![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
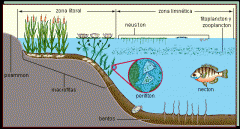
Aquatic habitats
 |
Lentic=lake,pond,marsh,fen &bog. Stll waters. Lotic=streams,rivers,brooks,creeks &springs. Flowing waters
Terrestrial=riparian zones. |
|
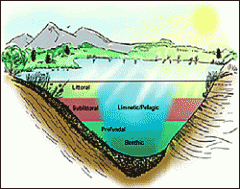
Habitat zones
|
Littoral=rooted plants around pond or lake (not river/stream).Profundal= zone past littoral in lakes. Planktonic=top area where fish can live in open water, bottom area is pelagic. Benthic= bottom of aquatic zones.
|
|

Umbrella species
|
Protecting one species consequently protects numerous other species
|
|
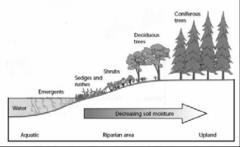
Riparian zone
|
area affected by water in rivers lakes and streams, influences plant type. Important b/c provides food,shelter,water and a cooler microclimate.
|
|
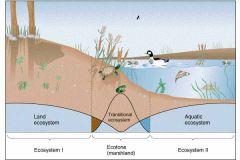
Ecotones
|
one ecosystem meets another and there's overlap= high diversity
|
|
|
Compensatory reproduction
|
one species population declines, the physiology of the animal changes to produce more offspring than average.(i.e. coyotes)
|
|
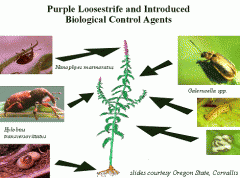
Biological control
|
finding a natural enemy for an invasive species, the enemy must be able to survive in conditions.
|
|
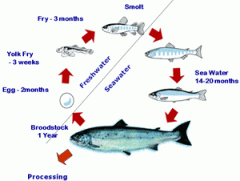
Smoltification
|
changes in physiology of fish to adapt to salt water conditions
|
|
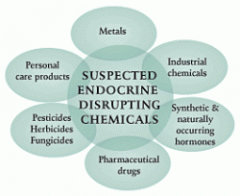
endocrine disruptors
|
interrupt smoltification process, come from sewage disposal into freshwater and/or saltwater
|
|
|
spatial dispersial
|
relates to the space between habitats, usually connected by corridors.
|
|
|
endemic
|
Local scale, the species with an endemic issue are only found in that one area
|
|
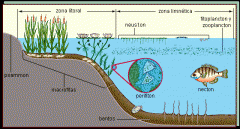
Necton
|
organism that moves independent of currents such as fish and invertebrates
|
|
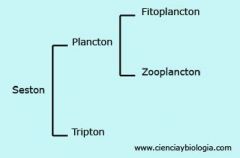
Seston
|
particulate matter in water, living and non, organic and non
|
|
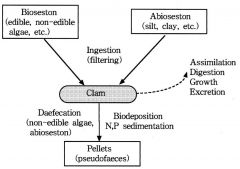
bioseston vs. abioseston
|
living particulate matter in water vs. non-living particulate matter
|
|
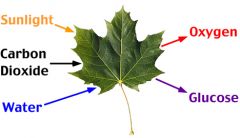
Photosynthesis
|
coverts solar energy to chemical energy of ATP & NADPH in plants and algae.
|
|
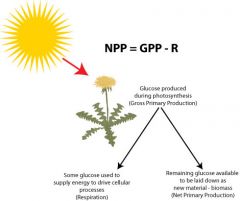
Primary productivity (PP)
|
production of organic compounds from atmospheric and aquatic carbon (photosynthesis). The PP of a community is the amount of biomass produced.
|
|
|
Autochthonous production
|
nutrient source produced inside stream (organism and plant matter)
|
|
|
Allochthonous production
|
nutrient source acquired from outside stream, detritus/leaf litter(seasonal sunlight dependant)
|
|
|
biofilm
|
community of microbial organisms interacting together as a mass
|
|
attached periphyton
|
algea that when die leaves glass shells that make good food source= filamentous green(spirogyra= on rocks) and non (pediastrum), diatoms,blue-green (microcytis=floating)
|
|
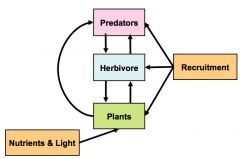
Community control
|
Top down= top of food chain controls bottom food chain. Bottom up= bottom of food chain controls top of food chain. top-down control by predation and herbivory or bottom-up control by nutrients and recruitment.
|
|
|
herbivory
|
consumption of living plants or their parts by animals
|
|

Convergent evolution
|
One organisms evolves to produce a trait of a non-related organism because it benefits them (i.e. caddisfly case built like snail shell for stability)
|
|
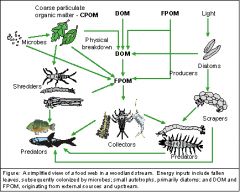
Food web
|
represents interactions between top and bottom of food chain
|
|
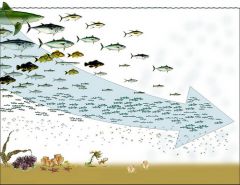
trophic casscades
|
represents what trophic level consumes another trophic level and so forth
|
|

Grazers/scrapers
|
file off algae to eat
|
|
|
Shredders
|
shred leaf litter and eat
|
|
|
Collector
|
brush like adaptations collect fine particles in water(some of which has been passed through guts of others)
|
|
|
Predator
|
eat other organisms
|
|
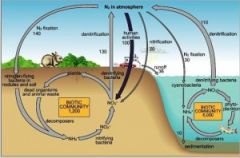
Biogeochem analysis
|
uses stable isotopes to determine food sources (Carbon) and trophic level (Nitrogen)
|
|

Paleolimnology
|
uses isotopic dating of past levels in C,Pb,Cs to quantify & classify organisms that once lived & limnological conditions of the past in water systems(using core-logging samples)
|
|
carbon dating
|
used to date carbon in sediments and create profiles of nutrient accumulation in soils
|
|
|
The boundary layer in the water column
|
due to affects of adhesion/cohesion=surface tension, is the layer air-water interface with low/no friction that traps oxygen and allows musquito larvae to survive.
|
|
|
eutrophic
|
no oxygen at deep for some part of the year
|
|

Epineuston
|
organisms living on top of water (i.e. wirleygigs)
|
|

Hyponeuston
|
organisms living below top layer making use of boundary layer (i.e. black fly larvae/snorkeler)
|
|
|
Respiratory adaptation
|
Gills, flapping (undulating) movements, increased surface area (flat bodies)
|
|
|
Mobility adaptations
|
Hooks & suckers,silk nets/ropes (non permanent i.e. dragonflies) & glues, roots (permanent i.e. caddisfly)
|
|
|
Behavioural adaptations
|
Hiding= avoiding prey, getting rest in slow current. Drift=when organisms let go of their habitat and float downstream to a better one, as an behavioural response to environmental disturbances (i.e. pollution). Catastrophic drift during floods.
|
|
|
Morphological adaptations
|
streamlined bodies,flat bodies, heavy casing
|
|
CPOM
|
Coarse particulate matter
|
|
FPOM
|
Fine particulate matter
|
|
|
Microdistribution
|
patchy distribution, require different habitats,fast flow, slow flow, rocks & mud
|
|
|
Macrodistribution
|
change in community based on stream order, different types of POM in each region
|
|
|
Headwaters
|
Orders 1-3, narrow stream, shaded, dominated by allochthonous CPOM
|
|
|
Middle
|
orders 4-7, wider stream, better lit for algeal growth, clear, food is FPOM and some CPOM
|
|
|
Lower
|
>8, wide and slow stream, turbid=blocked light (fine see. and dissolved matter), little shade
|
|
|
Community
|
association of plants and animals occurring in the same habitat interacting by trophic and production relationships
|
|
|
Diversity
|
is a community measurement for species richness ( how many of one species), equitability (how evenly spaced they are). good diversity depends on types of species.
|
|

Energy flow/production
|
production from top of food chain feeds bottom, bottom becomes energy for top's production.
|
|
|
Stability
|
persistance of a community
|
|
|
disturbance
|
reduces and/or removes biota, cause colonization
|
|
|
intermediate disturbances
|
maintains high diversity
|
|
colonization
|
the buildup of a community, 1st=opportunist (disperse well/compete poor), 2nd= competitors (disperse poor/compete well)
|
|
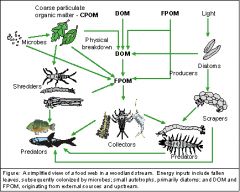
Functional feeding groups
|
classified by how they eat ( grazers/scrapers/collectors/predators)
|
|

Acadian forest trees? (not on exam??)
|
White spruce/pine/elm, Black spruce, balsam fir, eastern hemlock, red spruce/pine/oak, american beech, yellow birch, sugar maple
|

