![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
168 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cardiac Diseases with NO murmur
|
DCM
HCM HWD Pericardial Dzs Some Congenital Dzs |
|
|
Chronic Cough DDX (2)
|
LHF
Pulmonary Disease (Collapsing Trachea, Bronchitis, HWD, Asthma) PL |
|
|
Acute Cough DDX (7)
|
LHF
Tonsillitis Pharyngitis Tracheobronchitis Acute bronchitis Pleuritis Pneumonia P3T2LA |
|
|
Types of cough (8)
|
Loud, harsh, coarse dry - larynx, trachea, or bronchi
Cardiac - harsh and low Chronic Non-productive - tumor Rattling with whistling - Bronchiectasis Honking - Collapsing trachea After drinking - CT, Cardiac dzs, chronic tracheitis tracheobronchitis With an inciting factor - Cardiac/pulmonary dzs extrapulmonary disorder, neoplasia At eating - achalasia or vascular ring anomalies, esophageal diverticula |
|
|
How to tell upper airway cough from lower
|
rattling, wheeze - lower
|
|
|
Difference between dyspnea and tachypnea
|
Tachypnea = increased rate
Dyspnea = rate and effort |
|
|
Types of Dyspnea
|
Paroxysmal (comes and goes)
Exertional (early sign of Dyspnea) Orthopneic (when lying down) |
|
|
Inspiratory vs. Expiratory Dyspnea
|
Increased Inspiratory effort = upper airway
Increased Expiratory = lower |
|
|
Causes of hemoptysis
|
Pulmonary contusions from trauma
Pulmonary edema Lung/bronchi diseases Pulmonary embolism Clotting problems DIC |
|
|
Cause of head, neck, forelimb edema
|
mediastinal mass obstructing venous return
|
|
|
Causes of abnormal jugular pulses
|
RHF w/tricuspid regurg
Heart block or arrhythmia where right atrium contracts agains a closed tricuspid valve PSten Pulm hypertension |
|
|
Jugular distension caused by
|
RHF (congestive)
Obstruction Pulmonary Dzs |
|
|
PMI displacement caused by
|
Cardiac enlargement
Mass pushing on heart Collapsed lung lobe on R side Just got up from right lat recumbency |
|
|
Decreased intensity of heart sounds caused by
|
pleural/pericardial effusion
thoracic masses Hernia with liver/intestines in thorax Obesity Arrhythmias |
|
|
Causes of Hyperkinetic pulse (3)
|
PDA
Aortic regurg Left ventricular hypertrophy |
|
|
Causes of weak pulses (6)
|
myocardial disease
arrhythmia Pericardial dzs dehydration ASten Systemic Hypertension |
|
|
Normal HR for Dog
|
Dog - 70-180
|
|
|
Valve areas for ascultation
|
Left side
Pulmonic 2-4 ICS, sternal Aortic 4th ICS, costal-chondral junction Mitral 5th ICS, costal-chondral junction Right side Tricuspid 3-5 costal-chondral junction |
|
|
S1 Heart Sounds and causes
|
Blood surging to the AV valves to start AV closure; abrupt deceleration of blood as valves close
|
|
|
S2 Heart Sounds and causes
|
closure of semilunar valves
|
|
|
S1 splitting caused by
|
delayed closure of mitral or tricuspid valve from RBBB, VP beats
|
|
|
S2 splitting caused by
|
delayed closure of the pulmonic valve from
Pulmonic Hypertension (HWD) RBBB VP Beats from Left Ventricle ASD PSten RHF COPD (horses) |
|
|
S3 heart sound caused by
|
Rapid Ventricular filling
|
|
|
S4 heart sound caused by
|
Atrial contraction of blood into ventricles
|
|
|
Types of murmurs
|
1. Functional - increased velocity
2. Pathologic - structural problem |
|
|
Types of Pathologic murmurs
|
1. Stenosis (aortic, pulmonic)
2. Shunt (VSD, ASD) 3. Regurg (PAMT) |
|
|
Most common type of murmur
|
Systolic
|
|
|
These valves should be open during systole
|
Aortic & Pulmonic
|
|
|
Causes of systolic murmurs
|
flow obstruction (aortic/pulmonic)
Leaky valves (mitral/tricuspid) Holes (ASD/VSD) |
|
|
Causes of continuous murmurs
|
PDA
Arteriovenous connections Ateriopulmonary windows flow disturbance (pulmonary emboli) |
|
|
Significance of systolic clicks
|
Idiopathic. Leads to mitral valve problems.
|
|
|
99% of murmurs are ____.
|
Systolic
|
|
|
Endocardiosis is defined as _____ and is found two places (____ & _____ (with____ being the most common).
|
Chronic Valvular Disease; Mitral; Tricuspid; Mitral
|
|
|
Systolic murmur over the pulmonic region
|
psten
T of F ASD |
|
|
Systolic murmur over the aortic region
|
Subaortic Stenosis
|
|
|
Systolic murmur over tricuspid region
|
Tric. regurg
VSD Tric. dysplasia |
|
|
Continuous murmurs
|
PDA
AV Fistula |
|
|
Diastolic Murmurs
|
Aortic Regurg
Pulm Regurg Mitral Sten Tric. Sten |
|
|
4 most important things to do on a cardiac PE
|
Signalment
Complaint/Clinical History PE/Ascult Rads |
|
|
Common breeds with PSten
|
Bassett
Beagle Boxer Boykin Chihuahua Chow Cocker English Bulldog Lab Mastiff Newfie Samoyed Schnauzer Terrier (All) Westie |
|
|
Common breeds with PDA
|
Bichon
Chihuahua Cocker Collie Springer GSD Keeshond Lab Maltese Pom Poodle Shetland Corgi Yorkie |
|
|
Common breeds with SAS
|
Boxer
GSD GSP Golden Great Dane Newfie Rottie Samoyed |
|
|
Common breeds with ASD
|
Boxer
Dobie Samoyed |
|
|
Common breeds with MVD (mitral valve dysplasia)
|
Bull Terrier
GSD Golden Dane Mastiff Newfie |
|
|
Common breeds with CTD (Cor Toratatum Dexter)
|
Chow
|
|
|
Common breeds with AS
|
Bull Terrier
|
|
|
Common breeds with T of F
|
English Bulldog
Keeshond |
|
|
Common breeds with VSD
|
English Bulldog
Springer Spaniel |
|
|
Common breeds with TVD
|
GSD
Golden Dane Lab |
|
|
Tx for Acute heart failure Cat
|
Lasix
O2 +/- vasodilation (nitroglycerine) |
|
|
Tx for Chronic HF Cat
|
Lasix - NOTHING ELSE EFFECTIVE.
Enalapril MAY affect RAAS, but no evidence up to this point. |
|
|
Normal Hr for Cat
|
Cat 145-220
|
|
|
Normal HR for cattle
|
Cattle 60 - 80
|
|
|
Normal HR for Horse (and foal)
|
Horse 30-40 (80 in foals)
|
|
|
Normal HR for sheep/goats
|
Sheep/goats 70-90
|
|
|
Normal HR for pig
|
Pig 60-100
|
|
|
S3 and S4 normal in what species?
|
Cow and horse at rest
Always abnormal in small animals |
|
|
Respiratory abnormality found on both inspiration and expiration
|
Pleural Friction rubs
|
|
|
P wave reflects what?
|
Atrial depolarization
|
|
|
PR interval reflects what?
|
time for AV node conduction
|
|
|
P wave with NO QRS
|
AV node blockage
|
|
|
QRS reflects what?
|
Ventricular depolarization
|
|
|
T wave reflects what?
|
Ventricular repolarization
|
|
|
How many seconds should you count for HR?
|
3 sec. = 1 bic pen
50mm/sec = multiply by 20 25mm/sec = multiply by 10 |
|
|
Characteristics of a Sinus Rhythm
|
No sudden starts/stops
Positive P wave in 1, 2, 3, and aVF Normal QRS Can't sustain high rates for long |
|
|
Places non-sinus rhythyms can originate
|
Atrium (has a P wave, but might look weird
AV Node (abnormal PR) Ventricle (VPCs) |
|
|
Describe the Atrial Premature Contraction
|
Funny P wave
Normal QRS |
|
|
Describe the AV node/Junctional rhythm
|
+/- P wave
Weird PR interval |
|
|
Describe the propagation of a normal heartbeat
|
Starts at the Upper right atrium at the sinus node
Upper RA>Lower LA>Cross AV node>Upper R AV node>Lower LV |
|
|
Where is the normal Mean electrical axis (MEA)
|
LL quadrant
|
|
|
What happens with a Right Axis Shift?
|
MEA moves to Right side
|
|
|
What happens with a Left Axis Shift?
|
MEA moves to the Upper Left Quadrant
|
|
|
Which bundle branch feeds the upper L part of the LV?
|
Anterior. Posterior gets everything else.
|
|
|
What to expect in a RBBB?
|
Right axis shift
Wide and bizarre QRS |
|
|
What to expect in a LBBB?
|
Normal MEA
Wide and bizarre QRS |
|
|
RBBB makes you worry about?
|
Psten
tricuspid displasia tricuspid regurg RV CM |
|
|
LBBB makes you worry about what?
|
SAS
PDA Mitral sten Mitral regurg DCM |
|
|
3rd heart sounds come from?
|
Big Atrium
Big Ventricle Systolic Click (non-pathologic) Gallop Premature |
|
|
Why don't you usually have a murmur with ASD?
|
Pressure gradient NSF
|
|
|
Holosystolic/Pansystolic murmur causes
|
Mitral regurg
Tricuspid regurg VSD |
|
|
Mid-systolic murmur causes
|
Asten
Psten Tachycardia pleural effusion pericardial effusion anemia fever |
|
|
Most common Diastolic murmurs
|
Aortic regurg
Mitral regurg |
|
|
All causes of systolic murmurs
|
Obstruction to outflow (aortic and pulmonic)
Leaky valves (mitral and tricuspid regurg) Holes (VSD and ASD) |
|
|
Causes of diastolic murmurs
|
Leaky valves (aortic and pulmonic)
Stiff valves (mitral and tricuspid stenosis) - rare |
|
|
Causes of continuous murmurs
|
PDA
Pulmonary emboli |
|
|
True/False: APCs and VPCs are often associated with underlying structural heart disease
|
True
|
|
|
Tx for tachycardias
|
AADs
|
|
|
AADs targeting muscle (VeAt)
|
NCB
KCB |
|
|
AADs targeting nodal cells (AV/Sinus)
|
B
C D |
|
|
Tx for Sinus tachycardia
|
Treat underlying problem
B-blockers |
|
|
Tx for Atach
|
Target muscle
NBCs KCBs Bbs Slow conduction Bbs CCBs Dig |
|
|
Names of NCBs
|
Procainamide
Lidocaine (No FX in atrium) Mexiletine Quinidine |
|
|
Names of KCBs
|
Amiodarone
Sotalol |
|
|
Names of Bbs
|
Esmolol
Propanolol Altenolol |
|
|
Tx for JTach
|
B
C D |
|
|
Tx for VTach
|
Go on a hunt for extra cardiac dzs
NCBs KCBs Bbs MgSO4 (horses only) |
|
|
Tx for Afib
|
Rhythm control - Cardiovert
NCBs KCBs Electrical Rate control - slow conduction through AV Bbs CCBs Digoxin |
|
|
Names of CCBs
|
Diltiazem
|
|
|
About Quinidine
|
Class Ia NCB - most commonly used AAD for cardioversion
DO NOT USE IN SA! DO NOT GIVE ORALLY! Toxic levels cause: UR Stridor Wide QRS Ataxia But NOT: Tach Hypotension Diarrhea Colic |
|
|
About Digoxin
|
Direct Vagal FX - decreases Vent response in Afib
+ inotrope |
|
|
Class I AADs
|
NCBs
1A - Quinidine, Procainamide 1B - Lidocaine, Mexilitine |
|
|
Class 2 AADs
|
B-blockers
Selective - Altenolol, Esmolol Non-selective - Propanolol |
|
|
Class 3 AADs
|
KCBs
Sotalol, Amiodarone |
|
|
Class 4 AADs
|
CCBs
Diltiazem, Digoxin |
|
|
NCBs good for
|
Vent arrhythmias
Atach |
|
|
Bbs good for
|
Stach
Jtach Afib rate |
|
|
KCBs good for
|
Vent arrythmias
Atach |
|
|
CCBs good for
|
Afib rate
Atach Jtach |
|
|
About lidocaine
|
doesn't do anything in Atrial tissue
hypoK makes less effective Have to bolus then CRI |
|
|
About Mexiletine
|
Good for Atach, VtArr
Good for use with Altenolol or sotalol |
|
|
About Amiodarone
|
Lots of Side FX (hepatic toxicity, erythema, pruritus, swelling, hives, pain at injxn site)
Pretreat w/Benadryl or steroids Great at VtArr, Atach |
|
|
About Diltiazem + Digoxin
|
great to slow Vt response to Afib
|
|
|
Tx for AV Block and SSS
|
Pacemaker or + chronotropes
|
|
|
Names of + Chronotropes
|
Theophylline
Terbutaline Hycosamine |
|
|
Define HF
|
When the heart can no longer maintain normal function resulting in:
low arterial BP NSF perfusion of tissues at rest Increased Venous BP Increased Capillary pressures |
|
|
Define CO
|
CO=HR*[(Contractility*Preload)/Afterload]
|
|
|
Name the six major principles of cardiac performance
|
1. Preload - amount of blood that goes back into the heart
2. Afterload - what the LV works against 3. Contractility - can the heart contract? 4. Compliance - can the heart fill? 5. HR 6. Synergy - how well does it all come together? |
|
|
Types of Heart failure
|
1. Congestive
2. Low Output |
|
|
L CHF cascade
|
LV Pressure>LA Pressure>Pulmonary pressure>increased oncotic pressure>pulmonary edema>decreased O2 exchange in lungs
|
|
|
Causes of increased L Vt Diastolic Pressure
|
1. increased preload (leaking mitral due to endocarditis)
2. decreased compliance (HCM) 3. Increased after load (ASten, hypertension) 4. Combination |
|
|
Signs of L CHF
|
edema
dyspnea |
|
|
R CHF cascade
|
RV Pressure>RA Pressure>Central Venous pressure (jugular distension)>Systemic VP>Systemic Capillary Pressure>Hepatic Sinusoid pressure>Ascites (dogs)/pleural effusion (cats)/ ventral (horses) or brisket (cows) edema
|
|
|
Causes of increased R Vt Diastolic pressure
|
Increased RV Preload
Increased Afterload (plum art hypertension) Decreased compliance Combination |
|
|
Low output failure is a result of what?
|
Big, flabby heart. NSF blood pumped.
Symptoms: hypotension, cool extremities, depression, lethargy |
|
|
Pressure overload is a systolic dysfunction and a cause of heart failure. Name some causes.
|
SAS, PSten, ToF, Hypertension, HWD, L to R Shunt, pheochromocytoma
|
|
|
Volume overload/excessive preload is a systolic dysfunction and a cause of heart failure Name some causes.
|
M, T, or A Regurg
Shunts (PDA, VSD, ASD) AV Fistula |
|
|
Pump/low output failure (NSF contractility) is a systolic dysfunction and a cause of heart failure. Name some causes.
|
Cardiomyopathy
Infarct Cardiodepressive drugs (- Inotropes) |
|
|
Myocardial restriction is a diastolic dysfunction and a cause of heart failure. Name some causes.
|
HCM
Restrictive CM Pericardial Effusion Pericarditis Tumors |
|
|
High output states can cause HF. Name the causes.
|
Chronic anemia
Chronic fever Hyperthyroidism |
|
|
Differentiate between the stages of HF
|
Mild - Coughing, dyspnea, and fatigue with exercise
Moderate - with mild activity Severe - at rest |
|
|
Draw the RAAS
|
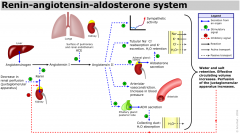
|
|
|
How does the SNS attempt to combat HF?
|
1. HR - speeds up conduction and discharge - at a certain point become detrimental because decr filling.
2. Contractility - E! and NE! released by SNS - incr contractility, but sensitizes the heart to arrhythmias 3. Systemic Art BP - causes vasoconstriction via A-!, but incr afterload |
|
|
Eccentric Hypertrophy caused by what and lays more sarcomeres down how?
|
Chronic volume overload; end-to-end
Internal dimensions increased |
|
|
Concentric hypertrophy caused by what and lays more sarcomeres down how?
|
Chronic pressure overload; parallel
Internal dimensions decreased>less compliant ventricle |
|
|
What's the deal with ANF
|
Comes from Atrial myocytes and is released when At is stretched
Increases GFR Antagonizes Renin, Ald. release, AT2 vasoc. Inhibits ADH Vasodilates |
|
|
What are the cardiac peptides?
|
ANF
Troponin Vasopressin |
|
|
What's the deal with vasopressin?
|
Increases with CHF
Retains water Causes vasoc |
|
|
What's up with Troponin?
|
Most commonly measured Cardiac peptide
Elevated in renal dz, PTE with dogs/cats Somewhat high in boxers with ARVC |
|
|
How can you detect CHF in dogs/cats?
|
1. Aldosterone ^ x 7
2. Renin ^ x 10 3. NE ^ 4. ANF ^ if Class 3-4 CHF 5. NT-proBNP - hi Sn/Sp |
|
|
What's up with NT-proBNP?
|
NOT a screening test.
Can tell you if it's cardiac and how bad. Hi Sn/Sp Poor prognosis if ^ AND ALT ^ |
|
|
Canine LHF CS
|
Rales
^ CRT Weak femoral pulses Pacing +/- murmur |
|
|
Canine RV failure CS
|
+/- murmur
Ascites Hepatomegaly Splenomegaly Distended jugular Cardiac cachexia |
|
|
Feline Vent Failure
|
dyspnea
murmur R - pleural effusion L - pulm edema |
|
|
Equine/Cow LHF
|
^ HR
^ RR +/-Murmur/gallop |
|
|
Equine RHF
|
^ HR
Murmur Legs swell Brisket edema |
|
|
Cow RHF
|
Brisket edema
^ HR +/- murmur |
|
|
Goals of HF Tx?
|
1. V fluid accumulation
2. ^ CO 3. V workload 4. Control rhythm 5. Find cause 6. Neurohormonal (RAAS, SAS, ADH) 7. Cardiac Remodeling |
|
|
ACEI do what to RAAS?
|
Prevent AT1>AT2
V preload V afterload |
|
|
Bb do what to RAAS?
|
V renin release from JG cells
|
|
|
Bbs do what to the SNS?
|
V contractility
|
|
|
Aas do what to the SNS?
|
Vasodilate
V afterload |
|
|
How can you prevent Cardiac remodeling?
|
ACEI - V fibrosis, V afterload, V preload
Aldant - V fibrosis Bbs - V remodel Lasix - V preload |
|
|
Name an Aldant.
|
Spironolactone
|
|
|
Why/How reduce preload?
|
v preload = v venous congestion
Lasix ACEI V sodium Venodilators |
|
|
Why/How reduce after load?
|
v afterload = v workload
ACEI Art.dilators |
|
|
Why/how alter contractility with systolic dysfunction?
|
Perfusion
+inotrope (pimo, dig, catecholamine) |
|
|
Why/how alter Compliance with diastolic dysfunction?
|
Improve filling time by v HR
CCB |
|
|
LHF vs. RHF TX?
|
LHF - Lasix, cage rest
RHF - tap it. |
|
|
Name the arterial vasodilators.
|
Hydralazine
Nitro ACEI |
|
|
How to slow HR?
|
Bb, CCB, Dig
|
|
|
Why use + Inotropes and how do they work?
|
Big Flabby Heart - ^ systolic contractility
alter Ca+ at actin/myosin level |
|
|
Name + inotropes
|
Dig
Pimo Catecholamines (emergencies) |
|
|
Name the catecholamines
|
Epi!
Isoproterenol Dopamine Dobutamine |
|
|
Name the types of diuretic
|
Xanthines
Thiazides Aldant Lasix |
|
|
Things that ^ blood digoxin levels
|
Quinidine
Aspirin Amiodarone Sotalol Spironolactone Cimetidine Phenobarb Hypothyroid CRF/ARF Hypokalemia |
|
|
When to NOT use dig
|
Sinus node dysfunction
HCM A/P Sten RCM Pericardial dzs Vt Arr A murmur Pulm Hypertension |
|
|
When to use Isoproterenol
|
SSS
3rd Degree AV Block DO NOT USE unless you're getting ready to put in a pacemaker |
|
|
When to use Dopamine
|
Sinus Tach
|

