![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Label the parts of a tree and their primary functions |

Crown: Photosynthesis, develops sap Trunk: Supports crown, pathway of nutrients Roots: Collects nutrients and moisture, support system for tree |
|

Label the parts of a trunk cross section |
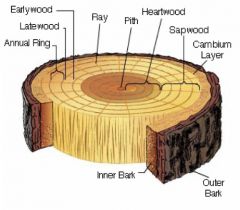
Pith Heartwood Sapwood Cambium layer Bast Bark |
|
|
What form of tree does softwood come from? |
coniferous (seeds are not protected and have needles rather than leaves) |
|
|
What form of tree does hardwood come from? |
most often deciduous trees that are angiosperms (broad leaves rather than needles and do not have resin) |
|

What type of milling is this? |
Quarter sawn |
|

What type of milling is this? |
Flat/plain sawn |
|
|
How do flat sawn and quarter sawn timber differ as they season? |
Flat sawn timber cups away from the pith as it seasons. Quarter sawn timber is more dimensionally stable as it seasons (it swells rather than cups). |
|
|
What is seasoning of timber? |
Reducing the amount of moisture in wood to a stable state |
|
|
Describe green timber |
Fresh cut timber: Up to 90% moisture content, water kept as free water inside the cells, bound water is trapped within cell walls |
|
|
Describe air dried timber |
About 12-20% moisture content: Requires one year of drying per inch of timber thickness, best for steam bending, placing evenly spaced and same thickness gluts between timber reduces warping |
|
|
Describe kiln dried timber |
About 6-10% moisture content: Dried in an oven (manipulation of moisture levels, temperature, and air flow), can be more stressful on timber |
|

Describe this timber distortion |
Twist: Angular rotation around the longitudinal axis (most difficult distortion to correct) |
|

Describe this timber distortion and the best way to correct it |
Cup: End distortion, reduce on the jointer, cut in half along the band saw to reduce cup if severe |
|

Describe this timber distortion and the best way to correct it |
Crook: Edge distortion, saw edges even on the band saw (easiest correction) |
|

Describe this timber distortion and the best way to correct it |
Bow: Face distortion, cut broad down to conserve wood |
|
|
What is the shortest board that can safely be put through the thicknesser? |
350-400mm |
|
|
What is short grain and what are the disadvantages? |
Where the length of the grain is shorter than the width of the board, which makes the board very weak |

