![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pyroclastics |
Molten Rock blown into air |
|
|
Types of Pyroclastics |
1. Bombs, large rocks 2. Cinder, small rocks 3. Ash, tiny rocks, reduces sunlight, causes cooling. Ben Franklin 1st one to notice ash from Vesuvius buried under Pompeii |
|
|
Type of Intrusive structure 1. Batholiths |
Cross cutting - deep rocks - largest type - source of others - formed by pressure relief melting (PRM) Ex: Llano uplift, TX. Ft enchanted rock |
|
|
Type of Intrusive structure 2. Dikes # |

Cross cutting and tabular. Forms along fractures Ex: Great Dikes, CO |
|
|
Type of Intrusive structure 3. Sills |
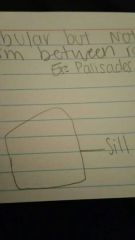
Tabular but NOT cross cutting. Form between rock layers Ex: Palisades Sill, NY |
|
|
Type of Intrusive structure 4. Laccoliths |

"Blister" "Rock" Not cross cutting. Forms when sill blister Ex: Devils Tower, Wyoming |
|
|
Extrusive Structures & types |
Features formed on the surface. Types: 1)Volcano 2)lava flow |
|
|
Types of lava flow |
1. AA (Ah ah). Rough surface 2. Pahoehoe (pah hoy hoy) smooth surface |
|
|
Types of volcanoes 1. Shield |
Largest, made of lava flows, gentle slope, quiet eruptions. Location: deep ocean Ex: Mauna Kea, Mamu Massif (largest) Ex: Galápagos Island Easter Island |
|
|
Types of volcanoes 2. Composite |
Medium size, made of lava flows and pyroclastics. -medium slope -violent eruptions (kills people) Location: cover gent plate boundaries. Ex: Cascades Mts a) Mt. St. Helens (Washington) b) Mt. Rainier (Washington) b) Crater Lake (Oregon) Ex: Andes Mts. Ex: Mt. Pele |
|
|
Types of volcanoes 3. Cinder |
Smallest size, made of pyroclastics. -steep slope -small explosions (usually only 1) Location: land Ex: Mt. Capulin, New Mexico Ex: Diamond Head, Hawaii Ex: Paricutin, Mexico. Birth witnessed |
|
|
Other Vomcanic Features 1. Columnar Jointing |
Hexagonal feature pattern forms when molten rock cools and contracts. Ex: Devil's Tower, Wyoming Ex: Devil's Postpile, California |
|
|
Other volcanic features 2. Volcanic neck |
Exposed vent after volcano is eroded. Ex: Shiprock, New Mexico |
|
|
Other volcanic features 3. Caldera |
Huge depression in volcanoes, possible causes: a) Top blown off Ex: Krakatoa, killer tsunami Ex: Yellow stone b) Collapse Ex: Crater Lake, Oregon Ex: Ngro-ngro (world's largest caldera) |
|
|
Other volcanic features 4. Lava tubes |
Caves formed by outside of flow hardening and inside flowing away. Ex: Thurston Lava Tube, Hawaii |
|
|
Other volcanic features 5. Pyroclastic Flows |
Fiery clouds. Steam mixed with glowing ash. Ex: Mt. Pele, 1902 |
|
|
Fissure flows |
Lava flows of fissure to cover large areas Ex: Siberian Traps (caused greatest extinction on earth) |

