![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List 3 things which would tell you it was unsafe to move a train in a yard as someone is still working on it |
A 'not to be moved board' Shore cables attached Red Flag Red Light Depot Protection system lit (red light) A 'not to go' sticker |
|
|
Before you make a shunting movement with a train what 2 things must you agree with the shunter? |
A clear understanding of exactly what is required to be done & how the movement will be controlled |
|
|
What 3 things would you check for underneath your train to ensure they are safe before moving the train? |
Scotches, derailers and facing points |
|
|
List the 3 methods available to control shunting movements in a yard, siding or depot. |
Handsignals Audible signals (bell or whistle) Radio |
|
|
How would you use the following during a movement in a yard, siding or depot? The warning horn Frontal lights |
Horn - Low tone only (except cauldwell) Lights - Marker lights only (switch off headlight) |
|
|
What is the maximum speed in a yard, siding or depot unless otherwise stated? |
5mph |
|
|
What lower speed might you have to adhere to and list one location in a yard where this might be necessary? |
3mph Through a washer or entering a building |
|
|
What do the following daytime handsignals mean? Both arms raised above the head |
Stop Immediately |
|
|
One arm moved slowly up and down at the side of the body One arm moved in a circular motion away from the body One arm moved horizontally across the body to the shoulder |
Slow down Move away Move towards |
|
|
What would the movements be if the shunter were given a handlamp? Stop Immediately Slow Down Move Away Move Toward |
A red light held prominently or any colour light waved violently Slow down - Using a green light Move away - A white or green light moved slowly up and down Move towards - A white or green light moved slowly back and forth across the body |
|
|
What are the three things you must do before entering a shed or building? |
Stop before the entrance Enter only if you have the shunters permission Sound the horn before entering (except at Cauldwell) |
|
|
List three things that would cause you to stop or not start a shunting movement being controlled by any of the 3 methods in the previous question. |
If the shunter goes out of view (shunting by handsignal) If unsure what a handsignal means (shunting by handsignal) If unsure if a handsignal applies to your train (shunting by handsignal) If you lose comms with the shunter (by radio) If unsure as to what a whistle or bell code means (shunting by audible signal) Any others that you feel relevant |
|
|
What is the handsignal to indicate that a train is clear of points to be turned that are worked from a ground frame where no signal is provided? |
By day - One arm raised above the head By night - A white light twisted |
|
|
What 4 things must you ensure when you leave a train after a shunting movement has finished in a yard, depot or siding? |
That the train is secured correctly, is not left foul of any other road and is not standing over derailers or pointwork |
|
|
What lights would you display on the rear of a unit left on a dead end road? |
The same lights displayed on the buffer stops. If there are white lights on the stops then switch on the marker lights at the rear, if red lights on the stops, switch on the tail lights and if no lights shown on the stops then switch off all lights. |
|
|
What are the meanings of the following audible shunting signals given by bell/buzzer or whistle? One Two Three |
One - Stop Two - Go Ahead Three - Set Back |
|
|
In what 2 exceptional occasions might you be required to drive a unit from somewhere other than the leading cab? |
When propelling a dead unit during a train failure or when unable to drive from the front cab of the train due to defective driving controls |
|
|
If you are required to drive from other than the leading cab where should you drive from if possible? |
From another forward facing cab if available |
|
|
Who will you need to position in the leading cab before you can make the movement? |
A competent person (another driver or someone who signs the route. Shunter if in a yard) |
|
|
What 4 communications options are there to control movements between you and the leading cab? |
Cab to Cab radio Bell/Buzzer code Radio Handsignals |
|
|
What speed would you be able to travel at during a propelling movement if: The person in the leading cab was able to apply the brake on the entire train in an emergency (brake continuity available) The person in the leading cab was not able to apply the brake on the whole train in an emergency (brake continuity not available) |
20mph 5mph |
|
|
What is the most basic principle of most signalling systems? |
One train in any one block or signal section at any one time |
|
|
A main aspect colour light signal with an associated position light signal normally guards the entrance to a line where what type of working is permitted? |
Permissive working |
|
|
How would you proceed if you received a main aspect signal at red with a lit associated position light signal. |
I can proceed past the signal cautiously towards the next stop signal or buffer stops. I must be prepared to stop short of any obstruction as the line ahead may be occupied |
|
|
How would you drive past a position light associated with a main aspect or a position light signal showing a proceed aspect in think fog and why would you do this? |
At extreme caution as the line ahead may be occupied and i will need to ensure i can stop within the distance i can see to be clear so that i do not collide with anything in the section or end up passing a signal at danger. |
|
|
Position light signals question |
|
|
|
If you receive a proceed aspect at a position light signal but do not get the required indication you should get, what would you do? |
You could either contact the signaller or if you can see the points are set for the route you take you can take the signal and proceed at caution as far as the line is clear. |
|
|
What does POSA stand for? |
Proceed on sight authority Rule Book module POSA |
|
|
When will POSA signalling be utilised? |
When the signal section ahead has suffered from a track failure, or failure of the signal associated with the section. In times of disruption due to signalling equipment failures or disconnecting of signalling for engineering works. |
|
|
When MUST the signaller stop and advise the driver that POSA's will be introduced? |
When authorising a train to pass a signal which is defective and unable to display a main aspect. When stopped at a signal approaching a platform where a mid platform signal or platform starting signal has failed. This is to prevent the train being stopped partially within a platform and reduces the risk of customers inadvertently opening train doors. |
|
|
What is the risk associated with approach controlled junctions and what must you do to ensure you do not fall into this trap? |
There is a risk that a driver could expect the junction signal to clear on approach and may end up passing the signal at danger if it does not. |
|
|
Draw 2 types of limit of shunt boards |
|
|
|
What does a limit of shunt board normally mark the limit of, and whos permission do you need to pass one? |
Normally marks the limit of a signalled wrong direction move You need the signallers permission to pass one |
|
|
Draw a stop for orders board. Where would you commonly find these? |
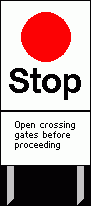
Normally found in yards, depots and sidings. The sign can have any relevant instructions displayed on it. |
|
|
What is a co-acting signal and why do we have them? |
A signal designed to mimic the aspect shown by another signal where that signal is positioned poorly due to sighting. It has the same signal number +CA after it as the poorly sited signal. The co-actor will be placed in a better position for sighting than the signal it co-acts with. |
|
|
What would a SPAD indicator show when lit and what would you do if you saw one lit in your direction? |
Three red lights vertically displayed. The top and bottom red lights will flash, the middle stays steady. You must stop immediately regardless of how far away from the SPAD indicator you are and contact the signaller. |
|
|
How would you know the following colour light signals were not in use:- A Main aspect signal A position light signal |
Main Aspect - Black cover placed over the signal head with a white cross on it Pos light - It will be covered over (bagged) |
|
|
If you were following another train down a permissive line, how would you follow it and why? |
Proceed with caution leaving enough distance between you and the other train so if it were to stop suddenly you can stop without running into them. |
|
|
If you are following a train down a permissive line, when can you proceed past the signal at the end of the permissive line? |
Only when the train you are following has passed the signal and you have seen the signal return to danger and re-clear for your train. |
|
|
You have taken a double unit into a dead end platform and they have been uncoupled to form 2 trains. The front unit leaves and you get into the rear unit. The unit has a fault and you want to proceed down the platform towards the signal to test out the unit. The signal is Red. What must you do before you make a movement towards the signal and why? |
You must contact the signaller and get permission to proceed towards the red signal as they may have signalled another train in on top of you. You should in addition liaise with the station staff before making the movement. |
|
|
List the 4 things you must do should you accidentally pass a signal at danger? |
Stop Immediately Tell the signaller you have passed a signaller at danger Answer a number of questions which the signaller is required to ask you Do not move until the signaller gives you permission |
|
|
List the 6 occasions you must set the DRA |
1. When stopping at a station platform where the starting signal is at danger 2. When stopping at a station platform where no signal is provided and the last signal you passed was displaying a caution aspect 3. When stopping at a station platform where no signal is provided after being authorised to pass the last signal at danger 4. When stopping at a station platform where no signal is provided on the authority of a position light or shunting signal 5. When stopped at any other type of signal at danger (stop boards, limit of shunt boards etc) 6. When entering/leaving the cab to: relieve, dispose, immobilise |
|
|
What are the risks involved with the DRA regarding: Not setting it when you should Using it on other occasions when it is not necessary |
If you havent set it, it cannot act as a reminder to you so you could end up passing a signal at danger. Overuse is dangerous as the equipment will lose its impact on you to act as a reminder. You may also remember to set it at other times but forget to set it when you should. |
|
|
List 5 things you would report as a signalling irregularity. |
It is not clear which aspect applies at a colour light signal There is no light shown One light is showing in a position light signal when there should be two A failure in the working of a signal An irregular aspect sequence No signal where there should be one A white light shown instead of a red, yellow or green light A signal, or associated indicator that is difficult to see because of, for example, sunlight, streetlights or light reflections affecting its readability A signal difficult to see because of foliage etc |
|
|
When would you fill in the RT3185 form for the following types of irregularity/failure? Wrongside Rightside |
Wrongside - Immediately. Dictated over the GSM with the signaller at the time of the incident Rightside - At the earliest opportunity but at least by the end of your shift |
|
|
Which section of the RT3185 form can be filled in later on in your shift regardless of what type of failure you have reported? |
Section 6 - Additional info section |
|
|
When should your RT3185 form be given in once completed? |
Asap so that the fault can be rectified. At least by the end of your shift that day. |
|
|
List 4 occasions when you will receive the AWS warning horn in the cab apart from at a signal displaying a restrictive aspect. |
At a warning board for a PSR At a warning board for a TSR At a warning board or Emergency indicator for an ESR At an AWS depot test magnet At a warning board for an ABCL ot AOCL level crossing When first livening up the cab |
|
|
What are the following signs and what do they indicate to you? St andrews flag type sign Yellow square with black diagonal cross Check understanding of AWS area boards |
St. Andrews - AWS cancellation indicator for a permanently installed magnet. Ignore the last AWS received. Yellow square - AWS cancellation indicator for a temporarily installed magnet - Ignore the last AWS received |
|
|
What are the two main reasons TPWS was designed? |
To reduce the number of spads and to reduce the consequences if a spad does take place |
|
|
List the 5 occasions when you might receive a TPWS brake intervention/application. |
You approach a TPWS fitted signal at danger too fast You pass a TPWS fitted signal at danger You approach buffer stops too fast You approach a TPWS fitted PSR too fast You take too long to cancel an AWS warning horn |
|
|
What is the name of the set of TPWS loops fitted at the signal? |
Overspeed loops |
|
|
What is the name of the set of TPWS loops fitted at the signal? |
Train stop loops |
|
|
At what distance are TPWS loops fitted from buffer stops and what speed should you do over them? |
50m No more than 10mph but preferably under this |
|
|
At a main aspect signal fitted with a position light, which tpws loops will remain energised even if the position light shows proceed and why is this? |
The overspeed loops. You should be braking the train and have it under full control if you are going to take the position light anyway as you are probably about to enter a permissive, yard or siding line. |
|
|
List the 5 peices of equipment in the cab associated with the AWS/TPWS system (includes original AWS equipment) |
TPWS control panel AWS sunflower AWS/TPWS cancel button TPWS Temporary Isolation Switch TPWS Full isolation switch AWS audible indications |
|
|
Identify each button on the TPWS control panel |
Brake Application/Demand Temporary Isolation/Fault Train Stop Override |
|
|
If you have a problem with the TPWS system such as a fault or cannot get the brakes to come off what should you try in the cab first before any isolation? |
Trying shutting down the desk (master switch to off) and re-energising several times. |
|
|
What do the following indications tell you for the red light on the control panel? Light Out Light Flashing Light Steady |
Out - System is normal no brake intervention Flashing - TPWS has initiated an emergency brake application which has not yet been acknowledged Steady - TPWS has initiated an emergency brake application which has been acknowledged |
|
|
Yellow Light Light Out Light Flashing Light Steady |
Out - System is working correctly Flashing - The TPWS has developed a fault Steady - The TPWS has been temporarily isolated |
|
|
Yellow Button Light Out Light Flashing Light Steady |
Out - Train Stop Override has not been selected Steady - Train stop override has been selected |
|
|
List 3 occasions when you would be required to operate the TPWS Temporary Isolation Switch |
For a fault on the system (yellow light flashing etc) Before entering temporary block working Before entering single line where working by pilotman is in operation and you are required to pass more than one signal at danger When authorised to enter a line under possession as described in rule book module T3 Before propelling a train or driving from other than the leading cab |
|
|
What part of the AWS/TPWS system will still operate even if temporary isolation is selected? |
The AWS system - audible bell/horn and visual sunflower
|
|
|
Is there any way a train can enter service with the TPWS Temporarily Isolated, fully isolated or faulty in a cab? |
Yes, provided the affected cab is in the middle of the train (boxed in) |
|
|
What would your immediate actions be if the AWS/TPWS became faulty or had to be isolated whilst in service? |
Stop the train immediately in a suitable location Contact the signaller (they will then contact SDC) Stop where you are and wait for instructions Act on the instructions given |
|
|
If you are to continue to a suitable location to take the train out of service in the previous question what restrictions are there if: You have a competent person with you: You have no competent person with you: You have a comp. person but visibility is poor: |
Comp person - Line Speed No Comp person - 40mph Comp, Poor Vis - 40mph |
|
|
For the above question, what is the definition of a competent person? |
Someone who signs all of the route you are working over (another driver or driver manager) |
|
|
What are the driver and competent persons duties en route to the place the train is to be taken out of service? |
Driver gives a running commentary especially on approach to restrictive signals. Com Pers. acknowledges all of this and takes action if the driver doesn't do this. Put emergency brake in etc. |
|
|
Why do we have strict procedures and place restrictions on trains when certain pieces of on train equipment become defective (such as AWS/TPWS), until these trains can be taken out of service? |
Because if on train systems are not working then the train poses a risk to itself and other trains until it is removed from service. We place restrictions on these trains to reduce the risk they pose until they can be taken out of service. |
|
|
Explain the 3 main AWS/TPWS wrongside failure faults |
1. Bell received when there should have been an AWS horn (5) 2. Nothing received when there should have been an AWS horn (7) 3. TPWS failed to initiate a brake application when it should have done (16) |
|
|
When would you be required to fill in the RT3185 form for the above fault codes? |
Dictate it over the GSM to the signaller at the time of the incident |
|
|
What should you do if your train experiences a TPWS brake intervention caused by loops at a location other than approaching buffer stops, and what is the risk to you and your train if you don't do this? |
Once you have stopped and acknowledged the brake demand, inform the signaller immediately, do not move, act on instructions given. you may have spadded without your knowledge and would run the risk of collision or other major incident if you continue without contacting the signaller. |
|
|
If your train was to stop with the AWS receiver in your cab directly over an AWS magnet and you couldn't cancel the horn, what 2 options in order of preference have you got? |
1.Request permission from the signaller to make a wrong direction move, change ends, reconfirm the details and drive off. 2. Fully isolate the AWS and proceed as per defective on train equipment |
|
|
What would you see on approach to a signal additionally fitted with TPWS plus? |
An additional set of overspeed loops before the normal set of overspeed loops. |

