![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four ageing terms used for the wines of Spain?
List the min. ageing requirement for reds from each category. |
Joven – bottled in the year following the vintage for immediate release.
Crianza – reds must be aged for a minimum of 24 months Reserva - must be aged for a minimum of 36 months Gran Reserva – must be aged for a minimum of 60 months |
|
|
List the 3 sub-regions of Rioja and the style of wine they produce.
|
Rioja Alavesa – the lightest of Rioja, these wines have finesse
Rioja Alta – similar to Rioja Alavesa with a bit more body Rioja Baja – Garnacha is the principal grape here and the wines have less ageing potential |
|
|
What are the 3 distinct climate zones of Penedes?
|
Coastal Plain – a hot Mediterranean climate making full bodied reds from Garnacha and Monastrell.
Inland Valleys – more temperate climate and whiter grapes for Cava production are planted here. In the Hills – 800 metres above sea level and the climate is cooler, international varieties such as Riesling, GW and Pinot Noir are grown here. |
|
|
How does a wine from Toro differ from a Rioja?
|
Toro grows a thicker skinned clone of Tempranillo.
Due to the heat and sunny conditions of Toro, the wines are full bodied, powerful, deeply coloured and are high in alcohol. |
|
|
Describe the climate of the Douro Valley in Portugal.
|
The Douro climate varies from warm maritime at the western end to hot and continental in the eastern part of the valley.
|
|
|
What is Ribera del Duero’s name for Tempranillo?
|
Tinto Fino
|
|
|
What grape is used for a wine from Rias Baixas?
|
Albariño
|
|
|
What style of wine does the Monastrell grape produce?
|
dark, powerful and spicy wines with a high tannin and alcohol content
|
|
|
What is the minimum ageing requirement in cask for a red Rioja Gran Reserva?
|
24 months
|
|
|
Which international grape is often blended into a Rueda wine?
|
Sauvignon Blanc
|
|
|
What is the grape variety used in the region of Bierzo?
|
Mencia
|
|
|
What is the Airén grape is used for?
|
Brandy de Jerez
|
|
|
In which region is the Graciano grape grown in?
|
Rioja
|
|
|
Which climate best describes Rias Baixas.
|
Maritime
|
|
|
What is the dominant grape in the regions of the Cariñena & Calatayud?
|
Garnacha
|
|
|
What is the Cariñena grape called in Rioja?
|
Mazuelo
|
|
|
Where is the region of Valdepeñas located in Spain?
|
south underneath the region of La Mancha
|
|
|
What does the term Vinos de Pago refer to?
|
single estates with high reputations often using international grapes
|
|
|
What style of wines are produced in Ribera del Duero?
|
reds and rosés
|
|
|
Which region in Portugal does the Trincadeira grape play an important role in?
|
Alantejo
|
|
|
What is Tempranillo called in the Douro region?
|
Tinta Roriz
|
|
|
Where is the region of Dão located in Portugal?
|
inland and south of the Douro region
|
|
|
What % of the Baga grape must be in a Clássico wine from Bairrada?
|
50
|
|
|
What style of red wines does Dão produce?
|
delicate wines with red fruit aromas and soft tannins
|
|
|
What is the average alcohol of a typical Vinho Verde?
|
8.5 – 11.5%
|
|
|
Where is the DOC of Palmela located?
|
Sétubal Peninsula
|
|
|
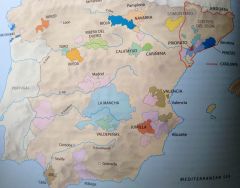
Spain
|
|
|
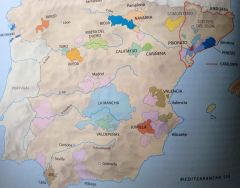
Spain
|
|
|
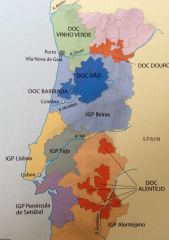
Portugal
|

