![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. The number of live births per 1,000 population.
|
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
|
|
|
2. The number of deaths per 1,000 population.
|
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
|
|
|
3. CBR (Crude Birth Rate) minus CDR (Crude Death Rate). The figure will be higher in the Third World.
|
Rate of Natural Increase (NR)
|
|
|
4. The average number of children that would be born to each woman if, during her childbearing years, she bore children at the current year’s rate for women that age.
|
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
|
|
|
5. The number of children per family just sufficient to keep total population constant. It is calculated to be between 2.1 and 2.5. Any situation over 3.0 would be considered overpopulation, while a figure below 2.0 leads to eventual ZPG – Zero Population Growth.
|
Replacement Level (from TFR [Total Fertility Rate])
|
|
|
6. The numbers of any population that can be adequately supported by the available resources upon which that population subsists. Estimates today show that the Earth can support between 8 and 11 billion people.
|
Carrying Capacity
|
|
|
7. The number of people per unit of land, e.g., Texas with a population of 24 million and a land area of 267,339 sq. mi. has a crude density of approximately 90 people per square mile.
|
Crude (Arithmetic) Density
|
|
|
8. The number of persons per unit area of arable or agricultural land. We know much of Texas land is uninhabitable, so it is no surprise that 2/3 of the state’s population resides on 10% of the land area, or ecumene, contained with “The Texas Triangle,” formed between Houston, Dallas, and San Antonio. Like Japan, that creates a much higher physiological density.
|
Physiological Density
|
|
|
9. Measures the ratio of deaths of infants one year or less per 1,000 live births. This is a telling indicator of a quality of life, as indicated by health care. This is a telling indicator of a quality of life, as indicated by health care. In a First World country the IMR would be something like 5.0 per 1,000 while a Third World country might be 100 per 1,000.
|
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
|
|
|
10. Indicates the number of dependents, old and young (>65 and <16), that each 100 in the productive years, on average, must support. A high figure in a Third World country would suggest a lot of kids running around while a high figure in a First World country would mean a lot of elderly denizens are headed to the nursing home.
|
Dependency Ratio
|
|
|
11. A graphic depiction of the age and sex composition of a (usually national) population.
|
Population Pyramid
|
|
|
12. Summarizes the contribution made to regional population change over time by the combination of natural change (difference between births and deaths) and net migration (difference between in-migration and out-migration).
|
Demographic Equation
|
|
|
1. The process by which the political, social, and economic structures of a country are imporved for the purpose of ensuring the well-being of its populace.
|
Development
|
|
|
2. Indices include high poverty, heavy concentration of population employed in agriculture; inadequate food supplies; health problems and epidemics; human productivity is low.
|
Low Developed Countries (LDC)
|
|
|
3. Life expectancy is high; wealth is abundant; people are well fed and housed; human productivity is high.
|
Highly Developed Countries (HDC)
|
|
|
4. One of the best measures of global economic development is GNI-PPP or Gross National Income Purchasing Power Parity, defined in your text as “a new, widely used statistical measure of ________ ______ which factors in differences in cost of living from country to another, so that the resultant figures are more comparable.”
|
One of the best measures of global economic development is GNI-PPP or Gross National Income Purchasing Power Parity, defined in your text as “a new, widely used statistical measure of (ECONOMIC OUTPUT) which factors in differences in cost of living from country to another, so that the resultant figures are more comparable.”
|
|
|
9. Countries evolving from Third World to First World status, with lots of bumps in the road, e.g., Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, and now China.
|
Newly Industrializing Countries (NICs)
|
|
|
1. Who were the ancient geographers?
|
Greece
|
|
|
2. What did the Greeks study when pioneering the study of Geography?
|
Earth-Sun Relationships
Attempts at Mapping MORE??? |
|
|
17. What is the oldest revolution, dating back 10,000 years ago?
|
Agricultural Revolution
|
|
|
18. What is the life expectancy for men and women living in the United States?
|
Men 75-76
Women 80-81 |
|
|
19. The period of rapid technological change and innovation that began in England in the mid-18th century and subsequently spread worldwide; accompanied by the development of inexpensive, massive amounts of inanimate energy through the use of fossil fuels.
|
Industrial Revolution
|
|
|
20. In contrast to the prehistoric cave dweller and his wall, our ability to produce, store, access, and apply information is massive and nearly instantaneous – truly revolutionary. It is how the information is produced, stored, and accessed that creates a revolution; in the Information Age it comes down to a single transforming technology: the microprocessor.
|
Information Revolution – total population divided by land (not arable, all land) = population density per sq. mile
|
|
|
21. Population density expressed as the number of people per unit of arable land.
|
Physiological density – uses arable land
|
|
|
26. What term is the number of years it takes to double a population?
|
Population doubling time
|
|
|
27. Gloom and Doom, who was it that forecasted the end of the world, population grows exponentially, the ability of the earth’s resources will be outstripped by demand of population, industrial revolution bought us time, but eventually we will run out of water, the technocratic theory – we will think our way out of this situation, recycling, windmills, alternative sources of energy?
|
Thomas Malfus
|
|
|
28. The growing integration and interdependence of world communities through a vast network of trade and communications links.
|
Globilization
|
|
|
29. What are the 2 components that make up weather?
|
Precipitation and Temperature
|
|
|
36. The plant life that can be expected in a particular environment if free of human impact.
|
Natural Vegitation – botanical products naturally growing without interference from man.
|
|
|
48. Animate energy
|
3rd world, horses to pull plow, animal energy, 3rd world
|
|
|
49. Inanimate Energy
|
Use gasoline, internal combustion engines, 1st world
|
|
|
50. World life expectancy
|
How long will we live in the U.S.
|
|
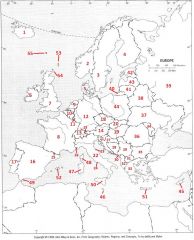
What Country is #1?
|
Iceland #1
|
|
What Country is #2?
|
Norway #2
|
|
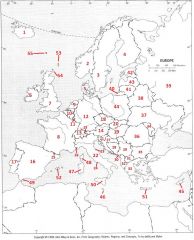
What Country is #3?
|
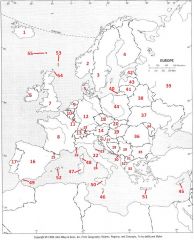
Sweden #3
|
|
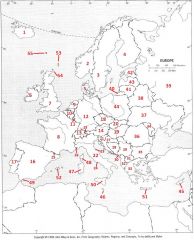
What Country is #4?
|
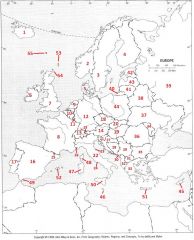
Finland #4
|
|
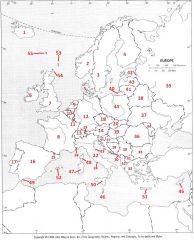
What Country is #5?
|
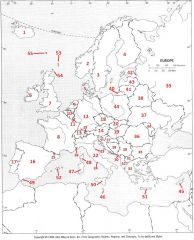
Denmark #5
|
|
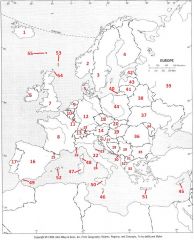
What Country is #6?
|
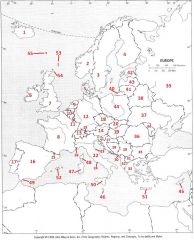
Republic of Ireland #6
|
|
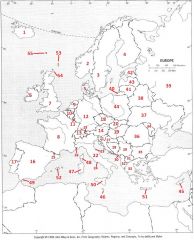
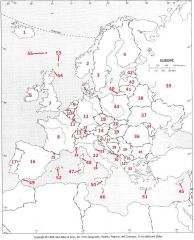
What Country is #7?
|
United Kingdom #7
|
|
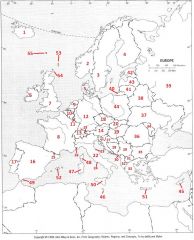
What Country is #8?
|
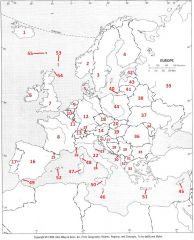
France #8
|
|
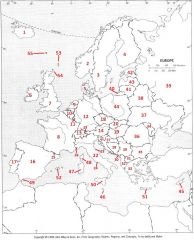
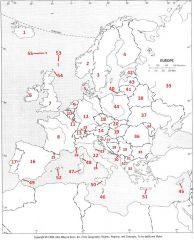
What Country is #9?
|
The Netherlands #9
|
|
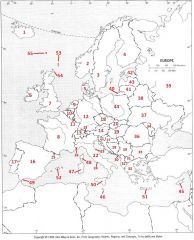
What Country is #10?
|
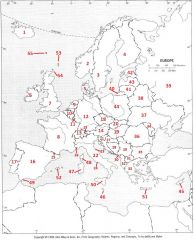
Belgium #10
|
|
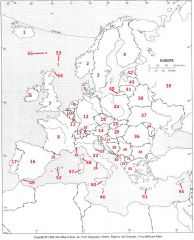
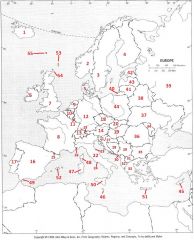
What country is #11?
|
Luxembourg #11
|
|
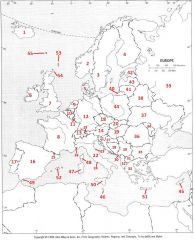
What country is #12?
|
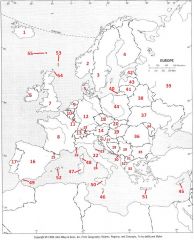
Germany #12
|
|
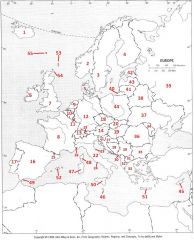
What country is #13?
|
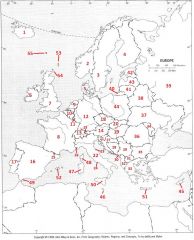
Switzerland #13
|
|
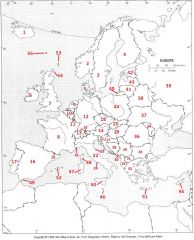
What country is #14
|
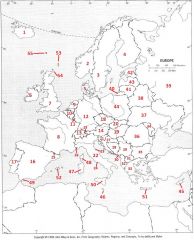
Austria #14
|
|
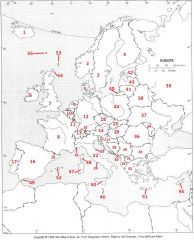
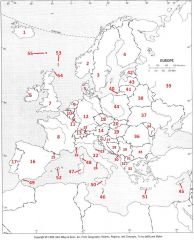
What country is #15?
|
Liechtenstein #15
|
|
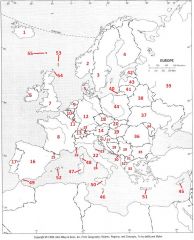
What country is #16?
|
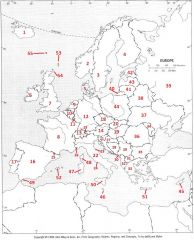
Spain #16
|
|
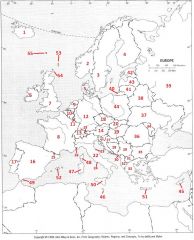
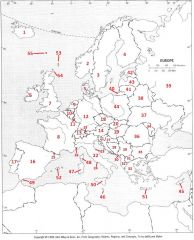
What country is #17?
|
Portugal #17
|
|
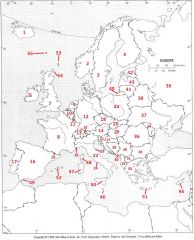
What country is #18?
|
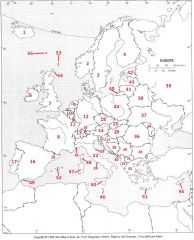
Czech Republic #18
|
|
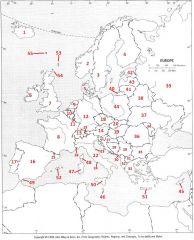
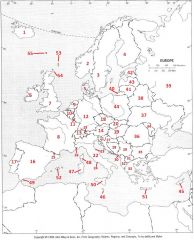
What country is #19?
|
Hungary #19
|
|
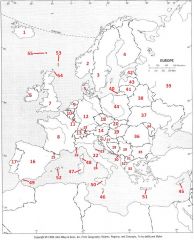
What country is #20?
|
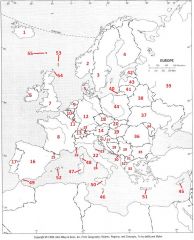
Slovakia #20
|
|
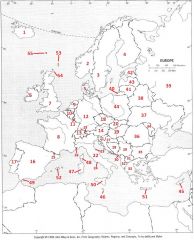
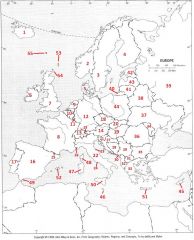
What country is #21?
|
Slovenia #21
|
|
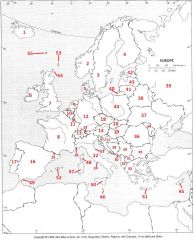
What country is #22?
|
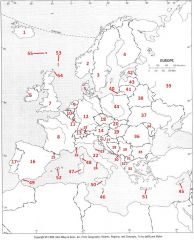
Italy #22
|
|
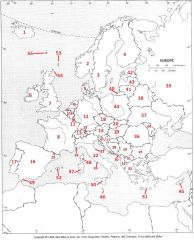
What country is #23?
|
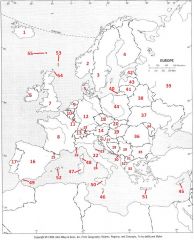
San Marino #23
|
|
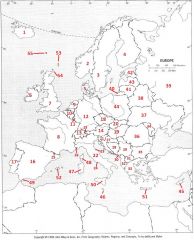
What country is #24?
|
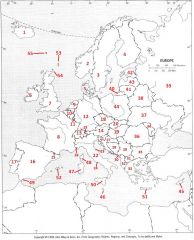
Vatican City #24
|
|
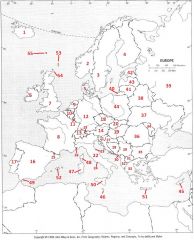
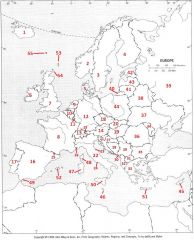
What country is #25?
|
Andorra #25
|
|
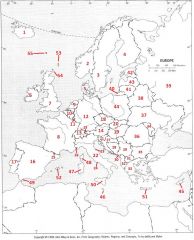
What country is #26?
|
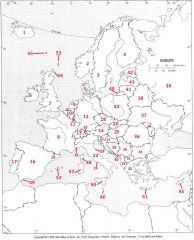
Monaco #26
|
|
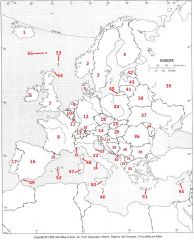
What country is #27?
|
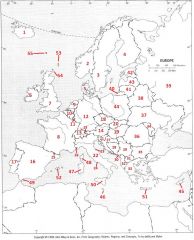
Croatia #27
|
|
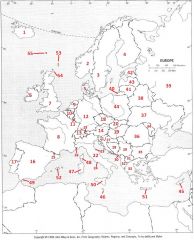
What country is #28?
|
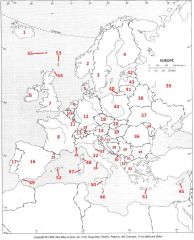
Bosnia-Herzegovina #28
|
|
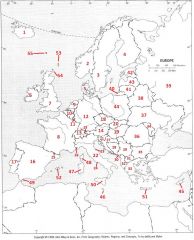
What country is #29?
|
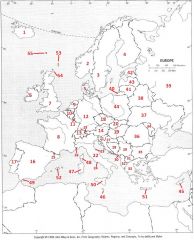
Serbia (former Yugoslavia) #29
|
|
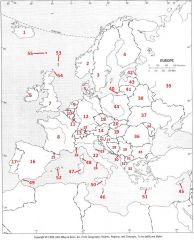
What country is #30?
|
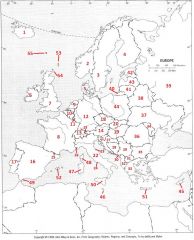
Montenegro #30
|
|
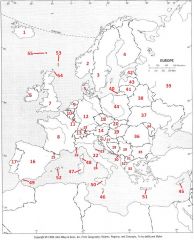
What country is #31?
|
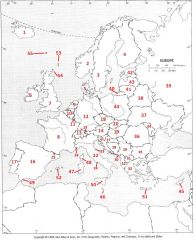
Macedonia #31
|
|
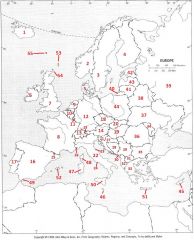
What country is #32?
|
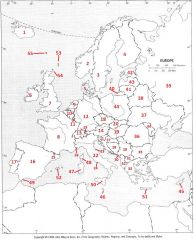
Albania #32
|
|
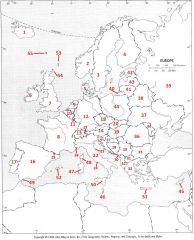
What country is #33?
|
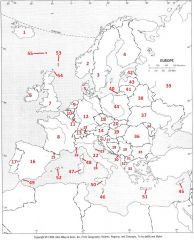
Greece #33
|
|
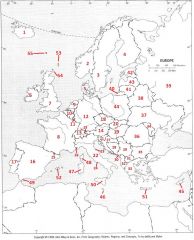
What country is #34?
|
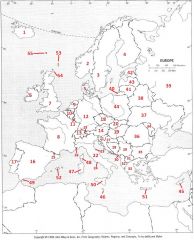
Moldova #34
|
|
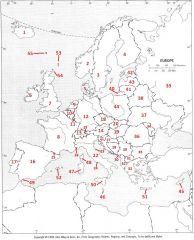
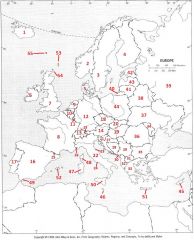
What country is #35?
|
Bulgaria #35
|
|
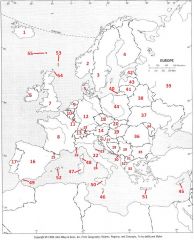
What Country is #36?
|
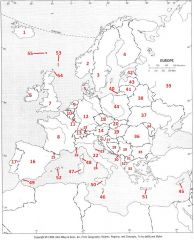
Romania #36
|
|
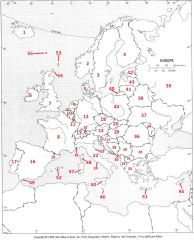
What Country is #37?
|
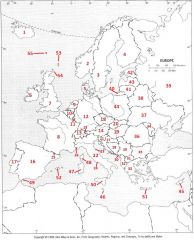
Ukraine #37
|
|
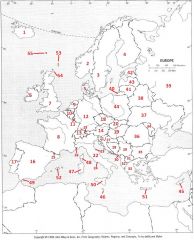
What Country is #38?
|
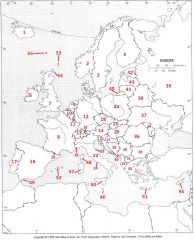
Belarus #38
|
|
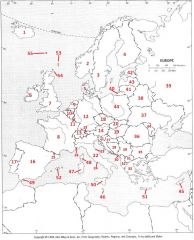
What Country is #39?
|
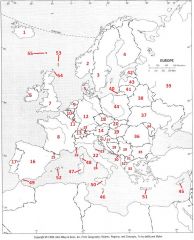
Russian Federation #39
|
|
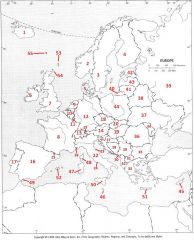
What Country is #40?
|
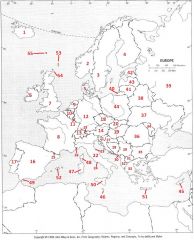
Kaliningrad #40
|
|
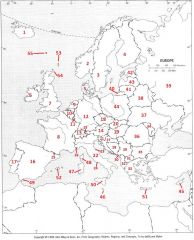
What Country is #41?
|
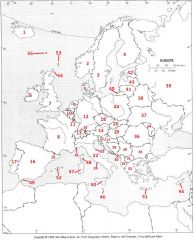
Lithuania #41
|
|
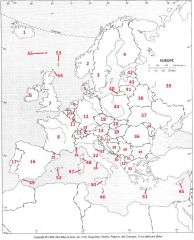
What Country is #42?
|
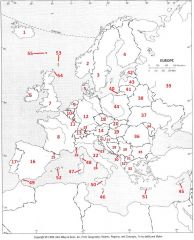
Estonia #42
|
|
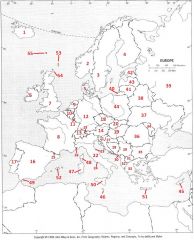
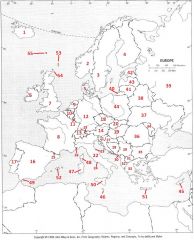
What Country is #43?
|
Latvia #43
|
|
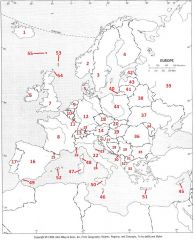
What Country is #44?
|
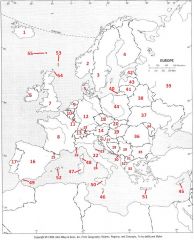
Poland #44
|
|
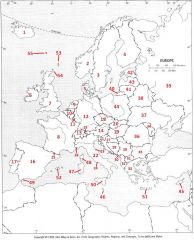
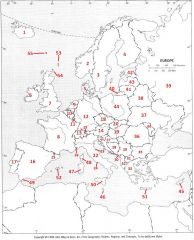
What Country is #45?
|
Cyprus #45
|
|
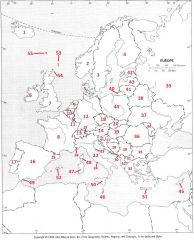
What Country is #46?
|
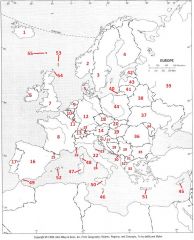
Malta #46
|
|
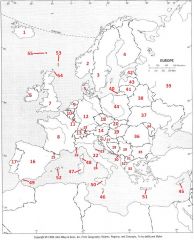
What Country is #47?
|
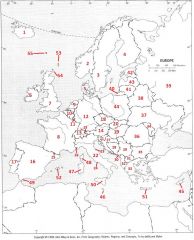
Sardinia #47
|
|
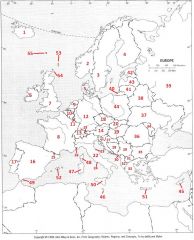
What Country is #48?
|
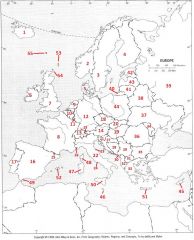
Corsica #48
|
|
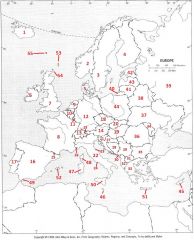
What Country is #49?
|
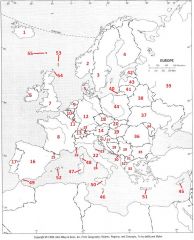
Gibraltar #49
|
|
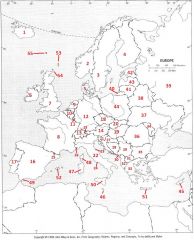
What Country is #50?
|
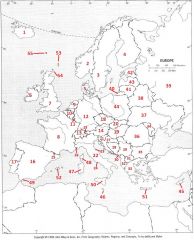
Sicily #50
|
|
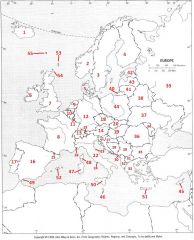
What Country is #51?
|
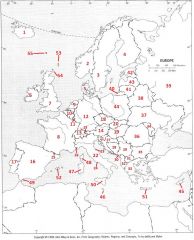
Crete #51
|
|
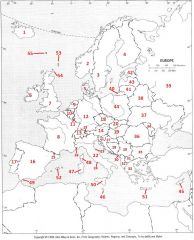
What Country is #52?
|
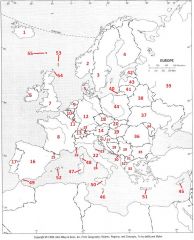
Balearic Islands #52
|
|
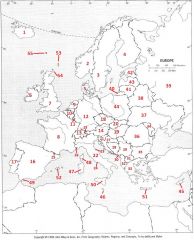
What Country is #53?
|
Shetland Islands #53
|
|
What Country is #54?
|
Orkney Islands #54
|
|
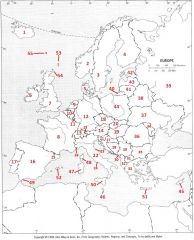
What Country is #55?
|
Faeroe Islands #55
|

