![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
144 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What material does a carpenter work with more than anything else?
|
wood
|
|
|
Wood resists the flow of heat energy how many times more than brick of the same thickness?
|
6
|
|
|
Wood resists the flow of heat energy how many times more than concrete of the same thickness?
|
14
|
|
|
What wood has a good ability to bend without breaking, and what are some things made with it?
|
hickory and ash, which are used to make baseball bats, diving boards, and tool handles.
|
|
|
What wood is often used for floors, and why?
|
oak and maple, because of their beauty, hardness, and durability.
|
|
|
What wood is often used in exterior situations, and why?
|
Redwood, cedar, cypress, and teak, because of their resistance to decay.
|
|
|
What wood is usually chosen for its beauty?
|
cherry, mahogany, and walnut
|
|
|
How long will wood last with proper care?
|
indefinitely
|
|
|
Wood is made up of many hollow cells held together by what?
|
lignin
|
|
|
Where within the tree does growth take place?
|
the cambium layer, just inside the bark (protective shield)
|
|
|
How does water pass into trees?
|
It is absorbed by the roots and passed upward through the sapwood to the leaves.
|
|
|
How does the tree eat?
|
Water from the leaves + CO2 from air + sunlight --> food, which is carried toward the centre of the trunk through medullary rays.
|
|
|
What is the pith of the tree?
|
The centre
|
|
|
What happens to inner tree cells as the tree grows?
|
They become inactive and turn into heartwood.
|
|
|
What is the colour of heartwood?
|
It is usually darker in colour.
|
|
|
What is more durable: heartwood or sapwood?
|
heartwood
|
|
|
What wood is extremely resistent to decay?
|
the heartwood of cedar, cypress, and redwood
|
|
|
What is the heartwood of cedar, cypress, and redwood often used for?
|
outdoor furniture, patios, exterior siding
|
|
|
What time of year does the tree grow most?
|
spring
|
|
|
What is the quality of wood grown in spring?
|
it is porous and light
|
|
|
What time of year is tree growth slower?
|
summer
|
|
|
When are rings formed?
|
during summer, when growth is slower
|
|
|
What is the quality of the ring wood?
|
it is darker and denser
|
|
|
How fast does the Douglas fir grow, and what happens to the rings as a result?
|
Very fast, and to great heights. The rings are very wide and pronounced.
|
|
|
How fast does Mahogany grow, and why? What happens to the rings as a result?
|
Mahogany grows in tropical climates, where the weather is more constant, and as a result the rings do not contrast as much and sometimes are hardly visible.
|
|
|
What are the two kinds of wood?
|
hardwood and softwood
|
|
|
Where does hardwood come from?
|
deciduous trees (trees that shed their leaves every year)
|
|
|
Where does softwood come from?
|
coniferous trees (cone-bearing trees) - aka evergreens
|
|
|
Which is stronger, fir or basswood? What type of wood is each?
|
Fir is stronger, even though it is a softwood and basswood is a hardwood.
|
|
|
What are some common hardwoods?
|
ash, birch, cherry, hickory, maple, mahogany, oak, walnut
|
|
|
What are some common softwoods?
|
pine, fir, hemlock, spruce, cedar, cypress, redwood
|
|
|
Ash: hardwood or softwood?
|
hardwood
|
|
|
Birch: hardwood or softwood?
|
hardwood
|
|
|
Cherry: hardwood or softwood?
|
hardwood
|
|
|
Hickory: hardwood or softwood?
|
hardwood
|
|
|
Maple: hardwood or softwood?
|
hardwood
|
|
|
Mahogany: hardwood or softwood?
|
hardwood
|
|
|
Oak: hardwood or softwood?
|
hardwood
|
|
|
Walnut: hardwood or softwood?
|
hardwood
|
|
|
Pine: hardwood or softwood?
|
softwood
|
|
|
Fir: hardwood or softwood?
|
softwood
|
|
|
Hemlock: hardwood or softwood?
|
softwood
|
|
|
Spruce: hardwood or softwood?
|
softwood
|
|
|
Cedar: hardwood or softwood?
|
softwood
|
|
|
Cypress: hardwood or softwood?
|
softwood
|
|
|
Redwood: hardwood or softwood?
|
softwood
|
|
|
What is open-grained wood?
|
Wood that has large cells that show tiny openings or pores in the surface.
|
|
|
How do you create a smooth finish with open-grained wood?
|
You have to fill the pores with paste wood filler.
|
|
|
What are some examples of open-grained wood?
|
oak, mahogany, walnut
|
|
|
What are some close-grained hardwoods?
|
birch, cherry, maple, poplar
|
|
|
What are some close-grained softwoods?
|
all softwoods!
|
|
|
What is the best way to learn the different kinds of wood?
|
by working with them
|
|
|
What should you look at when you handle a piece of wood?
|
Colour, grain, heavy or light, soft or hard, smell.
|
|
|
What is the facility that first processes logs?
|
sawmill
|
|
|
What is the first step at a sawmill?
|
remove bark from the log
|
|
|
What kind of saw is first used on a log?
|
bandsaw
|
|
|
What happens at a sawmill after the bark is removed?
|
A huge bandsaw slices the log into large planks, then a series of saws slice, edge, and trim them. The result: lumber.
|
|
|
What happens at a sawmill after lumber is trimmed?
|
It is stacked according to size and graded
|
|
|
What happens at a sawmill after lumber is graded?
|
It is taken outdoors and stickered
|
|
|
What is stickering?
|
Stacking the lumber on small cross-sticks that allow air to circulate between pieces
|
|
|
How long does air-seasoning take?
|
6 months to 2 years
|
|
|
What happens to lumber after air drying?
|
It is dried in huge ovens
|
|
|
What happens to lumber after it is dried?
|
It is surfaced to standard sizes and shipped
|
|
|
What are the different sides of a piece of lumber called?
|
face (the wide surface), edge, end (where the grain is)
|
|
|
What are the nominal length, width, and thickness of an 8-foot 2x4?
|
length = 8'
width = 4" thickness = 2" |
|

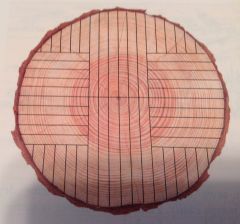
What lumber-cutting method is this?
|

plain-sawn
|
|
|
What is another name for "plain-sawn"?
|

slash-sawn
|
|
What lumber-cutting method is this?
|
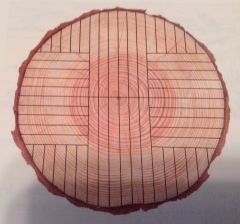
quarter-sawn
|
|
|
What sawing method is least expensive and produces greater width?
|
plain-sawing / slash-sawing
|
|
|
What sawing method results in greater wood shrinkage and warping?
|
plain-sawn (aka slash-sawn)
|
|
|
What sawing approach results in wood that shrinks less and more evenly, resulting in fewer warps?
|
quarter-sawn
|
|
|
Which sawing approach creates more durable wood, and why?
|
quarter-sawn, because the wear is on the edge of the annular rings
|
|
|
What sawing approach is typically used to generate wood for flooring?
|
quarter-sawn
|
|
|
What are two other names for "quarter-sawn" lumber?
|
vertical-grain or edge-grain
|
|
|
What sawing approach is most often used?
|
a combination of plain-sawn and quarter-sawn
|
|
|
The person who decides how to cut the log to create minimum waste and maximum efficiency is called what?
|
sawyer
|
|
|
What equipment aids a sawyer?
|
computers and laser-guided equipment
|
|
|
When a tree is first cut down, it contains a lot of what?
|
water
|
|
|
What is the name of lumber when it is first cut from the log?
|
green lumber
|
|
|
How much water might be in a 2x6x10' when first cut?
|
4.5 gallons, or 35 lbs
|
|
|
Why should green lumber not be used in construction?
|
It will shrink a lot and unevenly --> usually warps
|
|
|
What are some of the results of using green lumber in construction?
|
cracked ceilings and walls, squeaking floors, sticking doors, and more
|
|
|
What damaging thing is green lumber at risk of?
|
decay
|
|
|
What causes decay?
|
fungi
|
|
|
What is another term for decay, and why?
|
"dry rot", because it is not usually discovered until the lumber has dried
|
|
|
What moisture level does wood have to be at for decay to start?
|
In excess of 19%
|
|
|
What does MC stand for, with respect to lumber?
|
Moisture Content
|
|
|
What does MC indicate?
|
the percentage of the wood's weight that comes from water
|
|
|
What MC is best for framing and exterior finish lumber?
|
Ideally 15%, but not to exceed 19%
|
|
|
What MC is best for interior finish?
|
10-12%
|
|
|
Where is water held in green lumber?
|
in the hollow part of the wood cells and in the cell walls
|
|
|
What is water in the cell cavities of green lumber called?
|
free water
|
|
|
What MC is lumber's fibre-saturation point, and what does that refer to?
|
30%, when all the free water is gone
|
|
|
What is lumber called that has already dried (2 names)?
|
dry or seasoned
|
|
|
What dimension of wood is not usually affected by shrinkage?
|
length
|
|
|
What part of the wood is affected most by shrinkage?
|
Along the length of the annular rings. Longest rings shrink more than shorter ones.
|
|
|
Why does plain-sawn lumber warp?
|
unequal length of the annular rings
|
|
|
Why doesn't quarter-sawn lumber warp?
|
the length of the annular rings is about the same
|
|
|
What is the term for lumber with a moisture content equal to that of the surrounding air?
|
equilibrium moisture content
|
|
|
What is equilibrium moisture content usually?
|
10-12%
|
|
|
What are the methods for drying lumber?
|
air, kiln, or both
|
|
|
What is the main advantage and disadvantage of kiln-drying?
|
drying is much quicker, but it is also costlier
|
|
|
What is the recommended MC for lumber to be used for exterior finish at the time of installation?
|
12%
|
|
|
What should be the MC for lumber to be used for exterior finish in dry climates?
|
9%
|
|
|
What should be the MC for lumber used in interior trim and cabinet work?
|
8-10%
|
|
|
What are some techniques to prevent water from getting into wood?
|
sealing all joints on finish work, priming all bottom edges and ends, sealing all sides and edges of wood doors before hanging, priming all exterior wood trim on all sides and ends before installation, making joints that shed water, making joints that stop the entrance of water
|
|
|
How can you tell the MC of wood?
|
a moisture meter
|
|
|
Experienced workers can accurately estimate the MC of wood how?
|
Just by lifting it.
|
|
|
Where is wood straightened, smoothed, and uniformly sized?
|
planer mill
|
|
|
What is the abbreviation for wood surfaced on all 4 sides?
|
S4S
|
|
|
How should materials be delivered/stored?
|
So that what is needed first is on top
|
|
|
How should lumber be stored on the job site?
|
1. Not directly on the ground
2. Relatively level so it does not fall 3. Covered, with room at top and bottom for air circulation |
|
|
What is a lumber defect?
|
Any fault that detracts from appearance, function, or strength
|
|
|
What causes warp?
|
Drying lumber too fast, careless handling and storage, or surfacing the lumber before it's dry
|
|
|
What types of warps are there?
|
crooks (crowns), bows, cups, & twists
|
|
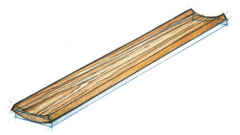
What defect is this?
|
cup
|
|

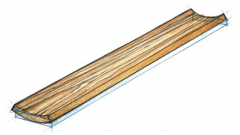
What defect is this?
|

bow
|
|
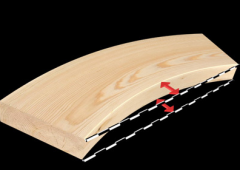
What defect is this?
|
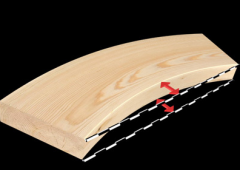
crook or crown
|
|

What kind of defect is this?
|

twist or wind
|
|
|
What is the name of a split in the end of the lumber running lengthwise across the annular rings?
|
check
|
|
|
What causes checks?
|
the end drying faster than the rest
|
|
|
How can checks be prevented?
|
sealing the ends of lumber with paint or wax during drying period
|
|
|
What are cracks that run parallel to and between the annular rings called?
|
shakes
|
|
|
What causes shakes?
|
weather or other damage to the tree
|
|
|
What is the pith?
|
the spongy centre of the tree
|
|
|
What is the youngest portion of lumber called?
|
juvenile wood (first 7-15 rings)
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of juvenile wood?
|
unstable, shrinks in different directions --> stress.
|
|
|
What is a knot?
|
a cross-section of a branch in the tree
|
|
|
When are knots defects?
|
only when they are loose or weaken the piece
|
|
|
What is a pitch pocket?
|
small cavities that hold pitch, some of which oozes out
|
|
|
What is the name for lumber that is missing an edge because it contained bark that has falled off?
|
wane
|
|
|
What is the name for small grooves or channels running with the grain, and what tree is known for this?
|
"pecky wood"; cypress is known for this.
|
|
|
What are some other decays?
|
stains, decay, wormholes
|
|
|
What size are boards?
|
under 2" thick
|
|
|
What size is dimension lumber?
|
2-4 inches thick
|
|
|
What are timbers?
|
5 inches and thicker
|
|
|
What are the grades of dimensional softwood lumber, from best to worst?
|
Select structural
No. 1 No. 2 No. 3 |
|
|
What are the grades of hardwood lumber, from best to worst?
|
Firsts and seconds (FAS) - min. 6" wide & 8' long, 85% clear cutting
Select - min. 4" wide & 6' long No. 1 common - 65% clear cutting |
|
|
How is hardwood lumber purchased?
|
in the rough; then straightened, smoothed, and sized as needed
|
|
|
What is the usual order format for softwood lumber? (example given)
|
35 pieces - 2" x 4" x 8' select
|
|
|
When is softwood lumber ordered in thickness, width, and linear feet?
|
When no particular lengths are required
|
|
|
How is hardwood lumber purchased?
|
By specifying the grade, thickness, and total number of board feet.
|
|
|
What is a board foot?
|
The volume of wood equivalent to a piece 1" thick x 1' x 1'
|
|
|
How do you calculate board feet?
|
number of pieces x thickness in inches x width in inches x length in feet ÷ 12
|

