![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Building Envelope |
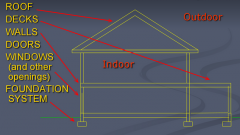
- an environmental separator - 3-D Envelope that extends all around the building |
|
|
Concepts of Thermal & Moisture protection |
1. Control Heat Flow
2. Preventing water infiltration |
|
|
Thermal and moisture protection
1. Control Heat Flow |
- Increase air tightness in bldg envelope - Add thermal insulation - Reduce radiation |
|
|
Thermal and moisture protection
2. Preventing water infiltration |
- Eliminate exterior water penetration (rainfall, run-off & splash / groundwater / snow & ice) - Control interior water vapour movement (ventilation / control air tightness in bldg envelope / vapour barriers) |
|
|
Exterior Environment (Climate) |
- Temp range: seasonal, daily highs & lows - Humidity range: seasonal, daily - Precipitation: rain, snow, seasonal, peak - Wind: direction, speed, gusting during rain - Geographic area - Sun: glare; heat, U/V, daylight, angle |
|
|
Regional Climates |
Coastal BC - mild temperature - high winter rainfall & humidity - low winter sunrise Interior BC - high temperature - low rainfall - extensive sunshine |
|
|
Indoor Environment |
- A regulated balance of temp & humidity - Modified by the activities of the occupant/equip - Regulated to meet human comfort |
|
|
Forces on the Building Envelope |
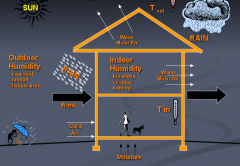
- wind/rain - warm/cold air - outdoor/indoor humidity - ground moisture
|
|
|
Barriers in the Building envelope |
- Thermal Barrier: aka insulation, slows down heat loss/gain - Air Barrier: Prevents the passage of air between inside/outside, air carries water/heat/sound/contaminants - Vapour Barrier: Prevents water vapour which can condense into liquid water and cause damge - Moisture Barrier: Prevents liquid water from entering, water resistant/proof |
|
|
Bitumens |
To control moisture movement - water proof/resistant - refined from coal tars from petroleum deposits(crude oil) - a component of asphalt and tar (black,sticky) |
|
|
Use of Bitumens |
- Foundation treatments: damp/water-proofing - Roofing: paper (under shingles), asphalt shingles (sloped), built-up roofing (flat) - On wall sheathing: building paper (provides water resistance under the exterior wall cladding) |
|
|
Foundation treatments |
Damp-proofing: sprayed/mopped on foundation wall where no water is present (only water resistance is required)
Water-proofing: required on foundation walls when there is water pressure (hydrostatic) in the soil |
|
|
Limitations of Bitumens |
- Limited strength - Must be bonded with a reinforcing substrate for increased strength (paper/fibreglass/plastics) - Exposure to sun (softens) and below freezing temp (becomes brittle) |
|
|
Elastomerics |
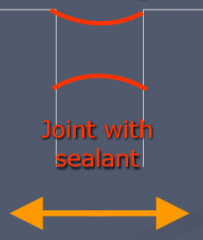
To control/contain material movement - rubber-like - will expand/contract along with material - able to absorb movement w/ adjacent materials - may be natural (rubber, latex) - or a synthetic polymer similar to plastic |
|
|
Use of elastomers |

- Sealants: to create waterproof joints between materials (Butyl, silicone, polyethurane) - High performance Roofing membranes (EPDM roofing membrane) |
|
|
Plastics |
Many components of the building envelope are plastics: -roof gutters (PVC) -flashings (PVC) -polyethylene vapour barriers -house wrap (TYVEC) -rigid insulation |
|
|
Cladding Materials |
- Wood: siding, shingles - Metals (steel, zinc, copper, stainless steel) - Stucco: cementitious - Plastic: vinyl siding - Cementitious composites: fibre cement board (mix of wood fibre and cement) |
|
|
Firestopping Products |
To seal holes in separations required to have a fire rating - Sealants: Intumescent, Elastomeric, Acrylic, Mineral fibre backing - Blocks/plugs: Intumescent, Cut and friction fit, reusable - Collars: galvanized frame, intumescent insert - Cast-in sleeves: plastic housing, Intumuscent insert |

