![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
on the 23rd day after fertilization, the mesoderm has just developed into ... and ...
|
somites and somitomeres
|
|
|
the gut tube is pulled ... with the ... during the early part of neural development
|
anteriorly and buccopharyngeal/oral plate
|
|
|
foregut
midgut hindgut |
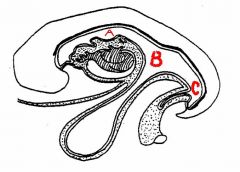
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. |
|
|
pharynx
allantois yolk sac connecting stalk |
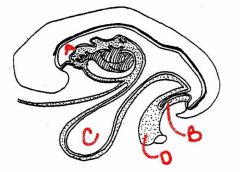
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. c |
|
|
where does the first branchial arch start developing?
|
on either side of the embryonic pharynx
|
|
|
the second brancial arch develops before or after the first brancial arch?
|
after
|
|
|
at 3 to 4 weeks, how many branchial arches does the embryo have? and name them
|
2
first and second pharyngeal arches |
|
|
as the first arch bends around the oral plate, it forms 2 parts ... and ...
|
maxillary division
mandibular division |
|
|
the ... arch develops behind the 2nd branchial or pharyngeal arch
|
3rd
|
|
|
maxillary prominence
mandibular prominence pharyngeal arches 2nd and 3rd stomadeum |
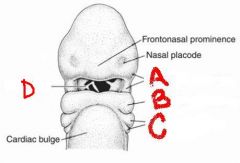
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. |
|
|
1
2 3 4-6 |
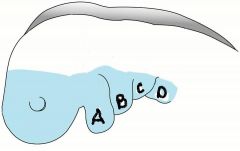
number the following branchial arches:
a. b. c. d. |
|
|
the 1st 2 branchial arches form (before/after) the neuropore closes
|
before
|
|
|
stomadeum (mouth)
anterior 2/3 of tongue posterior 1/3 of tongue esophagus |
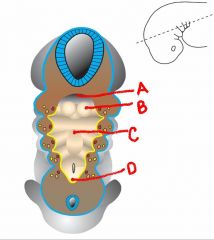
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. |
|
|
foramen cecum
epiglottic swelling laryngiotracheal groove |
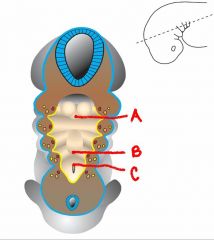
identify the following structures:
a. b. c. |
|
|
ectoderm
endoderm mesoderm |
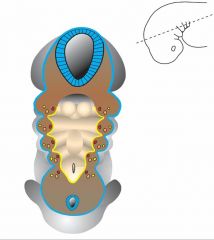
the blue represents?
the yellow represents? the brown represents? |
|
|
brancial means ...?
|
gills
|
|
|
another name for the 2nd branchial arch is ...?
|
hyoid arch
|
|
|
the 2nd branchial arch will develop into ...?
|
most of the hyoid bone
|
|
|
pharyngeal cleft
pharyngeal pouch |
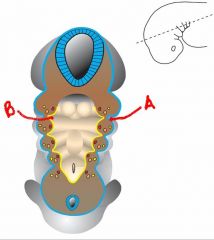
name the following structures:
a. b. |
|
|
aortic arch 1: degenerates
aortic arch 2: degenerates aortic arch 3: carotid arteries (left and right) |
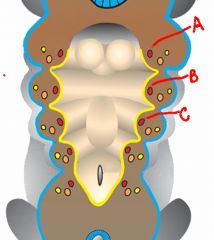
name the arteries and their fate:
a. b. c. |
|
|
aortic arch 4: left becomes arch of aorta
aortic arch 4: right becomes right subclavian artery aortic arch 6: pulmonary arteries |
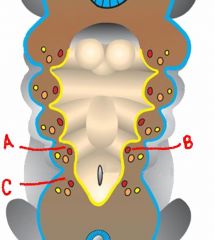
identify the arteries and their fates:
a. b. c. |
|
|
the maxillary division of the 1st branchial arch gives rise to what cranial nerve(s)? and the nerves are (sensory/motor/mixed)?
|
maxillary division of trigeminal
sensory only |
|
|
the mandibular division of the 1st branchial arch gives rise to what cranial nerve(s)? and the nerves are (sensory/motor/mixed)?
|
mandibular division of trigeminal
mixed |
|
|
the 2nd branchial arch gives rise to what cranial nerve(s)?
|
facial nerve
|
|
|
the 3rd branchial arch gives rise to what cranial nerve(s)?
|
glossopharyngeal nerve
|
|
|
the 4th and 6th branchial arches gives rise to what nerve(s)?
|
vagus nerve
|
|
|
facial nerves are said to be ... meaning that they they move only skin and do not move bone
|
superficial
|
|
|
what cranial nerve number is the maxillary division of trigeminal?
|
cn5
|
|
|
what cranial nerve number is the mandibular division of trigeminal?
|
cn5
|
|
|
what cranial nerve number is the facial nerve?
|
cn7
|
|
|
what cranial nerve number is the glossopharyngeal nerve?
|
cn9
|
|
|
what cranial nerve number is the vagus nerve?
|
cn10
|
|
|
the mandibular branch nerve (cn5) innervates the muscles of ...
|
mastication
|
|
|
1st branchial arch gives rise to what muscle?
|
muscles of mastication
|
|
|
2nd branchial arch gives rise to what muscles?
|
muscles of facial expression
|
|
|
3rd branchial arch gives rise to what muscles?
|
stylopharyngeus muscle
|
|
|
4th branchial arch gives rist to what muscles?
|
muscles of larynx and pharynx
|
|
|
the tongue is innervated by ...?
|
cn12
|
|
|
branchial groove 1 gives rise to what?
|
external auditory meatus
|
|
|
pharyngeal pouch 1 gives rise to what?
|
middle ear and auditory tube
|
|
|
merckel's cartilage is derived from ... and gives rise to ...?
|
1st branchial arch
degenerates and becomes nothing (gives rise to couple of osicles in middle ear) |
|
|
what is the fate of branchial grooves 2 through 6?
|
they fuse into a cervical sinus, which disappears (occasionally forms cyst)
|
|
|
pharyngeal pouch 2 gives rise to what?
|
palatine tonsil
|
|
|
pharyngeal pouch 3 gives rise to what?
|
inferior parathyroid and thymus
|
|
|
pharyngeal pouch 4/5 gives rise to what?
|
superior parathyroid and c-cells of thyroid (c-cells regulate calcium)
|
|
|
the anterior-most region of the gut tube becomes the ...
|
pharynx
|

