![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What shape plot does the psychometric function give in reality?
|

an S shaped or ogive plot
|
|
|
1. Is the adjustment under the observers or the patients control in the method of adjustment?
2. Is it tedious but accurate or fast and unreliable? |

|
|
|
Is the stimulus strength under the examiners or patients control in the method of limits?
|

|
|
|
In what psychophysical testing method does the stimulus tend to be changed in discrete steps?
|

|
|
|
What psychophysical testing method is usually performed by alternating ascending and descending limits to minimize habituation and anticipation?
|

|
|
|
Is the stimulus under the examiners or patients control in the method of constant stimuli?
|

|
|
|
Under which psychophysical testing method is a preset number of stimuli of different intenstities shown repeatedly to the patient in a different order and the patient asked to report when they detect the stimulus?
|

|
|
|
Under which psychophysical method is threshold derived from the psychometric function?
|

|
|
|
Would you say the method of constant stimuli is fast but inaccurate or accurate but slow?
|

|
|
|
What is the formula for the JND using the method of constant stimuli? What about the point of subjective equality (PSE)?
|
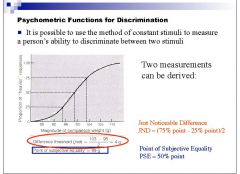
|
|
|
Would a large slope of the psychometric function be indicative of a low JND or a high JND?
|
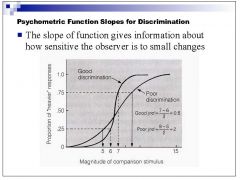
|
|
|
What law states that the difference threshold varies in direct proportion to the background stimulus?
|
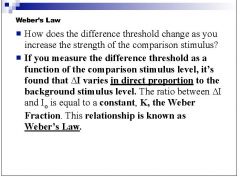
|
|
|
What method can be used to increase the reliability and speed of the method of limits?
|

|
|
|
What law states that as the stimulus intensity inctreases, a bigger increase in instensity is needed to produce the same effect?
|

same as Weber's except it holds under a wider range of stimulus intensities
|
|
|
How do you express contrast as a percent called the Michelson constrast?
|

|
|
|
what is the cutoff spatial frequency due to the optics of the eye?
|
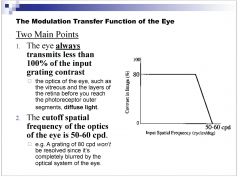
|
|
|
1. At what values in cycles/degree is the human contrast sensitivity function at it's maximum (1/2 to 1% contrast visible)
2. What is the highest spatial frequency visible to the average person before being limited by constrast sensitivity? |
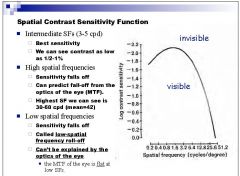
|
|
|
How would you figure out clinically which of the changes in the contrast sensitivity function are due to optical factors and which are due to neural factors?
|
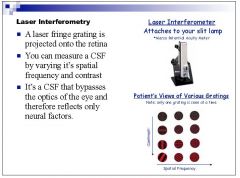
|
|
|
What causes the low frequency roll off of the contrast sensitivity function?
|
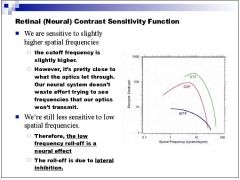
|
|
|
What spatial frequencies of the CSF are determined by receptive field organizaiton?
|
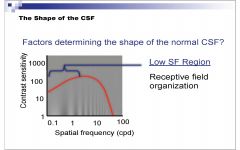
|
|
|
Does lens defocus remove high or low spatial frequencies?
|

high spatial frequencies
|
|
|
What medical condition would cause a patient to lose the ability to see contrast at middle spatial frequencies in what is called notch constrast sensitivity loss?
|

MS
|
|
|
Would you expect a cataract patient who had reductions at both high and medium spatial frequencies in contrast senstivity to be a complainer or a noncomplainer?
|

|
|
|
1. What type of glare might result from an insufficiently shielded light bulb?
2. What is another name for reflected glare? |
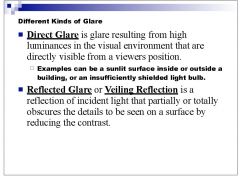
1. Direct glare
2. Veiling glare |
|
|
1. Does discomfort glare reduce the ability to see information for needed acitivites?
2. What type of glare is caused by light scattered within the eye, causing a haze and veiling luminance that decreases contrast and reduces visibility? |
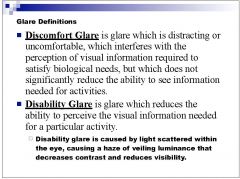
|
|
|
Is contrast sensitivity the same for horizontal, vertical, and oblique stimuli?
|
Oblique objects have reduced CS called the "oblique effect."
|
|
|
When refering to moving stimuli, would you call the CSF function a band pass shape or low pass shape?
|
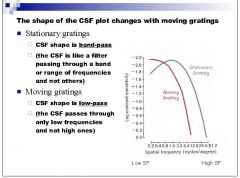
|
|
|
Is contrast reduced with duration?
|

maybe that's why patients take so long on VAs
|
|
|
At what spacing of letters is the crowding effect at its maximum?
|

|
|
|
How long does it take an electrical current to travel from the stimulating electrode in the retina to the receptor electrode in the visual cortex?
|
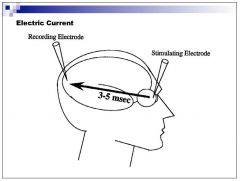
3-5ms
|
|
|
How long does it take a light stimulus to reach the cortex?
|
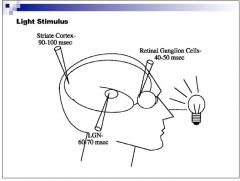
100ms, Incidentally this is how long it takes the VEP response to occur
|
|
|
What law states that the CFF is proportional to the log of the stimulus area?
|

|
|
|
What law states that the CFF is proportional to the log of the luminance?
|

Ferry Porter Law
|
|
|
Which law states that the apparent brightness of a stimulus presented above the CFF is equal to that of a continuous source with the same mean luminance?
|

Talbot-Plateau law
|
|
|
The Talbot Plateau law does not hold at low temporal frequencies. What do you call the effect that accounts for the increase in brightness at 10Hz flicker?
|

Brucke-Bartley
|
|
|
What type of masking is caused by an initially bright stimulus making a subsequent dimmer stimulus more difficult to see?
|

forward masking
|
|
|
What do you call the type of backward masking that uses spatial stimuli at different retinal locations?
|

metacontrast masking
|
|
|
What type of masking is responsible for the crowding effect?
|

metacontrast masking
|
|
|
What is the name of the experiment that shows us that motion percepts can be achieved even without spatial perception?
|
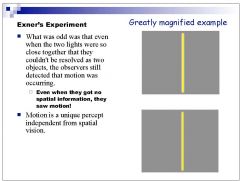
Exner's experiment
|
|
|
Which motion processing system gives visual information arising from the movement of the retinal image across the retina?
|
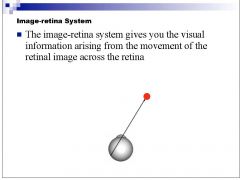
image retina system
|
|
|
What is the term for that provides nonvisual infput to the visual system system from efferent motor information?
|

Eye-head system
|
|

|

|
|
|
What theory of motion processing states that the eye-system is what discriminates real motion from self induced motion?
|
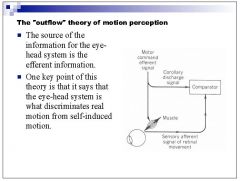
"outflow" theory of motion processing
|
|
|
What is the name for the type of motion in which an object is actually moving out in space?
|

real motion
|
|
|
What is the name for the percept of motion when there is more than one target and you must figure out how one target is moving relative to the other?
|

|
|
|
What is the principle of induced motion stating that the direction of induced movement is relative to the direction of the physical movement of the immediate surround?
|

principle of surroundness
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
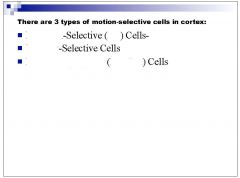
|

|
|
|
What velocities are most cells in V1, V2, and MT cortex tuned to?
|

Intermediate velocities 8-16 cycles/sec
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
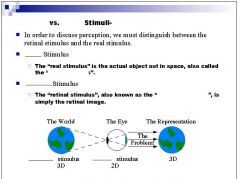
|
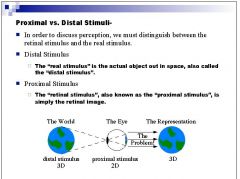
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
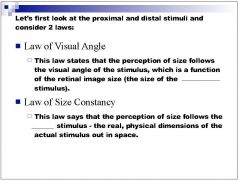
|
|
|
|
Under photopic conditions in the Holway-Boring experiment, did the subject adjust the comparison stimulus to matched the physical size of the test stimulus or the visual angle of the test stimulus?
|
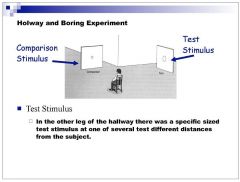
In the light the subject matched the comparison stimulus to the physical size of the stimulus (distal stimulus)
|
|
|
Under scotopic conditions in the Holway-Boring experiment, did the subject adjust the comparison stimulus to match the physical size of the test stimulus or the visual angle of the test stimulus?
|
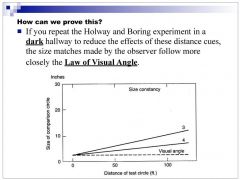
visual angle of test stimulus
|
|
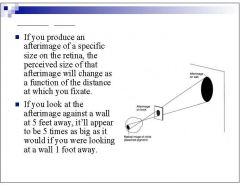
|
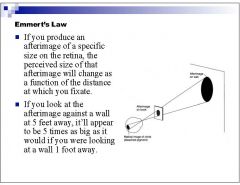
|
|
|
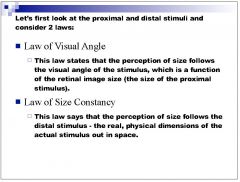
Is the moon illusion an example of the law of visual angle or the law of size constancy?
|

size constancy because the visual angle remains constant, only the perceived distance changes
|
|
|
Is the Mueller Lyre illusion an example of size constancy or the law of visual angle?
|
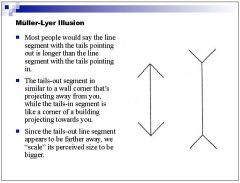
|
|
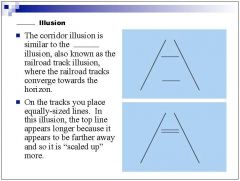
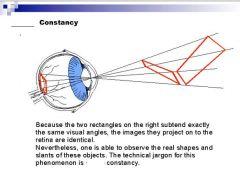
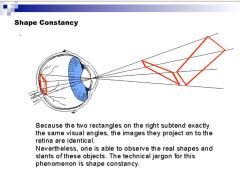
Is this an example of the law of visual angle or law of size constancy?
|
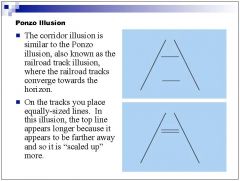
law of size constancy
|
|
|
Is an Ame's room an example of the law of size constancy or the law of visual angle? Why do equally size people appear the same size in an Ame's room?
|
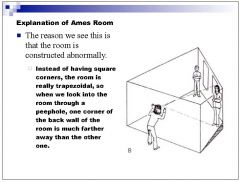
One person is further away but the peephole conceals this fact therefore you interpret further away as being smaller.
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

these rules being, proximity, similarity, continuity, closure, symmetry, and common fate
|
|
|
What type of illusion is the Kanisza triangle?
|
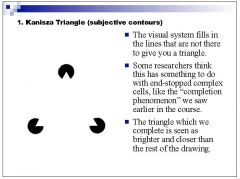
Filling in illusion, specifically an example of subjective contours
|
|

What filling-in illusion causes you to see distinct borders between different borders that don't actually exist?
|

illusory contours
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
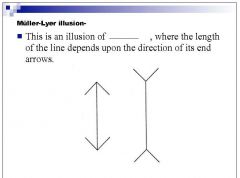
|
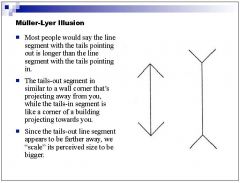
|
|
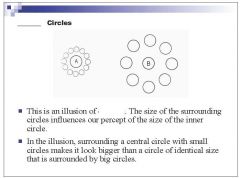
|
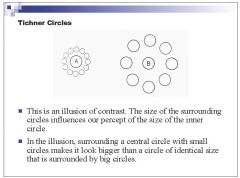
|
|

|

|
|
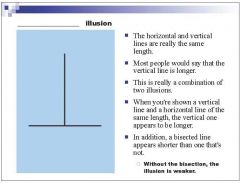
|
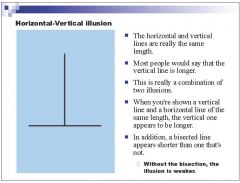
|
|
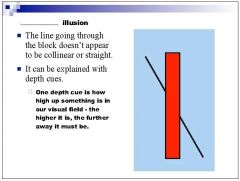
|
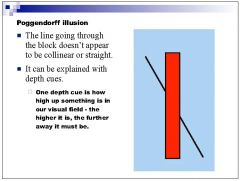
|
|
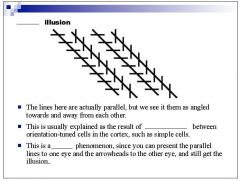
|
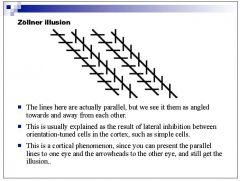
|
|
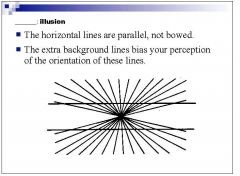
|
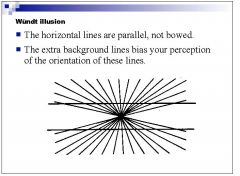
|
|

|

|

