![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Four main types of tissues |
- Connective - Epithelium - Muscle - Neural |
|
|
Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM) |
light/electrons go THROUGH the specimen |
|
|
Heterochromatin |
High density areas of DNA (dark part of TEM image) |
|
|
Euchromatin |
Less DNA (white space of TEM image) |
|
|
Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM) |
Light/electrons do NOT pass through specimen; gives a 3D image |
|
|
Most common stain used in histology
|
- H&E (hematoxylin - purple & eosin - pink) - Hematoxylin - acidic things (like RNA/DNA) stain purple (basophilic) - Picture on page "Cytology Notes"Eosin stains pink to orange, acidophilic |
|
|
Silver Stain |
reticular fiber stain - uses silver salt |
|
|
Mitotic Figure |
when a cell is going thru mitosis |
|
|
Interphase |

chromatin is inside nucleus in a dispersed way to facilitate transcription |
|

Which phase of mitosis? |
Interphase |
|
|
Prophase |
Looks like a ball of yarn - condensation of chromatin material. Very purple-blue. |
|
|
Metaphase |
Chromatids begin to line up |
|
|
Anaphase
|
Sister chromatid groups are dragged toward the poles. |
|
|
Telophase |
Nuclear envelope reforms & cells divide. |
|
|
Open-Faced Nuclei |
Dense nucleolus, can see nuclear membrane & a lot of chromatin. - Means cell is mitotically active. |
|
|
Closed-Faced Nuclei |
Looks like a dark lake; not mitotically active |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
Involved in packaging - things the cell wants a membrane around White near the nucleus - due to neutral pH. |
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Involved in protein synthesis Normally near the nucleus Purple-blue stain Purple haze near nucleus - means it's a very active cell making a ton of proteins |
|
|
Microvilli |
- on cell membrane - increase surface area for absorption |
|
|
Cilia |
- on cell membrane - sensory; move mucous and foreign material |
|
|
Tissue Artifacts |
Air bubble, hair, dye leakage, etc. |
|
|
Cell Inclusions |
Non-living material that the cell doesn't directly need to live ex: glycogen, lipids, crystals, pigments ***lipids & pigments most common in H&E staining*** |
|
|
Glycogen |
- most common form of glucose in animals - energy source for cells - especially abundant in cells of muscle & liver |
|
|
Lipids |
- triglycerides in storage form - energy source - fat cells - no membrane around it |
|
|
Crystals |
- crystalline forms of certain proteins - cells don't like this - can create a block in cell structure |
|
|
Pigments |
- various compounds found in cells which can sometimes serve a protective function (ex: melanin), mark cells age, or exposure to oxidative stress - ex: hemosiderin (byproduct of phagocytosis in red blood cells - rusty brown pigment) - ex: lipofuscin (things lysosomes couldn't digest) |
|
|
Hemosiderin |
byproduct of phagocytosis in red blood cells rusty brown pigment |
|
|
Lipofuscin |
things lysosomes couldn't digest tells us cells are really old or hit with a lot of oxidative stress (hasn't had an easy life) |
|
|
Stroma |
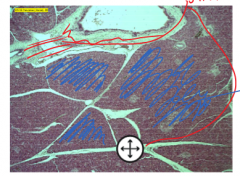
most of the white part - nonliving structural material - gives support - called 'septa' in pancreas - holds organ together |
|
|
Parenchyma |
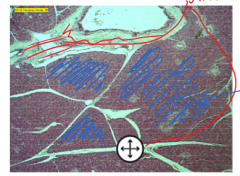
blue part (colored filling portion) - functional cellular material of an organ - specific cells that function to give the organ its identity |
|
|
Acinus Structure |
Cellular ARRANGEMENT whereby cells surround each other in a radial formation |
|
|
Lumen |
Opening in center of an acinus structure |
|
|
Apical |
Top of cell |
|
|
Basal |
Bottom of cell |
|
|
Zymogen Granuals |
- Apical side - acidophilic (pink/orange) - Digestive enzyme |
|
|
Shrinkage |
considered to be "artifact" empty space between cell membrane and rest of cell |
|
|
Lipid droplets |
- Cell inclusion - Show where lipid was |

