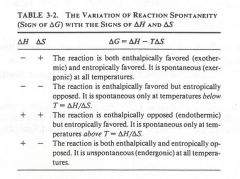
(see figure)
|
|
|
what does this equation represent:
ΔG˚' = ΔH˚' - TΔS˚' |
the standard state
|
|
|
the standard state is defined to be:
|
1 atm
25˚C |
|
|
Keq is the equilibrium constant and is defined as:
|
ratio of [B]/[A] where B is the product and A is the substrate
|

