![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the humoral immune response? [LO]
|
[LO]
Antibodies produced by B cells (lymphocytes) destroy extracellular pathogens and prevent the spread of intracellular infections. •‘antibody-mediated immunity’ •(as opposed to the ‘cell-mediated immune response’ effected by T cells (lymphocytes)) |
|
|
•Describe the general process of B cell development from the bone marrow to plasma cell or memory B cell.
[LO] |
![[LO]
- Lymph node
- paracortex where it is activated by T cell (CD4) or Ag/dendricyte
- dark zone germinal centre where B cell maturation and differentiation occurs
- Light zone accepted as memory cells or plasma cells](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/56/19/56/2561956_m.jpg)
[LO]
- Lymph node - paracortex where it is activated by T cell (CD4) or Ag/dendricyte - dark zone germinal centre where B cell maturation and differentiation occurs - Light zone accepted as memory cells or plasma cells |
|
|
Understand the link between myeloma and its properties used for monoclonal antibody production. [LO]
|
Properties of myeloma cells are used to produce large quantities of monoclonal antibodies
Plasma cell = long-lived & ability to continuously secrete antibody Fusion of plasma cell + spleen cell = hybridoma |
|
|
•Recognise the features of myeloma as a disease.
[LO] |
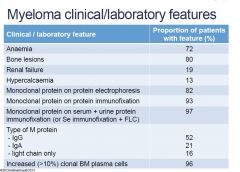
ABRH
EIU 10% |
|
|
•Describe the process of monoclonal antibody production and the role of key reagents. [LO]
|
![[LO]
1. inject with Ag
2. remove spleen HGPRT neg
3. MM with HGPRT neg cells = hybridomas
4. culture in HAT medium
5. test supernatant for Ab
6. Expland positive clones
7. Harvest in vitro or in vivo](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/56/19/89/2561989_m.jpg)
[LO]
1. inject with Ag 2. remove spleen HGPRT neg 3. MM with HGPRT neg cells = hybridomas 4. culture in HAT medium 5. test supernatant for Ab 6. Expland positive clones 7. Harvest in vitro or in vivo |
|
|
What is PEG?
|

polyethylene glycol and assists the fusion of spleen cells and myeloma cells to form the hybridoma
|
|
|
what is HAT?
|

hypoxanthine aminopterin thymidine
|

