![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
112 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A Type of neuronal storage disease
|
Gangliosidoses
|
|
|
What are the triggers for seizure pathophysiology
|
Genetic predisposition
Trauma, ischemia, stroke, malformation of cortical development Febrile illness, sleep deprivation |
|
|
What are the factors involving the excitatory/inhibitory imbalance of seizures?
|
GABA, K and Cl, Basal Ganglia
NMDAm AMPA; alteration of voltage gated channels Bursting neurons |
|
|
Tendency to have recurrent, unprovoked seizures
|
Epilepsy
|
|
|
Idopathic seizures
|
Genes are involved but not sure in what capacity
|
|
|
"We have no idea" seizures
|
Cryptogenic
|
|
|
Symptomatic seizures examples
|
Stroke, malformation
|
|
|
Consciousness is not impaired in this type of seizure
|
Simple partial seizure
|
|
|
Simple partial seizure presentation?
|
Depend on localization; can involve clonic movements of face, arm, leg
Brief; No post-ictal symptoms; Todd paralysis can occur |
|
|
Complex partial seizure presentation
|
Consciousness is impaired-cannot recall; lasts 30 sec to minute
Temporal lobe seizure-->proceded by an aura (fear, stomach pain, light headedness, distortion of memory or time) Often with Autonomic Symptoms Automatisms: Facial grimacing, gestures, chewing, lip smacking, finger snapping, repetitive speech Post-ictal impairment=lethargy, confusion |
|
|
Frontal Lobe origin presentation for complex partial seizures
|
Arrest of activity
Motor manifestations Versive head/or neck movements Blank stare Abrupt on and off |
|
|
Tonic clonic seizure presentation
|
Loss of consciousness with stiffening of limb (tonic)
Evolution to generalized jerking of muscles Deep sleep post ictal Focal onset Childhood |
|
|
Blank stare seizure?
|
Absence seizure; lasts 30 seconds
|
|
|
Clonic seizures presentation
|
Focal, multifocal; rarely ever generalized
associated with EEG change Migrating clonus indicates metabolic or anoxic damage In children (dont have the thalamic connections) |
|
|
Tonic Seizures presentation
|
Brief, 60 seconds
Sudden onset of increased extensor tone Impaired consciousness |
|
|
"Drop attack"
Sudden loss of tone |
Atonic seizure
|
|
|
Sudden, brief (<350 mS)
Shock-like Generalized or confined to face, trunk Sometimes a sign of diffuse brain injury |
Myoclonic seizure
|
|
|
30 minutes of sustained seizure activity
|
Status Epilepticus
|
|
|
For focal seizure follow up with
|
MRI
|
|
|
For primary generalized epilepsy follow up with?
|
EEG
|
|
|
What are the basic mechanism for antiseizure agents
|
Changes in voltage reg ion channels that lead to excessive depolarization
Increase GABA function Reduce excitation (block glutamate receptors) |
|
|
What is the only anti seizure drug that isnt metabolized
|
Gabapentin
|
|
|
Phenytoin mech of action
|
Use dependent effect on sodium channels; inhibits the generation of repetitive action potentials
|
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of Phenytoin
|
Highly protein bound
Pharmacokinetics are dose dependent Changes from 1st order to zero order as does is increased; often while in the therapeutic range |
|
|
Uses for Phenytoin
|
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
Partial seizures NOT abscence |
|
|
Toxicity of Phenytoin
|
Nausea
Gingival hyperplasia (not dose dependent) Hirsuitism Teratogenicity; fetal hydantoin syndrome; cardiac defects, cleft palate; Rash (not dose dependent) |
|
|
Carbamazepine mech of action
|
Similar to phenytoin; blocks Na channels at therapeutic concentration
|
|
|
Tx of Carbamazepine
|
Drug of choice for partial seizures
NOT in absence |
|
|
Toxicity of Carbamazepine
|
Increased risk of spinal bifida
Rare blood dyscasias |
|
|
Most common type of seizure?
|
Complex partial (temporal lobe)
|
|
|
Mech of action for Ethosuximide
|
Reduces low-threshold T-Type Calcium currents in thalamic neurons
|
|
|
Ethosuximide side effects and toxicity
|
Gastric distress, and lethargy/fatigue
|
|
|
First choice drug treatment of absence seizures
|
Ethosuximide
|
|
|
Mechanisms (3) of valproic acid
|
Blocks repetitive neuronal firing
May reduce T-tuep Ca++ currents Increases GABA concenrations |
|
|
Clinical uses of Valproic acid
|
Absence seizures
Absence seizures with concomitant-generalized tonic-clonic seizures Myoclonic seizures |
|
|
Side effects of Valproic acid
|
Weight gain, hair loss
Hepatotoxicity (not dose related) Spinal bifida (not dose related) |
|
|
NMDA antagonist (block glycine which makes Glutamates action more effective) and also potentiates GABA
|
Felbamate
|
|
|
use for Felbamate?
|
Partial seizures that dont work with other agents
|
|
|
TOXICITY of Felbamate
|
aplastic anemia and hepatic failure
|
|
|
Structural analog of GABA but is NOT a GABA agonist
|
Gabapentin
NOT metabolized and no protein binding making it devoid of the usual drug interactions |
|
|
Tx Gabapentin
|
Adjunct therapy in the treatment of partial seizures ir with secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures
Neuropathic pain and ALS |
|
|
More potent form of Pregabalin
|
Pregabalin; may interact with alpha 2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels
|
|
|
Tx pregabalin
|
Adjunctive therapy for partial seizures
Management of neuropathic pain ass. with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia and fibromyalgia |
|
|
Lamotrigine mech of action
|
Blocks repetitive action poteintials and may block Na+ channels
|
|
|
Lamotrigine use
|
Partial
Tonic-clonic Absence Bi-polar disorder |
|
|
Can cause Stevens-Johnson syndrome
|
Lamotrigine
|
|
|
Inhibits excitatory transmission by antagonizing the ability of excitatory amino acids to activate the kainate/AMPA subtype of glutamate receptor. May also block sodium channels similar to phenytoin.
|
Topiramate
Block the spread of seizures rather than raise the seizure threshold |
|
|
Topiramate Tx
|
Add-on therapy of adults with partial seizures
Also used for Migraine prevention Can cause WEIGHT LOSS |
|
|
Inhibits the GABA transporter, GAT-1, and thus reuptake of GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Increased GABA in synapse.
|
Tiagabine
|
|
|
Add on treatment for both complex and simple partial seizures
|
Tiagabine
Adverse effects include dizziness, tremor and somnolence |
|
|
Tx for Levetiracetam
|
Used as adjunctive therapy for partial seizures. Also indicated for adjunctive treatment of myoclonic seizures and primary generalized tonic-clonic
|
|
|
Acts at both sodium and Calcium channels
|
Zonisamide
Stops the spread of seizures and suppresses their focus Also newer drug Clobazam (also suppresses neuronal hypersynchronization and inhibits carbonic anhydrase) |
|
|
SE of Zonisamide
|
Ataxiam anorexia, nervousness, fatigue and speech impairment
Approved for adjunctive treatment of adults with partial seizures |
|
|
Acts by irreversible inhibiting GABA metabolism
|
Vigabatrin
|
|
|
Main SE for Vigabatrin
|
Permanent effects on vision ("blind as a vigaBATrin)
|
|
|
Tx for vigabatrin
|
Adjunctive tx of complex partial seizures and infantile spasms
|
|
|
Enhances slow inactivation of voltage gated sodium channels
|
Approved for adjunctive tx of partial seizures
|
|
|
Antiseizure drugs that can cause hepatotoxicity
|
Phenytoin, carbamaxepine, valproic acid
|
|
|
Antiseizure drugs that cause dermatologic effects
|
Carbamazepine, lamotrigine
|
|
|
Partial secondarily generalized seizure drugs?
|
Carbamazepone
Gabapentin Oxcarbaxepine Phenytoin |
|
|
Treats all seizures except absence
|
–topiramate
–zonisamide –levetiracetam –felbatol –rufinamide –lacosamide |
|
|
Treat absence seizures
|
Ethosuximide, valproic acid, lamotrigine
|
|
|
Medically resistant epilepsy options
|
Felbatol
Ketogenic diet Vagal nerve stimulation Epilepsy surgery |
|
|
Genetic inheritance of most Lysosomal storage diseases
|
Autosomal recessive (such as Niemann-Pick disease)
|
|
|
What are the X-linked recessive inherited lysosomal storage diseases
|
Fabry disease
Hunter syndrome |
|
|
Suspicions for a metabolic disorder
|
Unexplained lethargy, confusion, somnolence or coma and many more signs
Check glucose, ammonia, and pH Store a "critical sample" for hypoglycemia |
|
|
A type of neuronal storage disease
|
Gangliosidoses
|
|
|
Accumulation of ____ substrates/metabolites in a storage disorder
|
Inert (not active!!)
|
|
|
Tay Sachs disease genetics
|
High incidence in Ashkenazi Jews
On Chromosome 15 Alpha gene |
|
|
Presentation of Tay-Sacs
|
Normal at birth
Retardation at 6 months CHERRY red spot in macula Death by 2-3 years Blindness Flaccidity Prominent forehead |
|
|
Genetics of Sandhoff Disease
|
Chromosome 5
Beta subunit |
|
|
Microscopic findings in Tay-Sachs
|
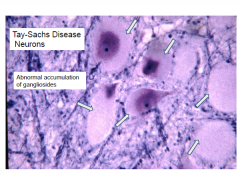
Enlarged neurons filled with PAS
Membranous cytoplasmic bodies |
|
|
Deficiency of Galactocerebroside-B-galactosidase
|
Krabbe's disease
Autosomal recessive gene on Chromosome 14 |
|
|
Krabbe's disease pathophys
|
Globoid cell leukodystrophy
Psychosine injures the oligodendrocytes Galactocerebroside accumulates in the Globoid cells Both the CNS and PNS are affected |
|
|
Dx of Krabbe's disease
|
Enzyme assay of WBC or cultured fibroblasts
|
|
|
Clinical course and tx of Krabbe's disease
|
Normal at birth
Irritability Deterioration of motor function (tonic spasms) Optic atrophy, blindness CSF protein elevated Tx: umbilical cord/bone marrow transplantation (in presymptomatic phase) |
|
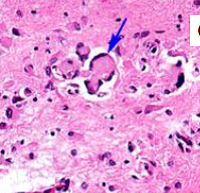
?
|
Globoid Cells (Krabbe's disease)
In EM globoid cells contain crystalloid straight or tubular profiles |
|
|
Deficiency in Aryl sulfatase A
|
Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
On Chromosome 22 |
|
|
Lipids (sulfatides) accumulate in brain, peripheral nerves and kidney
|
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
Lipid accumulation leads to breakdown of myelin |
|
|
Clinical presentation of metachromatic leukodystrophy
|
Can present in different stages of childhood (most common is late infantile)
Present with gait disorder and motor symptoms Treat with bone marrow stem cell tranplantation |
|
|
Brain is externally normal but the white matter is very firm
Marked loss of myelin with preservation of U fibers |
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
|
|
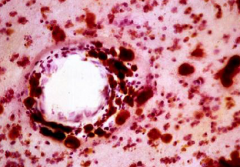
Acidified cresyl violet stain (brown of white matter deposits)
|
Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
|
|
|
Decreased activity of very long chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase
|
Adrenoleukodystrophy (schilder's disease)
|
|
|
Excess of very long chain fatty acid esters in plasma, cultured fibroblasts and affected organs
|
Adrenoleukodystrophy-Peroxisomal disorder-cytoplamic spherical "microbodies"
Involved in fatty acid B-oxidation X-linked |
|
|
Onset of Adrenoleukodystrophy and presentation
|
Classic form: 5-9 years or 11-21 years; dementia, visual hearing loss, seizures, adrenal insufficiency FOLLOWS Neuro signs and sx
Adrenomyeloneuropathy form: Adults (20-30 years); slowly progressive leg clumsiness/stiffness; eventual spastic paraplegia; Adrenal insufficiency precedes Neuro signs |
|
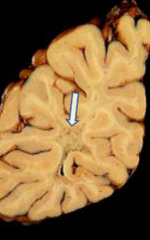
Gray discoloration of white matter; marked firmness
Severe demyelination with U fiber preservation |
Adrenoleukodystrophy
|
|
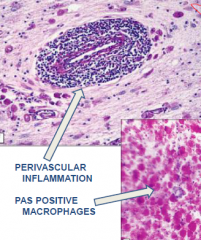
******Pervascular inflammation and PAS positive macrophages
|
***Adrenoleukodystrophy****
|
|
|
Hepatic encephalopathy occurs d/t
|
severe liver disease or chronic portocaval shunting
may be d/t hyperammonemia |
|
|
Manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy
|
Early manifestations: inattentiveness and short term memory impairment
Later features: confusion, asterixis, stupor Foul breath, hyperventilation |
|
|
MRI abnormalities of Hepatic encephalopathy
|
Increased T1 signal in the globus pallidus, subthalamus and midbrain
Cortical edema |
|
|
Alzheimer Type II astrocytes
|
Hepatic encephalopathy
|
|
|
Hypoglycemia affects which parts of the brain?
|
Changes in the temporal, occipital, and insular cortices, hipocampus, and basal ganglia, often with thalamic sparing
|
|
|
Mitochondrial diseases genetics
|
Shows maternal inheritance
Mitochondrial proteins are encoded wtihin the mitochondrial and nuclear genome |
|
|
Presentation of myocardial myopathy
|
Progressive weakness, ataxia, hearing and vision deficit and autonomic dysfunction
MRI of brain showed a cyst and general atrophy Decreased Cytochrome c reductase |
|
|
Heteroplasmic point mutation in mt-tRNA^leu
|
MELAS (mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes)
|
|
|
Heteroplasmic point mutation in mt-tRNA^lys
|
MERRF (myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers
|
|
|
–Usually caused by large single mtDNA mutation
–Causes pigmentary retinopathy and opthalmoplegia before 20 years of age |
Kears-Sayre Syndrome
|
|
|
Mutation in nuclear DNA
deficiency in pathway converting pyruvate to ATP Decreased activity of cytochrome C oxidase recessive Lactic acidema |
Leigh's disease (subacute necrotizing encephalopathy)
|
|
|
Leigh's disease (subacute necrotizing encephalopathy)
|
Arrest of development, hypotonia, seizures, extraoxular palsies
Death between 1 and 2 years |
|
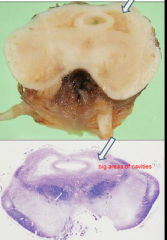
Periventricular gray matter tissue destroyed; around cerebral aqueduct and 3rd ventricle
|
Leigh's disease
Histologically has a spongiform appearance and vascular proliferation |
|
|
Wernicke encephalopathy cause and presentation
|
Vitamin B1 deficiency
Ophthalmoplegia, nystagmus Ataxia Confusion, disorientation, eventual coma Gray-brown discoloration with petchial hemorrhages (acutely) Atrophy and discoloration of mamillary bodies (chronic state) |
|
|
Korsakoff Psychosis presentation
|
Loss of anterograde episodic memory, confabulation
preserved intelligence and learned behavior D/t thiamine deficiency and repeated episodes of Wernicke's Damage to medial dorsal nucleus of thalamus |
|
|
Presentation of Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency
|
Ataxia, romberg, spasticity, decreased reflexes, mental status changes
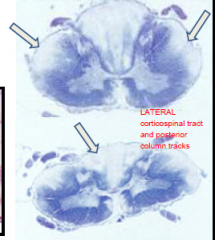
Subacute degeneration of the spinal cord Usually d/t pernicious anemia Anterior and lateral corticospinal tracts and posterior columns are vacuolated and demyelinated |
|
|
Vitamin B12 deficiency
|
|
|
Where does carbon monoxide bind?
|
Globus pallidus (rick in iron)
binds irreversible to hemoglobin, displacing oxygen CO poisoning usually accompanied by hypotension/ischemia |
|
|
CO poisoning presentation
|
Motor, cognitive, psychiatric, and parkinsonian s/s
|
|
|
Cerebellar degeneration; atrophy of the anterior superior vermis
|
Chronic ethanol toxicity
|
|
|
Fetal alcohol syndrome presents with?
|
Growth retardation, facial deformities, cardiac defects (ASD), delayed development and mental deficiency
Small eye openings, smooth philtrum, thin upper lip |
|
|
large areas of coagulative necrosis primarily in white matter (months to years later)
|
Radiation Toxicity
Also induction of neoplasms years after treatment |
|
|
Methotrexate (in combo with radiation) causes
|
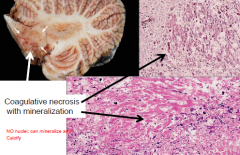
Disseminated necrotizing leukoencephalopathy
coagulative necrosis with axonal loss and mineralization |
|
|
Effects of Phenytoin
|
Ataxia, nystagmus, slurred speech and sensory neuropathy
Atrophy of cerebellar vermis and loss of purkinje cells and granule cells |
|
|
Cocaine casues
|
Seizures, strokes, hemorrhages
Infarcts/hemorrhages d/t vasospasm, emboli, hypercoaguability, hypotension |

