![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where does the hematopoietic system happen after birth?
|
Bone marrow
Gut-associated lymphoid tissues Spleen Lymph nodes Thymus Waldeyer's ring |
|
|
What is the overallpattern of hematopoiesis?
|
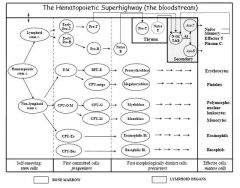
Memorize!
|
|
|
Broadly, what is the difference in development between the myeloid and the lymphoid cells?
|
Lymphoid: most of the differentiation happens after the bone marrow
Myeloid: most of the differentiation happens IN the bone marrow |
|
|
What cells give rise to the lymphomas?
|
B-cells
T-cells |
|
|
As there is aging, what happens to the bone marrow?
|
More fat.
|
|
|
What are the major groups of stem cell neoplasms?
|
Myeloproliferative disorders
Myelodysplastic syndromes Acute leukemias |
|
|
What are the general properties of the myeloproliferative disorders?
|
Uncontained growth, but good differentiation of the cells that are there
Way too many cells in the marrow; you have a rise of precursors in the periphery You have a risk of progression to an acute leukemia |
|
|
What is the classic example of myeloproliferative disorders?
|
Chronic myelogenous, granulocytic leukemia.
All kinds of precursors out in the periphery. |
|
|
What are the general properties of the myelodysplastic syndromes?
|
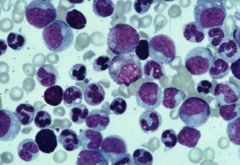
Abnormal differentiation from the outset; dysplastic precursors! Things look odd.
Dysplastic cells in the marros; some are released to the the blood Normal hematopoiesis is suppressed. Some progression to acute leukemias |
|
|
What are the general properties of the acute leukemias?
|
Transformation occurs of the stem cells, but there is an arres ot fhte cells in an immature form of the cell, and these are the cells that go out into the blood
Normal marrow is crowded out-->cytopenias |
|
|
What are the different types of leukemias?
|
Lymphoid: acute lymphoblastic leukemias
Non-lymphoid: acute myeloid leukemias |
|
|
What's the major difference between lymphomas and leukemias?
|
Lymphoas happen in the secondary lymphoid organs and has the appearance and features of a mature lymphocyte (T and B cells)
|
|
|
What virus can cause lymphoid tumors?
|
EBV
|
|
|
What is the largest group of the mature lymphoid neoplasms?
|
Lymphomas
|
|
|
What cells give arise to lymphomas?
|
B and T cells of lymphoid organs
|
|
|
What are the findings in a lymphoma?
|
Overgrowth of a secondary lymphoid organ: lymphadenopathy, mediastinal mass, splenomegaly, infiltrates in the submucosa of the GI tract
|
|
|
What are the two different categories of lymphomas?
|
Hodgkin's
Non-hodgkin's |
|
|
What cells are pathologic in hodgkin's lymphomas?
|
B-cells
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of spread for hodgkin's lymphomas?
|
Lymphatics first, then bloodstream
|
|
|
What are the cell types implicated in non-hodgkin lymphomas?
|
B, T, NKs
|
|
|
How do Non-hodgkin lymphomas spread?
|
Bloodstream, then lymphatics
There's more of a bloodstream involvement than lymph. |
|
|
What's the basis for separating between hodgkin vs.non-hodgkin lymphomas?
|
Histological characteristics
|
|
|
What is the definition of a "leukemic phase" in a non-hodgkin's lymphoma?
|
You can actually see the malignant cells in a blood smear
|
|
|
What cells are altered in the myeloproliferative disorders?
|
Hematopoietic stem cells
Non-lymphoid stem cells |
|
|
In general, what are the findings in the blood of a myeloproliferative disorder?
|
More of everything
|
|
|
What myeloproliferative disorder shows increased RBCs?
|
Polycythemia vera
|
|
|
What myeloproliferative disorder shows increased platelets?
|
Essential thrombocytosis
|
|
|
What myeloproliferative disorder shows increased WBCs with precursors and blasts?
|
Chronic myelogenous (or granulocytic) leukemia: CML, CGL
|
|
|
What cells become disordered in the myelodysplastic syndromes?
|
Stem cells
|
|
|
Generally, what are the findings in the blood in the myelodysplastic syndromes?
|
Less of everything normal; normal hematopoiesis is inhibited
Increased numbers of undifferentiated cells. |
|
|
What cells are altered in the acute myeloid leukemias?
|
Hematopoietic stem cells
Non lymphoid stem cells CFU- G/M CFU-G CFU-M |
|
|
What kinds of cells are seen in the acute myeloid leukemias?
|
Lots of precursor cells in the peripheral blood
Myeloid blasts indicative of the lineage of the cells. |
|
|
What cells go awry in the acute lymphoblstic leukemias?
|
Hematopoietic stem cells
Lymphoid stem cells Early Pre-T, B cells |
|
|
What cells go awry in the lymphomas?
|
Pre-T cells
Rescirculating T and B cells Active T and B cells These can be inside the primary or secondary lymphoid organs |

