![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Granite
|
crystalline igneous rock consisting of alkali feldspar and quartz.
|
Characteristics of continental crust
|
|
|
Basalt
|
Fine grained igneous rock black and greenish black Rock in iron magnesium and calcium
|
characteristics of the ocean crust
|
|
|
Isostasy
|
A condition of Equilibrium comparable to buoyancy in which the rigid crustal units float on the under lying mantle
|
|
|
|
Absolute Dating
|
the use of radio isotope half lines the determining the age of rock unit in years
|
|
|
|
Radioactive Dating
|
a technique used to date materials such as rock or carbon based on a comparison between the observed abundance of a natural occurring radioactive isotope and its decay rates
|
|
|
|
Radiometric Dating
|
The process of determining the age of rock from the decay of their radioactive elements
|
|
|
|
Half life
|
Time required for the decay of one half the atoms of a radioactive substance
|
|
|
|
Relative dating
|
The determination of whether certain rock and units are older or younger than others by the use of fossil assemblages
|
|
|
|
Lithosphere
|
The outer layer of Earth structure including the crust and the upper mantle. It is this layer that breaks into plates that are the major elements of the theory of plate tectonics
|
|
|
|
Asthenosphere
|
Upper zone of Earth's mantle extending from the base of the lithosphere to about 250 kilometers beneath continents and ocean basins that allow lateral movement of lithospheric plates and isostatic adjustments
|
|
|
|
Convection cell
|
A distant volume of circulating fluid in a fluid medium under gravity that is heated from below and cooled from above usually found in large groupings
|
|
|
|
Global plate tectonics
|
Global geology theory of global dynamics having to do with the movement of a small number of semi Ridge sections of earth crust with seismic activity and volcanism occurring primarily at the margins of these sections
|
|
|
|
Alfred Wegener
|
A German meteorologist and geophysicist was the first to advance the idea of mobile continent in 1912. He envisioned that the continents were slowly drifting across the globe and called this idea a continental drift
|
|
|
|
Harry Hess
|
American geologist and United States Navy officer during World War 2 who is responsible for creating the theory of seafloor spreading. He suggested that new ocean crust was created at the ridges, split apart, moved away from the ridges and later disappeared back into deep earth trenches
|
|
|
|
Continental drift
|
A theory that the continents had once formed a single landmass before breaking apart and drifting to their present locations. The movement of continental masses drifted across the Earth's surface.
|
|
|
|
Fossil
|
Any remains, trace or imprint of an organism that has been preserved in rocks
|
|
|
|
Laurasia
|
A proto continent of the Northern which is composed of what are now North America Europe and Asia
|
North, Supercontinent
|
|
|
Gondawanaland
|
A proto continent or supercontinent of the southern hemisphere composed of what are now South America Africa India Australia and Antarctica
|
South, supercontinent
|
|
|
Pangaea
|
An ancient super continent of the geologic past that contained all Earth's continents
|
one earth, protoearth
|
|
|
Panthalasia
|
A large ancient ocean that surrounded Pangaea
|
one ocean, proto ocean
|
|
|
Tethys Sea
|
In ancient body of water that separated lower Asia to the North and Gandawanaland to the South
|
|
|
|
Divergent
|
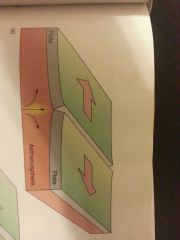
A lithospheric plant boundary where adjacent plates diverge producing an oceanic ridge or rise (spreading center)
|
two plates move away from each other CONSTRUCTIVE BOUNDARY
|
|
|
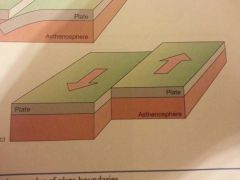
Convergent
|
A lithospheric plate boundary where adjacent plates converge producing ocean trench island are systems or volcanic arcs or folded mountain ranges
|
When two tectonic plates move toward each other and collide- one plate subducts beneath the other DESTRUCTIVE BOUNDARY
|
|
|
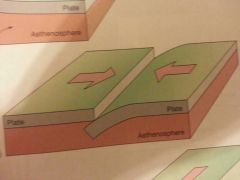
Transform
|
The boundary between two lithospheric plates formed by a transform fault.
|
Where lithospheric plates slowly grind past one another SHEAR BOUNDARY
|
|
|
Spreading Center
|
A divergent plate boundary the axis of the mid ocean Ridge where seafloor spreading occurs
|
|
|
|
Subduction
|
A process by which one lithospheric plate descends beneath another
|
|
|
|
Seafloor Spreading
|
A process producing the lithospheric when convection upwelling of magma along the oceanic ridges moves the ocean floor away from the Ridge axis at rates between 2 to 12 centimeters (0.8 to 5 in.) per year
|
new ocean floor is split in two and carried away from the axis, replaced by the upwelling of volcanic material that folks the void with new strips of sea floor
|
|
|
Transform Fault
|
A fault characteristics of oceanic ridges along which they are offset
|
two tectonic plates slide past one another
|
|
|
Hawaiin Islands
|
An undersea mountain range in the Pacific Ocean that reaches above sea level consisting of shallows banks and reefs and contains so identified undersea volcanoes
|
|
|
|
Iceland
|
A Nordic County that lies on the divergent boundary between the Eurosian plate and the North American plate it also lies above a hotspot the Iceland plume which is believed to have caused the formation of Iceland itself
|
|
|
|
Hotspot
|
The relatively stationary surface expression of a persistent column of molten mantle material rising to the surface
|
|
|
|
Island Arc
|
A linear arrangement of Islands many of which are volcanic usually curved so that the concave side faces a seas separating the Islands from a continent
|
|
|
|
Continental VOLCANIC Arc
|
A volcanic arc confined to the margin of a continent and associated with an ocean trench
|
|
|
|
Oceanic Ridge
|
A portion of the global mid ocean Ridge system that is characterized by slow spreading and step slopes.
|
slow spreading
|
|
|
Oceanic Rise
|
A portion of the global mid ocean Ridge system that is characterized by fast spreading and gentle slopes
|
fast spreading
|
|
|
Mid Atlantic Ridge
|
A slow spreading divergent plate boundary running North-South and bisecting the Atlantic Ocean
|
|
|
|
East Pacific Rise
|
A fast spreading divergent plate boundary extending southward from the Gulf of California through the Eastern South Pacific Ocean
|
|
|
|
Trench OCEAN
|
A long narrow and deep depression on the ocean floor with relatively step sides that is caused by plate convergence
|
|
|
|
San Andreas Fault
|
A transform fault that cuts across California from the Northern end of the Gulf of California to point arena North of San Francisco
|
|
|
|
Paleogeography
|
Branch of geography pertaining to the shapes and positions of ancient continents and oceans
|
|
|
|
Paleoceanogeaphy
|
Branch of oceanography pertaining to the biological and physical character of ancient oceans
|
|
|
|
Paleomagnetism
|
The study of Earths ancient magnetic field
|
|
|
|
Magma Chamber
|
A version of molten rock that lies underground, found beneath segments of the mid ocean Ridge
|
|
|
|
Marine Transgression
|
1. Result of global warming (Greenland & Antarctica)
2. Ice on land melts 3. Sea level rises 4. Shoreline migrates inland 5. Percentage coverage of ocean increases (<71%) |
to move forward
|
|
|
Marine Regression
|
1. Result of global cooling
2. Ice forms on land (due to snow) 3. Sea level falls (decreases) 4. Shoreline migrates seaward 5.Percent coverage of ocean decreases (>71%) |
to go back
|

