![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the purpose of the microscopic portion of the routine UA? |
Detect and identify insoluble materials in the urine. |
|
|
What does the term Sediment refer to? |
Cells, casts, crystals, and amorphous deposits. |
|
|
What are the 9 Cellular Elements? |
1)RBC's 2)WBC's 3)Epithelial Cells 4)Fat Droplets/ Lipids 5)Sperm 6)Bacteria 7)Yeast 8)Casts 9)Crystals |
|
|
What does RBC's indicate? |
Bleeding somewhere in the urogenital tract.
It can also indicate Renal Disease, Dysfunction, Infections, Tumors, Lesions, Stone Formation, or Anticoagulant use. |
|
|
What happens to RBC's in concentrated urine/ Dilute (Akaline) urine? |
Concentrated RBCS: Shrink or Crenate
Dilute RBCS: Swell or Lyse |
|
|
When is RBCS in urine normal? |
When female is in heat.
From traumatic sample colection. |
|
|
How do WBCS enter the urine? |
At any point in the urinary tract or from secretions from the genital tract. |
|
|
What is the normal # of WBCS? |
0-5 WBCs per HPF. |
|
|
What is Pyuria? |
Pus (WBCs Neutrophils) in the urine which indicates infection. |
|
|
What are the two types of Urinary Tract Infections? |
Cystitis
Pyelonephritis |
|
|
What is Cystitis? |
-Lower Urinary Tract Infection (Bladder)
Will see WBCs and Bacteria
No casts
Little or no protein on chem. strip |
|
|
What is Pyelonephritis? |
-Upper Urinary Tract Infection (Kidneys, Ureters)
Will see WBCs and Bacteria
Casts will be present (White, mixed, granular, bacterial, epithelial casts)
Protein will be positive on chem. strip |
|
|
Where are Epithelial Cells found? |
They line the inside of the Urogenital Tract. |
|
|
What are the three types of Epithelial Cells? |
-Squamous Epithelial Cells
-Transitional Epithelial Cells
-Renal Epithelial Cells |
|
|
Where are Squamous Epithelial Cells found? |
In the lining of the inside of the lower urethra, and the vagina and the vulva in females and the prepuce in males. |
|
|
Are Squamous cells significant? |
No, they are commonly found. |
|
|
Where are Transitional Epithelial Cells found? |
Lining the inside of the upper urethra, bladder, ureters, and renal pelvis. |
|
|
Are Transitional cells significant? |
Yes, increased number may suggest inflammation.
But clusters of Transitional cells may be seen after Catheterization and Bladder washings. |
|
|
Where are Renal Epithelial Cells found? |
Lining the Nephron through the Collecting Tubules. |
|
|
Are Renal cells significant? |
Normally rare and increased numbers indicate renal disease.
Can be seen with Fevers, Toxins, Inflammations and Infections. |
|
|
When are Fat Droplets seen and from commonly? |
Catheter lubricants or contaminants.
But fat is most commonly seen in cats. |
|
|
What illnesses are often seen with Fat Droplets? |
-Diabetes Mellitus
-Hypothyroidism
-Obesity |
|
|
Does Sperm have any significance? |
No, but still report findings. |
|
|
What are the two types of bacteria? |
-Cocci
-Rod |
|
|
When is bacteria seen in urine? |
When left standing at room temperature. |
|
|
What does bacteria indicate? |
Indicates infection if seen along with WBCs.
Small amounts of Bacteria is normal. |
|
|
What does Yeast indicate? |
Contamination
In rare instances Yeast infections, but RARE. |
|
|
What are the types of casts? |
1) Hyaline Casts 2)Cellular Casts 3)Granular Casts 4)Waxy Casts 5) Fatty Casts |
|
|
What gives casts their shape? |
Their shape results from precipitation of proteins in the tubules of the kidney.
They appear BIG on a microscope, even 10x. |
|
|
What are Hyaline Casts? |
-The most difficult to see casts.
-Dissolve in Akaline urine.
-Seen because of strenuous exercise, fever, poor renal perfusion or general anesthesia. |
|
|
What are the four types of Cellular Casts? |
-WBC
-RBC
-Renal Tubular
-Bacterial |
|
|
When are WBC Cellular Cast seen? |
Most often Neutrophils are in WBC casts.
Most Commonly seen in Pyelonephritis |
|
|
When are Renal Tubular Cellular Casts seen? |
Resulted from destruction or desquamation of the epithelial cells that line the Renal Tubules. |
|
|
When are RBC Cellular casts seen? |
Resulted from Glomerular disease.
They are the most FRAGILE. |
|
|
When are Bacterial Cellular casts seen? |
In Pyelonephritis. |
|
|
What are the Variations of Granular Casts? |
Fine and Course. |
|
|
What do the Granular casts resembles? |
Hyaline Casts. |
|
|
Where are Granular casts seen? |
Renal, Glomerular or Tubular Disease.
Result from the breakdown of cells within the Renal Tubules. |
|
|
What are the stages on Casts Degeneration? |
Cellular Casts --> Granular Casts --> Waxy Casts |
|
|
What are Waxy Casts? |
A serious pathological finding and implies severe renal disease, also called a broad cast or renal failure cast.
Very refractive.
Squared ends. |
|
|
When are Fatty casts seen? |
In cats with Renal Disease and sometimes dogs with Diabetes mellitus.
Large numbers indicate degeneration of Renal Tubules
Glimmer and Glisten |
|
|
What are some things commonly confused with casts? |
-Mucus -Rolled squamous -Fibers, hair -Scratches on slides -Yeast |
|
|
What affects crystal formation? |
-Urine pH
-Urine Temperature
-Urine SG (Concentration) |
|
|
How are crystals classified? |
By whether they appear in acid urine or alkaline urine. |
|
|
How are crystals identified? |
Shapes and pH of the urine. |
|
|
What are the Acid Crystals? |
-Amorphous Urates -Calcium Oxalate -Uric Acid -Tyrosine -Leucine -Cystine |
|
|
What are the Alkaline Crystals? |
-Amorphous Phosphates -Triple Phosphates -Ammonium Biurates -Calcium Carbonate |
|
|
What are Amorphous Urates? |
Seen as shapeless, pink or red granulation.
Low water intake causes Amorphous Urates.
Seen in Acid or Neutral urine |
|
|
What two forms of Calcium Oxalate crystals? |
-Dihydrate
-Monohydrate |
|
|
What are Dihydrate crystals? |
Envelope looking.
Normal in small amounts
Large amounts seen with Urolithiasis |
|
|
What are Monohydrate crystals? |
Fence Picket looking.
Seen in Ethylene Glycol (antifreeze) Poisoning |
|
|
What is Uric acid crystals? |
Seen as plates, or rhombic shapes. |
|
|
What are Tyrosine crystals? |
Seen as fine, dark needles.
Indicates Liver Disease. |
|
|
What are Leucine crystals? |
Oily Spheres
Indicates Liver Disease. |
|
|
What are Cystine crystals? |
6 sided, flat plates.
Seen with Renal Tubular Disorders. |
|
|
What are Amorphous Crystals? |
Seen as a whitish granular precipitate.
UTIs. |
|
|
What are Triple Phosphates Crystals? |
Seen in Akaline, Neutral, or slightly Acidic urine.
Resembles coffin lids and called STRUVITE.
Small amounts normal, but can mean Urolithiasis or Bladder Infection. |
|
|
What are Ammonium Biurates? |
Appear as dark yellow or brown thorny apples.
Seen in animals with Liver Disease and Portocaval Shunts |
|
|
What are Calcium Carbonate? |
Appear as dumbbell shapes.
Commonly and normal seen in Horse and Rabbit urine. |
|
|
What is the Drug related Crystal? |
Sulfonamides. |
|
|
What are Sulfonamides? |
Seen in animals being treated with Sulfonamide Antibiotics.
Can cause Kidney damage. |
|
|
What is haziness or cloudiness caused by? |
Large amounts of WBCs, RBCs, bacteria, crystals, and epis. |
|
|
What correlates with urine pH? |
Types of crystals. |
|
|
What is caused along with large amounts of blood? |
Large amounts of protein. |
|
|
What happens to urine left at room temp? |
Increased: pH, protein, bacteria, and crystals.
Decreased: Casts, ketones, bilirubin. |
|
|
What disintegrates in alkaline urine? |
Casts and WBCs. |
|
|
What do Ammonium Biurates Crystals look like? |
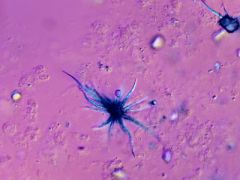
|
|
|
What do Tyrosine Crystals look like? |
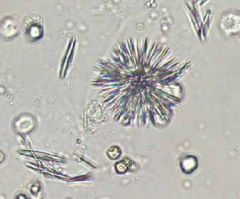
|
|
|
What do Calcium Oxalate Crystals look like? |
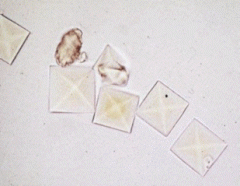
|
|
|
What do Triple Phosphate Crystals look like? |

|
|
|
What do Transitional Epithelial Cells look like? |
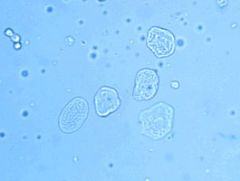
|
|
|
What do Waxy Casts look like? |
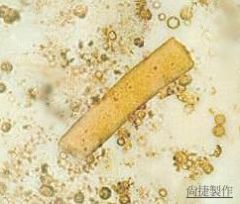
|
|
|
What do Granular Casts look like? |
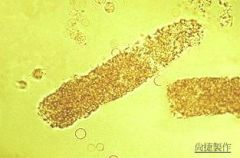
|
|
|
What do Hyaline Casts look like? |

|
|
|
Epithelial Cells and 3 types and what they look like? |
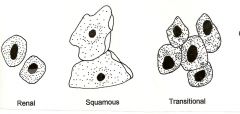
-Renal
-Squamous
-Transitional |
|
|
RBC and types and what they look like? |
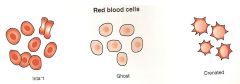
-Intact
-Ghost
-Crenated |
|
|
RBCs Microscope look? |
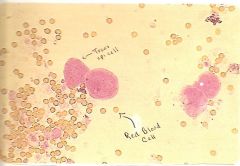
-Trans Epi Cells
-RBC |
|
|
Transitional Epithelial Cells and look? |
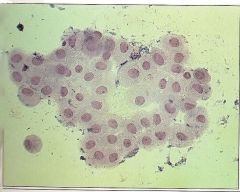
|
|
|
What do Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells look like? |
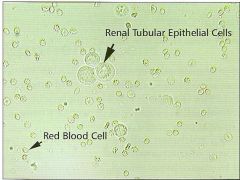
|
|
|
What do Casts? |
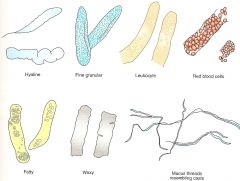
-Hyaline -Fine Granular -WBC -RBC -Fatty -Waxy -Mucus Threads |
|
|
What do Squamous Epithelial Cells look like? |
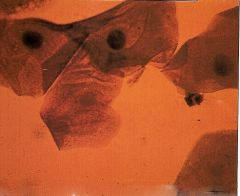
|
|
|
Sqamous Epithelial Cells look like? |
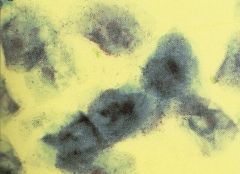
|
|
|
What do Renal Cellular Casts look like? |
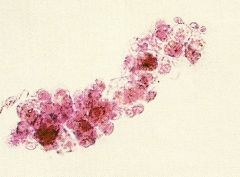
|
|
|
WBC Cast? |
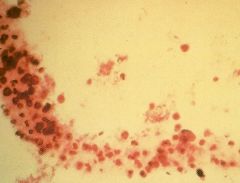
|
|
|
RBC Cast? |
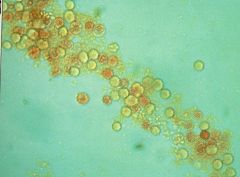
|
|
|
Fine Granular Cast? |
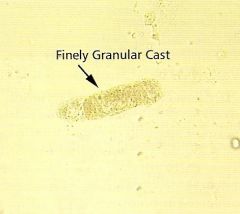
|
|
|
Course Granular Cast? |
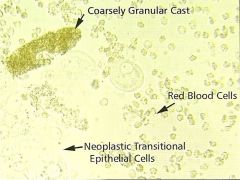
|
|
|
Fatty Cast? |
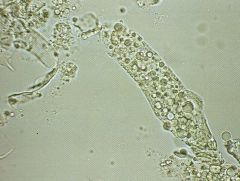
|
|
|
Akaline Crystals? |
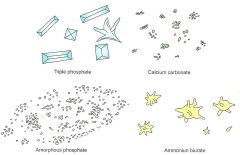
-Triple Phos. -Calcium Carbonate -Amorphous Phosphate -Ammonium Biurates |
|
|
Ammonium Biurates? |
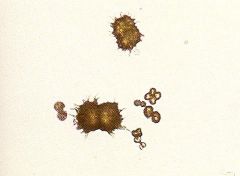
|
|
|
Calcium Carbonate? |
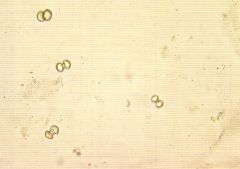
|
|
|
Acidic Crystals? |
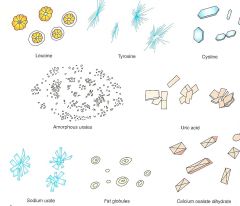
-Leucine -Tyrosine -Cystine -Amorphous Urates -Uric Acid -Sodium Urate -Fat -Calcium Dihydrate Oxalate |
|
|
Dihydrate Calcium Oxalate? |
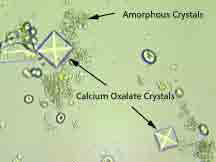
|
|
|
Monohydrate Calcium Oxalate? |
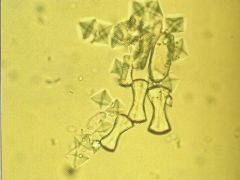
|
|
|
Cystine? |
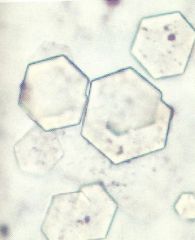
|
|
|
Tyrosine? |

|
|
|
Leucine? |
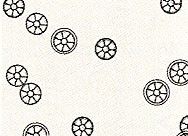
|
|
|
Uric Acid? |

|
|
|
Sulfa Drug Crystal? |
|

