![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Case 1- An 18 year old man died of suddenn cardiac arrest whilst playing a soccer match. He was a healthy young male. The only recent illness they can think of is a flu-like illness he had a week ago. Give a differential diagnosis
|
1. Eschiamic- MI + atherosclerosis + myocarditis + cardiomyopathy + congenital condition
2. Valvular- aortic stenosis + arrhythmia or ventricules + fibrillation or Wolf Parkinson White syndrome 3. Myocarditis- infectious and non-infectious causes |
|
|
Name the possible infectious causes of case study 1?
|
Myocarditis
Viral: Come- Coxsackie group A + B Enter- Enteroviruses My- Mumps Inner - Influenza virus Cells - Congenital Rubella Bacterial: Come- Corynebacterium diptheria- has a vaccine Closer- Chlamydia To- treponema pallidum Big- borrelia burgdorferi Myocardium- mycoplasma Fungal- candida spp Parasites- trypanosomiasis- chaga's disease |
|
|
If the patient was still alive what would be your management for case 1?
|
Teatment should be directed at the specific aetiological agent
Supportive therapy Treat symptoms of heart failure Bed rest |
|
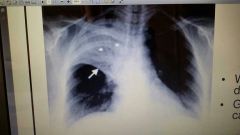
Case study 2- A 65 year old man present to the emergency compartment with complaints of- chest pain- relieved via sitting up and leaning forward + cough + shortness of breath + fever. Five days ago he started coughing and having fever but never sought medial attention. He has been progressively getting worse until his family decided to bring him to the hospital. On examination he was:
Acutely ill Fever of 39 degrees celcius Respiratory distress Decreased breath sounds of his right upper lobe Pericardial friction rub What is your presumptive diagnosis? |
Pericarditis
|
|
|
Give the possible infectious causes of case 2?
|
Purulent- bacteria- secondary to other infections- streptococcus pneumonia + sepsis after surgery due to staphylococci + enteric flora
Tuberculous- mycobacterium tuberculosis Viral- Coxsackie group A + B + Enteroviruses + Mumps + Influenza virus + Varicella (chickenpox) Amoebic Fungal |
|
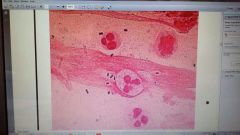
Blood and sputum is collected from the patient and submitted fro MCS. This is a photo of the gram stain. What is the aetiological agent?
|
Streptococci pneumonia- lanceolate diplococci and gram +
|
|
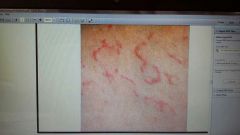
Case 3- a 6 year old girl is brought in by her mother with complaints of- fever + joint pains + rash. On examination- fever= 38.5 degrees celcius + rash + heart murmur- what is your presumptive diagnosis?
|
Rheumatic fever
|
|
|
Case 3- which further history will you obtain from the mother?
|
If there was a recent throat infection
Hx of rheumatic fever |
|
|
Case 3- which criteria would you use to assist in making a diagnosis and name the different components?
|
Modified Jones criteria- 2 major OR 1 major and 2 minor PLUS evidence of a Strep group A infection
Major criteria- carditis (cardiac failure and arrythmias) + polyarthritis (migratory + involving large joints) + erythema marginatum (faint fleeting rash) + subcutaneous nodules (over bony prominences or tendons and remains for 1-2 weeks) + Sydenham's criteria Minor criteria- history of rheumatic fever + arthralgia + acute phase reactants elevated (ESR + CRP + WCC) |
|
|
Case 3- which special investigations would you perform?
|
I would investigate the major criteria + minor criteria
Look for evidence of Strep infection- esp strep pyogenes- via positive culture or positive anti-streptolysin O titre + elevated DNAse + Hx of scarlet fever/erythrogenic toxin |
|
|
Case 3- what type of autoimmune hypersensitivity reaction is this?
|
Type 2 hypersensitivity reaction
|
|
|
Case 3- describe your management of the patient?
|
In the acute phase- penicillin oral for 10 days + anti-inflammatories (aspirin + corticosteroids) + bed rest + monitoring
Follow up- long term penicillin prophylaxis + duration depends on extent of disease- if residual valvular disease present- 10 years or up to 40 ears of age + once follow up has been stopped follow up minor procedures (ESP dental) should be preempted with prophylaxis |
|
|
Case 4- a 24 year old male presents to you with a history of fever for a week. On examination you find the following- fever 40 degrees Celsius and a heart murmur + on further questioning he admits to being an IV drug user. What features number one on your differential diagnosis?
|
Infective endocarditis
|
|
|
Case 4- where would you expect to find a pathology?
|
In the venous system on the right side of the heart because he is an IV user- injected into venous system
|
|
|
Case 4- What is the most common pathogen in this setting?
|
Staphylococcus Aureus
|
|
|
Which criteria would you use to assist you in diagnosing this condition? Name the different components?
|
Duke's criteria
Definite- tissue vegetation positive histology or culture OR 2 major OR 1 major and 3 minor OR 5 minor Possible- 1 major and 1 minor OR 3 minor Rejected |
|
|
Case 4- which further investigations would you perform?
|
Blood cultures- the most NB lab test- bacteraemia is continuous and low grade + first two cultures will yield the aetiology in 90% cases
3 Blood culture sets within 24 hours- no more than 2 bottles from a venepuncture site Aim= recovery of all organisms including anaerobic and fastidious Echocardiography- trans thoracic echocardiography ( TTE ) + trans oesophageal echocardiography ( TEE ) - more sensitive |
|
|
Case 4- What would be your management of the patient?
|
Appropriate AB- often combination therapy based on blood culture results
Duration= 4 - 6 weeks Monitoring required- follow up blood cultures- which you want to become negative + imaging- to shown a reduction in vegetation size |
|
|
Case 5- a 50 year old lady is admitted to the intensive care unit for observation following a hysterectomy for endometrial carcinoma. Three days following the procedure she starts spiking in temperature and deteriorating clinically. On examination the skin around her central venous catheter seems red and inflamed. You take a blood culture and an E coli W's cultured. What is your assesstment?
|
Septicaemia
|
|
|
Case 5- what is SIRS?
|
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
An abnormal generalised inflammatory reaction in organs remote from the initial insult Non-septic causes can lead to SIRS- ex truama |
|
|
Case 5- what is sepsis
|
SIRS + proven or suspected infection
|
|
|
Describe how you would collect blood cultures from a patient?
|
I would use a sterile technique- hand washing etc
Management of wastes- sharps etc Collect from different venepuncture sites- ie peripheral sites Apply a tourniquet Palpated vein Disinfect skin with alcohol- 70% alcohol + tincture of Iodine/2% chlorhexidine- 2 minute contact time Take 3-3 blood culture sets Do not add more blood to a blood culture bottle than the maximum volume Taking blood cultures during a temperature spike- before or after has no difference |
|
|
Case 5 What is the volume of blood you would collect for a blood culture in an adult and a child?
|
Adult= 10 ml per bottle (anaerobic + aerobic) the higher the volume the better the yield
Peads= 1-5ml only one bottle |

