![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Compare weather and climate |
Weather is the daily atmospheric conditions, while climate is the average atmospheric conditions |
|
|
Name the layers of the atmosphere (starting closest to earth) |
Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere |
|
|
List a characteristic of the troposphere |
Contains all weather |
|
|
List a characteristic of the stratosphere |
Contians ozone layer |
|
|
List a characteristic of the mesosphere |
Meteors burn up there |
|
|
List characteristics of the thermosphere |
Contains auroras |
|
|
Where is the ozone layer, and why is it so important? |
The ozone layer is in the stratosphere, and it protects us from harmful UV radiation released from the sun |
|
|
How does temperature change as you go into the troposphere? |
The further up in the troposphere you are, the cooler the temperatures become |
|
|
What happens to air pressure as you go further into the atmosphere? Why? |
Air pressure decreases as air molecules spread out and it becomes less dense. |
|
|
What happens to air pressure as elevation increases? |
Air pressure decreases |
|
|
What happens to air pressure as water vapor decreases? |
Air pressure increases |
|
|
What happens to air pressure as temperature decreases? |
Air pressure increases |
|
|
What instrument do you use to measure air pressure? |
A barometer |
|
|
What part of the global wind system do we live in? |
The westerlies |
|
|
How does air pressure move (low-->high, high-->low, both)? |
High to low
|
|
|
Process in which warm fluids rise and cool sink |
Convection |
|
|
What effect makes winds appear to curve due to earth's rotation? |
Coriolis force |
|
|
Would the air at the equator rise or sink? |
Rise |
|
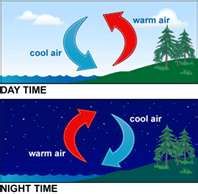
The day time diagram shows __________, and the night time diagram shows_________. |
Daytime diagram-sea breeze Night time diagram-land breeze |
|
|
Humidity |
The amount of moisture in the air |
|
|
Relative humidity |
Percentage of saturation in the air |
|
|
Absolute humidity |
Weight of water in a given volume of air |
|
|
Capacity |
Maximum weight of water vapor that a given volume of air can hold at a definite temperature |
|
|
Dew point |
Temperature at which the air much cool in order to be saturated |
|
|
Saturation |
Air that is filled to capacity with water vapor |
|
|
Condesation |
The change of water vapor into liquid water |
|
|
When air is cooled, it can hold ______ vapor than before |
Less |
|
|
Why does dew form on the grass in the morning? |
During the day, the air is warmer and can hold more moisture. At night, air cools and can't hold hold moisture so the water vapor condenses out of the air and onto surface in the form of dew. |
|
|
List the three steps of cloud formation |
1.) Sun's heat warms the ground 2.) Warm air forms above the ground and begins to rise 3.) As a warm air bubble rises, it cools it to its dew point temperature and condenses on particles in the air to form clouds |
|
|
What are the two most common gases in the atmosphere, and what are their percentages? |
Nitrogen (78%) and Oxygen (21%0 |
|
|
Why do we have seasons? |
Earth's axis is tilted, resulting in unequal amounts of heat energy year round |
|
|
What are some greenhouse gases? |
Water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, ozone |
|
|
What are some ways that carbon is put into the atmosphere? |
Humans, animals, industry, plants, oceans
|
|
|
What is the largest source of pollution to our atmosphere? |
Burning fossil fuels |
|
|
What are some possible consequences of climate change?
|
Melting glaciers, water shortages, wildfires, etc. |
|
|
Albedo |
The percentage of light reflected by an object |
|
|
How does elevation affect climate?
|
As you go higher in elevation, the average temperature of region decreases |
|
|
How does latitude affect climate? |
As latitude increases (moving towards the poles), average temperatures decrease |
|
|
How does proximity to water bodies affect climate? |
Being located to a body of water moderates temperatures, keeping them fairly constant as well as increasing the amount of rainfall |
|
|
How do global winds affect the climate? |
Global wind belts carry heat around the globe as well as large amounts of water. |
|
|
How does topography and mountain ranges affect the climate? |
Mountain ranges affect the amount of rainfall in an area by forcing them upwards, creating a large amount of rainfall on one side of a mountain and none on the other. |
|
|
Greenhouse effect |
The natural warming of earth due to the trapping of heat by greenhouse gases |
|
|
How are winds named? |
By the direction in which they move |
|
|
Isobars |
Lines of equal air pressure |

