![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
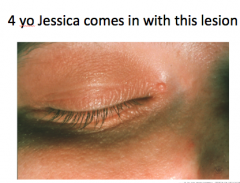
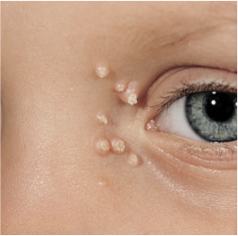
What does Jessica have? A. Molluscum contagiosum B. Carbuncle C. Herpes zoster D. Verruca vulgaris |
A. Molluscum contagiousum |
|
|
What causes molluscum contagiousum? A. Bacteria B. Fungus C. Parasite D. Virus |
D. Virus |
|
|
What kind of virus causes molluscum contagiousum? A. A herpes virus B. Pox virus C. HIV D. HPV E. VZV |
B. Pox virus |
|
|
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a _______ (DNA or RNA) poxvirus of the __________ genus.
What age are HEALTHY patients?
Describe the lesions. (rough or smooth, shape of lesion, type) |

|
|
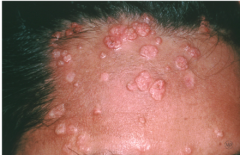
Rash on forehead which has not gone away for months. What is probably in the past medical history? A. Psoriasis B. Eczema C. HIV D. Acne E. Rosacea |
C. HIV |
|
|
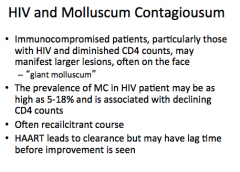
In immunocompromised patients (HIV and low CD4 counts), where are larger lesions located? What are they called? What is the prevalence of MC in HIV patients? What is it associated with? What type of course? What leads to clearance but may have a lag time before improvement? |
|
|
|
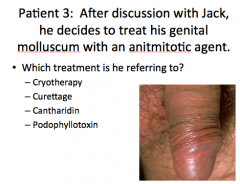
Jack is a healthy 31 yo. He knows he has molluscum contagiousum. Where are his lesions most likely to be?
A. axilla B. Popliteal fossae C. Antecubital fossae D. Genitals |
D. Genitals |
|
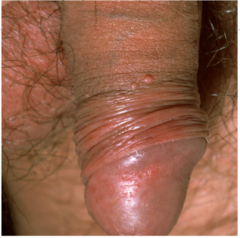
What is this? |
Molluscum contagiousum of the genitals |
|
|
Most adults with MC present with ____________ disease (location of MC).
When MC occurs in the genital region of sexually active patients, what is is classified as?
|

|
|
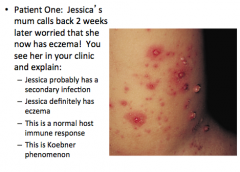
|
This is a normal host immune response |
|
|
In molluscum contagiousum, what may the host immune response cause? What percent of patients develop this?
Which population is less likely to clear on their own?
Molluscum can cause inflammation that can exacerbate _________________. |

|
|
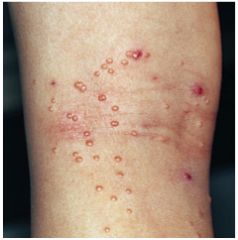
What is shown? |
Molluscum contagiousm eczema |
|
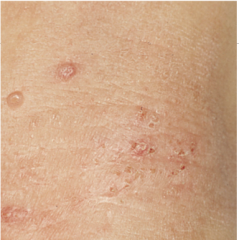
What is shown? |
Molluscum contagiosum eczema |
|
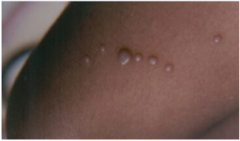
What is shown here? What is the pattern? When does this occur? |
Molluscum contagiosum: Koebner phenomenon => papules grow in a linear configuration following autoinoculation |
|
|
How is MC spread (3 ways)?
What is it associated with (we have one)?
Socioeconomic status of communities with highest prevalence?
What sport is particularly at risk?
|

|
|
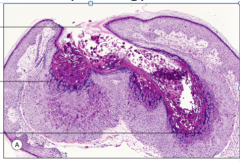
What would you expect to see on histopathological examination of these lesions of MC? A. Nuclear molding B. Multinucleated acantholytic keratinocytes C. Henderson-Patterson bodies D. Margination of chromatin and steel grey nuclei |
C = Henderson-Patterson bodies
ALL OTHER CHOICES SEEN IN HERPES! |
|
|
Describe Henderson-Patterson bodies |
Intracytoplasmic inclusions within keratinocytes |
|
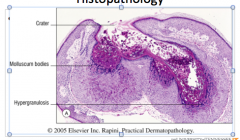
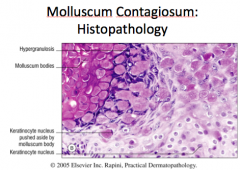
Identify the three areas.
Hypergranulosis, crater, molluscum bodies |
|
|
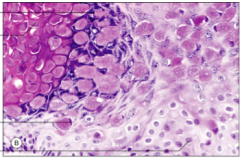
Identify the four areas:
Molluscum body, keratinocyte nucleus pushed aside by molluscum body, keratinocyte nucleus, hypergranulosis |
|
|
|
What is the treatment for MC in healthy individuals? What may hasten resolution? |

|
|
|
Is MC usually self-limited in immunocompromised? Is electing not to treat a satisfactory option?
What can picking and scratching lead to?
Should you treat genital molluscum? Why? |

|
|

|

|
|
|
D = podophyllotoxin |
|
|
There is not much data on MC treatment efficacy, but if patient want treatment, what are the four options? |
1. Cryotherapy 2. Curettage 3. Cantharidin 4. Podophyllotoxin |
|
|
What is the compound in cyrotherapy? What are some possible adverse effects? |

|
|
|
How does cantharidin work? Is it uncomfortable? Can you send it home with your patients? What areas should you avoid? Should you treat all lesions at once or a few lesions at a time? |

|
|
|
What is curettage? What population would it be uncomfortable for? Adverse effect? |

|
|
|
What type of agent is podophyllotoxin? What are some adverse effects? Is it safe in young children? |

|
|
|
Three other treatments that have also been used for MC? Is there data to support efficacy? |

|
|

|
D = she can go back to school today |
|
|
What should you do to prevent spread of MC?
MC may be protracted in those with __________ or in ___________ patients.
Immunocompromised patients are at risk for ___________ and _________ disease (qualities)? |

|
|
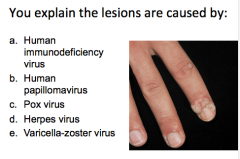
While in your office, Jessica's mom explains her brother, 9 yo John has "gotten molluscum" on his hands from his sister. |
B = HPV (warts) |
|
|
Warts are caused by human _______viruses that are ____________ viruses (type) that ONLY infect humans. |

|
|
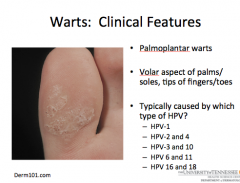
|
A = HPV-1 |
|
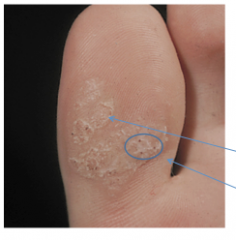
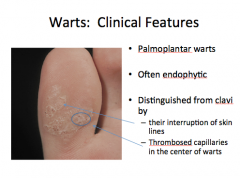
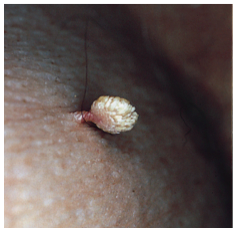
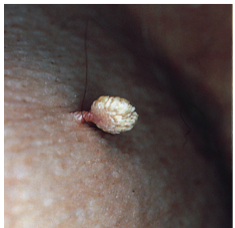
What type of wart? Are they endophytic or exophytic? How are they distinguished from clavi (the two lines)? |
|
|
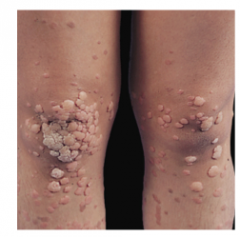
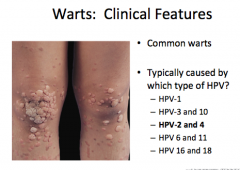
What type of warts? What type of papules? What virus(es) usually cause them? |
|
|
|
|
|
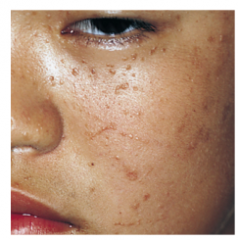
What type of warts? Describe (Eelevated or flat, color, smooth or hyperkeratotic). What virus causes them? |
|
|
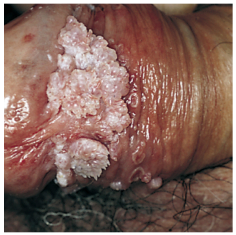
What type of warts? Most common what? Range of appearance? Locations (3)? What virus(es) cause 90%? Other 10%? |
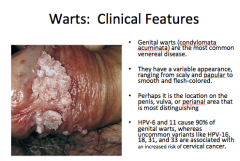
|
|
|
What is important for transmission of cutaneous warts? How are anogenital and cervical infections spread? Both represent transmission from what to what (think surfaces)?
|

|
|
|
What are the buzzwords for wart histology? Think keratin, papilla, granular, what type of keratinocytes with what type of nuclei? |

|
|
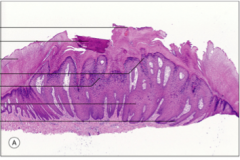
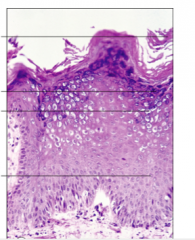
Label the wart histology:
Tissue fold, acanthosis, koilocytes, focal hemorrhage, rete ridge slopes inward, hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis |
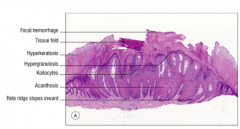
|
|
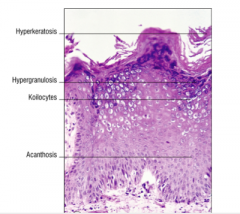
Label the wart histology:
Acanthosis, koilocytes, hypergranulosis, hyperkeratosis |
|
|
|
For treatment of warts, who population should get the least painful treatment?
What areas should destructive therapy be reserved for?
What will you see in two-third of warts after two years?
|

|
|
|
B = cryotherapy |
|
|
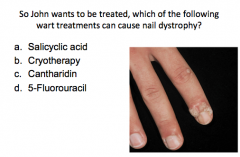
What population should not receive cryotherapy? What can result from cryotherapy of the nails?
What populations and locations should not receive cryosurgery and why? |

|
|
|
What is an effective therapy for warts that can be use in both adults and children?
What is essential for successful treatment?
What is a sign that treatment is effective and results in sloughing of tissue with dead wart virus? |

|
|

|
B = cantharidin |
|
|
What is cantharidin an extract from?
It is used in resistant cases in conjunction with or before what?
Is it useful in patients with multiple lesions or with children? Why or why not?
What is a side effect that could occur 2-24 hours after application? When should you repeat treatment? |

|
|
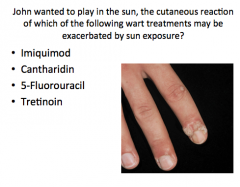
|
5-fluorouracil |
|
|
What does 5-fluorouracil cause at the site of application?
What is the predominant adverse effect (from question)? What should you do to avoid? |

|
|
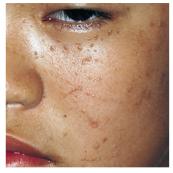
What is the treatment for flat warts? How long does it take and how often applied? |

|
|
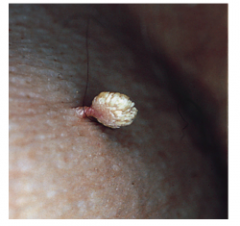
What is the treatment for warts like this (filiform warts)? |
Snip or shave excision |
|
|
Which treatment is a topical immunomodulator believed to act by local cytokine induction?
What wart type is it commonly used for?
Does it leave a scar? Is it painful to apply?
Any side effects? |

|
|

|
A. Quadrivalent vaccine (Gardasil) |
|
|
What virus types does gardasil protect against?
What is approved to PREVENT for males and females? |

|
|
|
What virus types does ceravix (bivalent) vaccine protect against?
What does it prevent in females (nothing for males)? |

|
|
|
Are warts more pronounced, recalcitrant to therapy, and in more unusual locations in the context of HIV? |

|
|
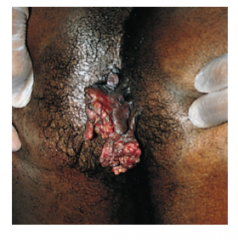
What is happening here? |
Wart from HPV in a patient with HIV. |
|

|

|
|
|
What are the three neoplasms of the skin associated with HIV? |

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
What can be used to stage a patient once he or she is diagnosed with HIV? |

|
|

|
A and C |
|
|
For the previous cases, scraping of what location of the lesion will give a higher yield for fluorescent antibody than obtaining exudative fluid?
What is not considered a recommended drug for the treatment of HSV infections? What is the drug good for?
What is the diagnosis of AIDS regardless of CD4 cell count? |

|
|
|
Where does HSV infection most commonly cause disease? What about in IC patients?
What duration is considered "chronic" HSV infection?
|

|
|
|
How does HSV cutaneous disease present? How does HSV infection spread to another areas of the skin?
What is the typical course of HSV infection (rupture of blisters time and healing time)? Is this prolonged in IC hosts? $ |

|
|
|
What is the treatment of HSV (3 options)?
What will severe or disseminated disease patients need (of the three treatment options)?
What do patients taking acyclovir need to do to reduce risk of acyclovir-mediated renal failure? |

|
|
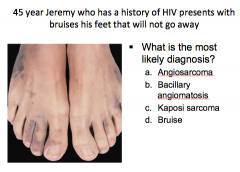
|
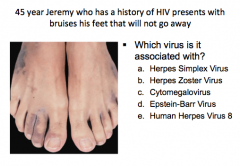
C = Kaposi sarcoma, bruising from extravasated blood cells |
|
|
E = Human Herpes Virus 8 |
|
|
What is the most common tumor arising in HIV-infected persons?
What lead to a marked decline in the incidence of this disease? |
KS (Kaposi sarcoma)
Potent combination antiretroviral therapy |
|
|
What should you do to diagnose KS? |

|
|
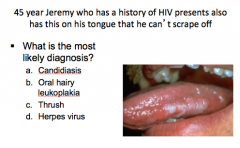
|
B = oral hairy leukoplakia |
|
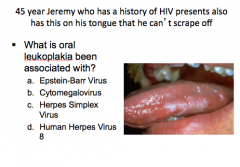
|
A = Epstein-Barr virus |
|
|
Oral hairy leukoplakia is an unusual disease of what epithelium?
What portions of the mouth/tongue are usually affected? |

|
|
|
What is the difference between candida and oral hairy leukoplakia in terms of scraping?
What condition is pathognomonic of HIV infection? |

|
|

|
TRUE! |
|
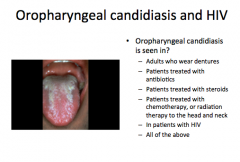
|
ALL OF THE ABOVE |
|
|
What has the appearance of "cheesy plaques that can be rubbed off?"
Will you likely see it in patients taking effective antiretroviral therapy? |

|
|
|
What will confirm oropharyngeal candidiasis? What treatment for mild disease? What treatment is severe and persistent? |

|
|

|

|
|
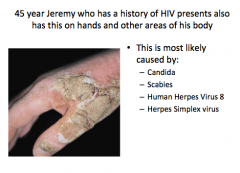
|
Scabies |
|
|
Where are scabies infections normally found in adults and children? Do they itch? What may scrapings reveal? |

|
|
|
HIV-infected patients with advanced disease can experience a variant of scabies know as "crusted scabies" or "Norwegian scabies," which is characterized by generalized scaling and enlarged, crusted plaques. |

|
|
|
HIV-infected individuals have a two to three fold increased risk of what type of skin cancers?
Are the risk factors similar to HIV-uninfected individuals?
What are the minor differences? |

|
|
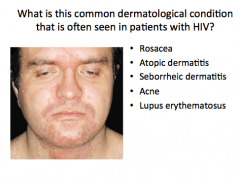
|
C = seborrheic dermatitis |
|
|
Thick, yellow scaling areas that may have surrounding erythema (redness) and may occur on the scalp, face, skin folds, and/or diaper area. Occurs in up to 85% of adults and children and may be an early sign of HIV? |

|
|
|
What is the treatment for seborrheic dermatitis? What can you apply to decrease inflammation? |
Selenium sulfide or ketoconazole shampoo, topical coal tar, or salicylic acid
1% hydrocortisone cream |

