![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is soil? |
Mixture of weathered mineral debris and plant material (<1m) top soil = plant rich, sub-soil = clay-rich |
|
|
|
What is weathering? |
Natural decay and breakdown of rock, or drift, that is in contact with air and water; generally depth of <10m |
|
|
|
What is drift? |
Transported, superficial sediment deposited on top of the bedrock; mostly unconsolidated clay, sand and coarser clastic debris |
|
|
|
What is colluvium? |
Slope debris, moved downslope largely by gravity alone; so relative extent of sediment transport drift>colluvium>soil; includes debris from creep and sheetwash, also head and scree. Increases with loss of vegetation |
|
|
|
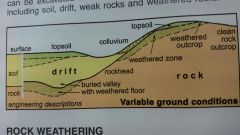
What is rockhead? |
The buried drift/rock interface ; commonly a conspicuous boundary between weak soils and drift and the underlying strong rock; may be less well defined in deep profile of weathered rock ; formed as erosion surface before drift deposition so it's topography may be totally unrelated to modern surface |
|
|
|
Define engineering soil |
Weak material that can be excavated without ripping or blasting, therefore including soil, drift, weak rocks and weathered rocks |
|
|
|
Describe 6 physical weathering processes |
Unloading joints: stress relief fractures, due to over-burden material removal Thermal expansion: fracturing, due to daily temperature changes Frost shatter: fracturing, as fissure water or porewater freezes and expands. Wetting and drying: movement, due to loss or gain of water in clays Root action: tree root expansion in fissures, and rootlet growth in pores. Crystallisation: growth of salt crystals, where groundwater evaporates |
|
|
|
Describe 4 chemical weathering processes |
Solution: mainly of calcite and gypsum, in sandstone cement, veins and limestone. Leaching: selective removal of solutes or specific elements Oxidation: notably rusting and breakdown of iron Hydrolosis: most silicates react with water to form clay minerals |
|
|
|
Weathering profiles in rock |

|
|
|
|
Describe pinnacled rockheads in the weathering of limestone |
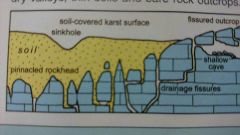
Have deep fissures, mostly filled with soil, between weathered limestone pinnacles, all beneath soil or drift cover (creates difficult foundation conditions prone to sinkhole subsidence) |
|
|
|
What is a karst? |
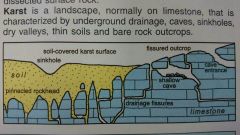
A landscape, normally on limestone, characterised by underground drainage, caves, sinkholes, dry valleys, this soils and bare rock outcrops |
|
|
|
Describe fluvial processes |
the action of rivers and flowing water - dominant in all climate regions except arid and permanently frozen regions |
|

