![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
pH |
Negative logarithm of the hydrogen concentration of H+ ions. A measure of acidity of a solution. |
|
|
|
Monomer |
A small molecule, two or more of which can be combined to form oligomers or polymers. |
|
|
|
Molecule |
a chemical substance made up of 2 or more atoms joined by covalent bonds or ionic attractions |
|
|
|
Base |
A substance that can accept a hydrogen ion in a solution |
|
|
|
Acid |
A substance that can release hydrogen ions in solution |
|
|
|
Buffer |
A substance that can transiently accept or release hydrogen ions and thereby resist changes in pH |
|
|
|
Ion |
An electorally charged particle that forms when an atom gains or losses one or more electrons |
|
|
|
Element |
A substance that cannot be converted to a simpler substance by ordinary chemical means |
|
|
|
Compound |
A substance made up of atoms of more than one element |
|
|
|
Hypothesis |
A tentative answer to a question, from which testable predictions can be generated |
|
|
|
Atom |
Consists of a dense, positively charged nucleus around which one or more negatively charged elections move |
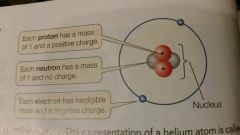
|
|
|
Life |
All organisms descended from a single celled ancestor |
|
|
|
Water |
Substance that allows chemical reactions to occur inside living organisms and it's necessary for the formation of certain biological structures |
|
|
|
Carbon |
Versatile, organic element that can bond itself with 4 potential covalent atoms |
|
|
|
Tree of Life |
A term that encompasses the evolutionary history of all life, or graphic representation of that history. |
|
|
|
Chemistry |
Deals with the identification of the substances of which matter is composed; the investigation of their properties and the ways in which they interact, combine, and change. |
|
|
|
Cell |
The smallest unit with the capacity to live and reproduce, independently or a part of a multicellular organism |
|
|
|
Theory of Evolution |
A change in allele frequency in a population over time |
|
|
|
Biology |
The scientific study of living things |
|
|
|
Polymer |
A larger molecule made up of similar or prudential subunits called monomers |
|
|
|
Polymerization |
In polymer chemistry, polymerization is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. |
|
|
|
Protein |
Long chain polymer of amino acids w/ 20 different common side chains. "True workhorses of the cell - do almost everything, versatile" |
|
|
|
Amino Acid |
An organic compounds containing both NH² and COOH groups. Proteins are polymers of amino acids. |
|
|
|
Peptide |
Naturally occurring biological molecules. They are short chains of amino acid monomers linked by peptide (amide) bonds. |
|
|
|
Carbohydrate |
Made up of a large group of molecules that all have similar atomic compositions but differ greatly in size, chemical properties, and biological functions. Ex: sugars, starch, and cellulose. Organic compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in the ratio 1:2:1 |
|
|
|
Lipid |
Non-polar, hydrophobic molecules that include fats, oils, waxes, steroids, and the phospholipids that make up biological membranes. |
|
|
|
Nucleic Acid |
A polymer made up of nucleotides, specialized for the storage, transmission, and expression of genetic information. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. |
|
|
|
Nucleotide |
The basic chemical unit in nucleic acids, consisting of pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen- containing base. |
|
|
|
Nitrogenous base |
A nitrogen containing molecule that has the same chemical properties as a base. They make up the building blocks of DNA and RNA. |
|
|
|
Theory |
An explanation of facts that is supported by a wide body of evidence, with no contradictions, and is scientifically accepted as a fact. |
|
|
|
Scientific law |
A statement based on repeated experimental observations that describes some aspects of the universe. |
|
|
|
Biomolecule |
Any molecule that is present in living organisms, including large macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and nucleic acids |
|
|
|
Prokaryote |
Unicellular organisms that do not have nuclei or other membrane- enclosed organelles. Includes bacteria and archaea. |
|
|
|
Eukaryote |
Organisms whose cells contain their genetic material inside a nucleus. Includes all life other than viruses, archaea, and bacteria. |
|
|
|
Organelle |
Any of the membrane enclosed structures w/in a eukaryotic cell. Ex: nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria. |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
Random movement of molecules or other particles, resulting in even distribution of particles when no barriers are present. |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
Movement of water across a differentially permeable membrane, from one region to another region where the water potential is more negative. |
|
|
|
Hormone |
A chemical signal produced in minute amounts at one site in a multicellular organism and transported to another site where it acts on target cells. |
|
|
|
Receptor |
A protein that can bond to a specific molecule, or detect a specific stimulus, within a cell or in the cell's external environment. |
|
|
|
Energy |
The capacity to do work or move matter against an opposing force. The capacity to accomplish change in physical and chemical systems. |
|
|
|
Enzymes |
A catalytic protein that speeds up a biochemical reaction. |
|
|
|
Inhibition |
Input from a neuron that causes hyperpolarization of the recipient cell. |
|

