![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
alternate day fevers
|
Plasmodium vivax
|
|
|
Every third day fevers
|
plasmodium malariae, and P. ovale
|
|
|
Relapsing 3-6 day fever at 1 week intervals
|
Borrelia species (Lyme disease)
|
|
|
5 day fevers(trench fever)
|
bartonella quintana, B. bacilliformis
|
|
|
continuous "undulating fever"
|
brucellosis
|
|
|
Mononucleosis a chronic/cyclic disease with fever
|
Epstein-Barr virus
|
|
|
amebas- feeding and movement
|
free living, feed by phagocytosis, move bby pseudopodia
|
|
|
flagellates- feeding and movement
|
free living, feed by cytosome, have whip-like projections called flagella
|
|
|
ciliates - feeding and movement
|
move by hair-like projections, feed by way of a cytosome groove
|
|
|
sporozoa (spicomplexans) ex?
|
obligate intracellular parasites ex- plasmodiums
|
|
|
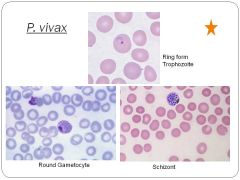
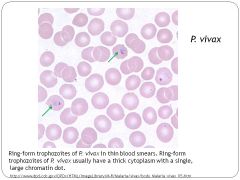
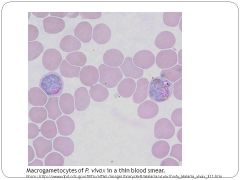
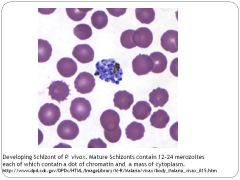
What is the etiological agent for malaria?
|
P. vivax
|
|
|
What family does P. vivax belong to?
|
plasmodium spp
|
|
|
What are paroxysms?
|
Paroxysmal attacks are short, frequent and stereotyped symptoms that can be observed in various clinical conditions.
|
|
|
How many hosts are required for malaria?
|
2
|
|
|
Signs and symptoms of malaria?
|
"Vague influenza-like symptoms with headache, muscle pains, photophobia, anorexia, nausea and vomiting. As the disease progresses the patient begins to have a typical pattern of chills, fever, sweating & malarial rigors that appear periodically.
|
|
|
Morphology of Borrelia
|
coiled, gram (-), periplasmic flagella, linear chromosome and plasmids
|
|
|
Borrelia energy derivation
|
Microaerophilic and very fastidious
|
|
|
Borellia diseases
|
lyme disease and relapsing fever
|
|
|
What makes Borellia difficult to diagnose?
|
strick nutrient requirements and slow growth for cultivation. Relapsing fever is microscopy not serology. Lyme disease is serology or PCR but not microscopy. Symptoms are variable and non-specific
|
|
|
What little critters carry borellia?
|
ticks and lice (thus history is very important for diagnosis)
|
|
|
See Picture
|
|
|
|
Rickettsia, ehrlichia and coxiella general characteristics
|
obligate intracellular aerobe. Gram (-) rods. INTRACELLULAR PARASITES
|
|
|
Why do rickettsia, ehrlichia and coxiella stain poorly?
|
low peptidoglucan and because they are intracellular
|
|
|
Why is vaccine treatment difficult for intracellular bacterial pathogens?
|
intracellular lifestyle is protective, immune response must include both humeral and cellular responses (live attenuated), ID of protective subunits is difficult
|
|
|
In what organism is rock mountain spotted fever?
|
rickettsia rickettsii
|
|
|
What are the hosts of RMSF?
|
small mammals, dogs, rabbits, birds
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of RMSF?
|
HIGH FEVER, headache. Macular rash on ankles and wrists
|
|
|
Can RMSF become dormant and relapse after yesrs?
|
Yes
|
|
|
What percent of RMSF is fatal without treatment?
|
10-25%
|
|
|
Ehrlichia chaffeinsis disease
|
Ehrlichiosis ranges from asymptomatic to fatal. Flu like illness. Rash occurs in 3-40% of cases
|
|
|
What are the hosts of Ehrlichia chaffeinsis?
|
humans and deer
|
|
|
What is the vector organism of Ehrlichia chaffeinsis?
|
Lone star Ticks
|
|
|
What causes Q-fever
|
Coxiella burnetii
|
|
|
What are the animal reservoirs of Q-fever?
|
cattle, sheep, goats
|
|
|
Tranmission of Q-fever?
|
inhalation of barnyard dust with dried urine, feces, placenta and other birth products
|
|
|
Who is at greatest rish with Q fever?
|
Those with underlying heart disease
|
|
|
Brucella morphology
|
coccobacilli, non-encapsulated, non-motile
|
|
|
Brucella cell wall
|
gram (-)
|
|
|
Where is the greatest concentration of brucella found/
|
Mexicans in US
|
|
|
How is brucellosis transmitted?
|
eating or drinking, inhalation, wound contamination
|
|
|
Brucellosis Tissue tropism
|
in tissue with high levels of erythritol- breasts, uterus, placenta, epididymis
|
|
|
Brucellosis Disease
|
"Undulant Fever.Initially non specific: malaise, chills, sweats, fatigue weakness, myalgias weight loss, arthralgias and dry cough. All patients have a fever which becomes intermittent and hence is called undulant fever.
|
|
|
What species cause Bartonella
|
B. bacilliformis, B. quintana, B. henselae
|
|
|
What is bartonella morphology
|
short, gram (-) aerobic rods
|
|
|
Bartonella metabolism
|
fastidious
|
|
|
Diseases of Bartonella
|
Trench Fever, Cat-scratch
|
|
|
Bartonella bacilliformis causes severe______
|
anemia
|
|
|
Bartonella bacilliformis cause are gram _____ rods that penetrate_____
|
negative, RBCs
|
|
|
Bartonella bacilliformis causes _______ disease, which is ______
|
Carrion disease, acute febrile illness
|
|
|
Where is bartonella bacilliformis restricted to?
|
Andes Mountain range
|
|
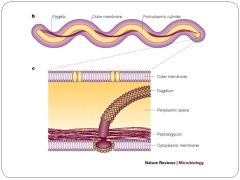
Borellia
|
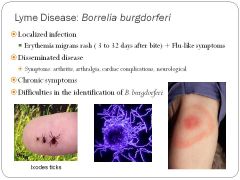
Lyme disease
|
|
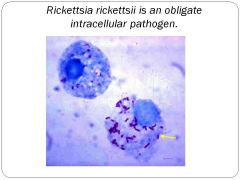
RMSF
|
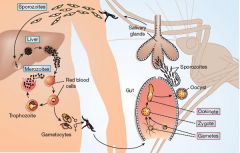
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
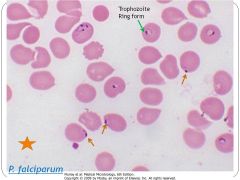
|
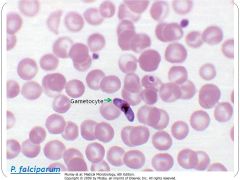
|
|
|
|
|
|
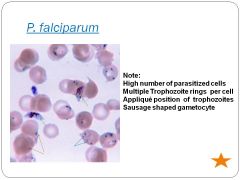
|
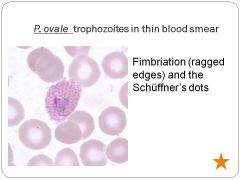
|

