![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Elements that are macro minerals |
Ca |
|
|
Elements that are micro minerals |
B, Co, Cr, Cu, Fl, Fe, I, Mn, Mo, Se, Si, Zn |
|
|
What are vitamins? |
essential organic nutrients required in small amounts
Cannot be synthesized by the body, must be obtained through diet, rumen bacteria, and sun
Required for growth, maintenance, reproduction, and lactation |
|
|
2 classes of vitamins |
Fat Soluble (stored in tissues) and Water Soluble (not stored in tissues) |
|
|
Examples of Fat Soluble vitamins |
Vitamins A, D, E, and K |
|
|
Examples of Water Soluble vitamins |
B-vitamins and Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) |
|
|
What is an International Unit (IU)? |
measures biological activity, or effect, of a substance. Used to quantify vitamins. |
|
|
Sources and function of vitamin K |
Sources: green leafy forages, soybeans, fish meal, liver, rumen, intestinal bacteria, synthetic compounds
Function: blood clotting, synthesis of prothrombin in liver (which converts fibrinogen to fibrin) |
|
|
Signs of Vitamin K deficiency |
- generally not seen in livestock or companion animals - blood loses clotting ability or takes a long time to clot. Serious hemorrhages from slight wounds - in chicks: anemia, easily injured, delayed clotting time, may bleed to death |
|
|
sweet clover disease in cattle |
coumarin (a fragrant compound of sweet clover) turns into dicoumarol due to fungi in mouldy clover. Dicoumarol is an anticoagulant and a competitive inhibitor of vitamin K epoxide reductase (an enzyme that recycles vit K). This causes depletion of vitamin K in the body. |
|
|
Vitamin A sources |
whole milk, fish oils, fresh forages (as B-carotene), synthetic |
|
|
Other names for Vitamin A |
retinol, retinal, retinoic acid |
|
|
Which species cannot convert B-carotene to active vitamin A? |
Cats, ferrets, and herptiles (reptiles and amphibians) |
|
|
Which animals require a source of vitamin A? |
ALL ANIMALS! |
|
|
Functions of Vitamin A |
- vision (light sensitivity), especially night vision - maintenance and growth, reproduction - formation of epithelial tissues and mucous membranes - immune responses |
|
|
Vitamin A deficiency in cattle and pigs |
cattle: rough hair coat, swollen legs, retarded growth in calves, blindness, abortion
pigs: posterior paralysis, xerophthalmia, blindness, dry scaly skin, poor litters |
|
|
Is loss of night vision and blindness due to vitamin A deficiency reversible? |
Yes! Response to treatment in severe cases is often rapid, but it may be irreversible in chronic cases |
|
|
Vitamin E sources |
cereal grains, protein concentrates, oil seeds (peanut and soybean), fresh forages (preserved in silages but high losses in hay), synthetic. |
|
|
Utilization of vitamin E is dependent on adequate... |
selenium |
|
|
When storing vitamin E as an oil, what do you need to add? |
antioxidants, or else it goes bad |
|
|
Vitamin E functions |
- antioxidant, prevents free radicals breaking down cell membranes - immune system - formation of RBCs - reproduction (maintenance of functional integrity of repro organs) - gene expression - platelet aggregation - muscle growth - prevention of oxidation of PUFA |
|
|
Vitamin E deficiency |
- muscular dystrophy - weakness and collapse - stiffness - mulberry heart disease in pigs (white stripes) |
|
|
What causes encephalomalacia and exudative diathesis in chicks? |
vitamin E deficiency |
|
|
Two forms of Vitamin D |
ergocalciferol (D2) in sun dried forages
cholecalciferol (D3) in animal products |
|
|
Converting Vitamin D to active form in the body |
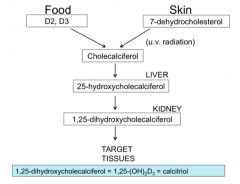
|
|
|
How vitamin D increases blood calcium |
low blood calcium stimulates secretion of parathyroid hormone. This stimulates 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol release from the kidneys. This release increases intestinal absorption of calcium and more calcium can be reabsorbed by the kidneys and bones. Net result is increased blood calcium. |
|
|
Signs of Vitamin D deficiency |
uncommon
- reduced productivity - decreased appetite - poor weight gains - poor reproductivity |
|
|
Vitamin D deficiency effects in young animals, cattle, pigs, and poultry |
young animals: rickets young cattle: swollen knees and hocks, arched back pigs: enlarged joints, broken bones, joint stiffness, paralysis poultry: soft bones and beak, reduced egg production, poor eggshell quality |
|
|
calcium distribution in the body |
99% stored in skeleton (bones and teeth) 2:1 ratio with P as hydroxyapatite In plasma as free ions, bound to proteins, or complexed with acids like citrate or phosphate |
|
|
functions of calcium |
- structural skeletal component - muscle contraction - nerve transmission - blood coagulation - milk production - fetal growth |
|
|
maintenance of blood calcium concentration |
Low calcium levels stimulate parathyroid glands to release PTH. PTH goes into kidneys and bones. Kidney releases 1,25(OH)2D which increases small intestine absorption of calcium. Kidneys increase calcium reabsorption and phosphate excretion. Bones increase calcium pumping to ECF and bone resorption. Net effect is increased ECF calcium. |
|
|
Primary calcium deficiency vs. secondary calcium deficiency |
primary: not enough calcium in the diet secondary: enough calcium in the diet but absorption is inhibited by some other compound in the diet |
|
|
Effects of primary deficiency |
young animals: decreased growth rate, dental mal-development, gum deformities, poor incisor development
adults: inappatence, stiffness, tendency of bone fracture, can't stand, reduced milk flow, reduced fertility |
|
|
effects of secondary deficiency |
rickets. Animal's parathyroid gland becomes hyperactive to hang onto the little calcium it has. Leads to bone resorption, especially in the nose. Horses will get a big swollen nose. Pigs will get a twisted snout. |
|
|
3 types of bone disorders |
osteomalacia - softening of mature bone osteodystrophy - secondary deficiency, swollen heads osteoporosis - light, porous, fragile bone that easily fractures |
|
|
Eclampsia in bitchesss |
a secondary deficiency caused by excessive calcium ingestion during gestation. When dog gives birth its lazy parathyroid gland has atrophied and cannot meet the body's demand |
|
|
Phosphorous is available through plants as |
phytic acid |
|
|
phosphorous distribution and function |
-80% in skeleton as hydroxyapatite - vital for life. needs to be in a 2:1 ratio with calcium - skeletal component, phospholipid component, RNA and DNA component, enzyme component - needed for ATP (obviously) |
|
|
What is pica? |
when animals eat dirt and fence posts because of phosphorous deficiency |
|
|
Magnesium distribution in body |
3rd highest concentration - 50% in bone - highest concentration in liver and skeletal muscle for soft tissue - blood: 75% in RBC, 25% in serum |
|
|
Magnesium function |
skeletal development required for oxidative phosphorylation of heart muscle enzyme activation for multiple body functions |
|
|
Grass tetany in cattle |
due to magnesium deficiency - when grass rapidly grows in the spring, Mg isn't taken up by the plant in correct ratios. The ratio of K to calcium and magnesium isn't correct and becomes a problem |
|
|
Sodium roles |
- helps maintain osmotic and pH balances - principal solute for water reabsorption in kidneys - needed for nerve transmission and muscle contraction - activates carrier proteins for intestinal absorption |
|
|
Potassium roles |
- principal intracellular cation - maintains osmotic balance - needed for insulin release - needed for nerve transmission - maintains proper muscle function |
|
|
Chlorine roles |
- body's primary anion. balances sodium in extracellular fluids and potassium in intracellular fluids - important for pH, electrolyte, and fluid balance |
|
|
Ascites |
"water belly" in chicks. due to sodium toxicity |
|
|
Sulfur roles |
- makes cartilage - a part of feathers, gizzard, and muscle - part of wool - blood clotting - protein, lipid, and CHO metabolism |
|
|
Overall summary of mineral functions |
Fluid balance (K, Na, and Cl) Structure (Ca, P, Mg, Fl, Fe, S) Hormones (I) Metabolism Cofactors (Cu, Zn) |
|
|
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) source and role |
source: citrus, vegetables
roles: oxidation-reduction reactions, collagen synthesis, transfer of iron from transferrin to ferritin, anti-oxidant |
|
|
B vitamins |
required for enzyme function - synthesized by ruminants in the rumen - synthesized by horses in the hindgut - monogastrics food is supplemented with VitB |
|
|
niacin is synthesized from? |
synthesized from tryptophan
cats can't do this, so they need to be supplemented |
|
|
types of B vitamins |
riboflavin, biotin, folic acid, choline, niacin, cyanocobalamin |
|
|
thiamine sources and roles |
cereal grains, brewer's yeast, egg yolk, liver, kidney, pork muscle
a coenzyme involved in oxidative dephospho rylation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, and a-ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA |
|
|
animals with thiamine deficiency will stretch their head backwards. This is a sign of |
opisthotonus |
|
|
riboflavin (B2) sources and roles |
rich sources (yeast, liver, milk, green leafy crops
chemical reactions involving H transport. oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
a tell-tale sign of riboflavin deficiency is |
curled toe paralysis |
|
|
Pyridoxine forms, sources, and roles |
3 forms: pyridoxine, pyridoxal, pyridoxamine sources: yeast, cereals, liver, milk roles: amino acid absorption from intestine, RBC formation |
|
|
pantothenic acid sources and roles |
yeast, peas, molasses, liver, egg, milk, cereal
constituent of CoA |
|
|
biotin sources and roles |
liver, milk, yeast, oilseeds, vegetables
prosthetic group on enzymes involves in CO2 transfer |
|
|
Folic Acid sources and roles |
green leafy materials, cereals, oilseed meal
converted to tetrahydrofolic acid which is a coenzyme involved in methylation reactions. Involved in synthesis of RNA, DNA, and neurotransmitters |
|
|
Vitamin B12 is a complex molecule containing |
cobalt |
|
|
vitamin B12 source and roles |
liver is a rich source
coenzyme in several systems. In ruminants, involved in conversions of propionic acid to succinic acid |
|
|
choline sources and roles |
yeast, green leafy vegetables, egg yolk, cereals, can be synthesized in liver from methionine
structural integrity and signalling for cell membranes. coverts fat to lecithin in liver. utilizes fatty acids. transmits nerve pulses. donor of methyl groups in transmethylation reactions |

