![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
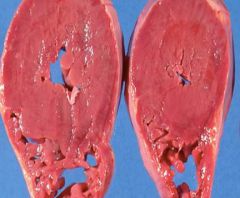
What is this? Characteristics
|
Concentric hypertrophy
- Enlargement of cardiomyocytes - Thicker myocardium - Increase in heart weight - Increase in ratio of wall thickness - No dilation of chamber |
|
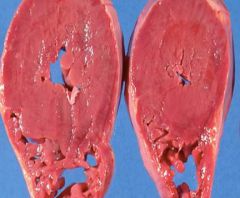
Is this due to pressure or volume overload?
|
Concentric hypertrophy
PRESSURE overload |
|
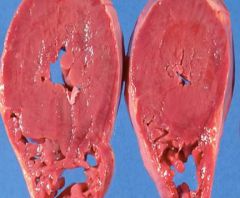
What are the complications?
|
Concentric hypertrophy
- Ischemia - Myocardial infarction - CHF - Angina |
|

What is this? Characteristics
|
Eccentric hypertrophy
- Hypertrophy on the OUTSIDE - Enlargement of cardiomyocytes - Thicker myocardium - DILATION of chamber - Increase in wall thickness and chamber size are proportional |
|
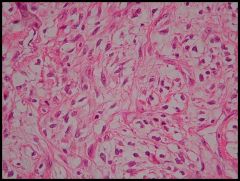
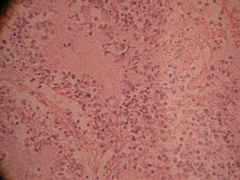
Histologically what kinds of cells are here? What do they resemble?
|
- Sarcomatoid cells
- Smooth muscle cells |
|
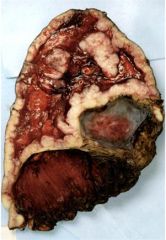
What is this?
|
Mesothelioma
Cancer of the pleura |
|
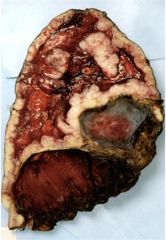
What is this due to?
|
Mesothelioma
-Asbestos exposure |
|
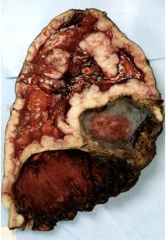
15 - 20 years may elapse between what?
|
Mesothelioma
- 15 - 20 years may elapse between EXPOSURE and DEVELOPMENT of the tumor |
|
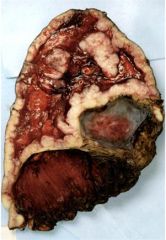
This will grow to encase what?
|
Mesothelioma
- The lung |
|
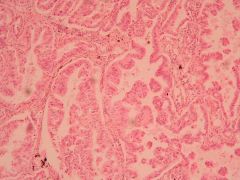
Pulmonary effects?
|
Alevolar cell carcinoma of the lung
- Cough - Dyspnea - Hemoptysis - Chest pain - Obstructive pneumonia - Pleural effusion |
|
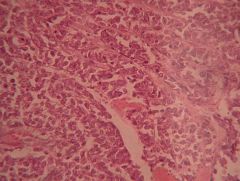
What is this? From what cells does it arise?
|
Small (oat) cell carcinoma
- Arises from NEUROENDOCRINE cells |
|
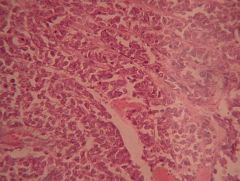
What does this secrete?
|
Small (oat) cell carcinoma
- Secrete ectopic hormones like ADH, ACTH (look for these in a blood analysis) |
|
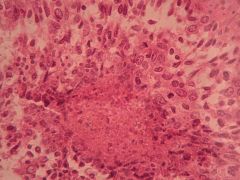
What is this? Where is it located?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
* THIS IS THE MOST COMMON! * - Located near the center of the lung |
|
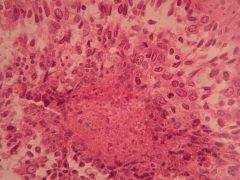
This is silent until what?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
- Silent until narrowing of the bronchi |
|
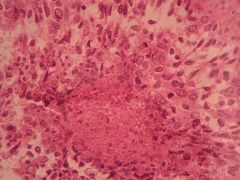
What is characteristic about this?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
- Squamous epithelial pearl with keratinisation |
|
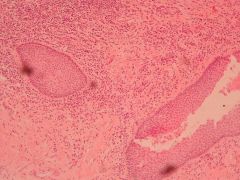
What is this?
|
Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
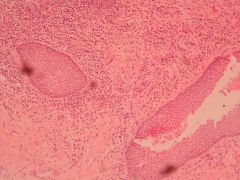
Risk factors?
|
Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Smoking and alcohol |
|
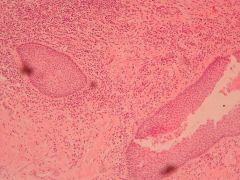
Clinical feature?
|
Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Hoarseness of voice |
|
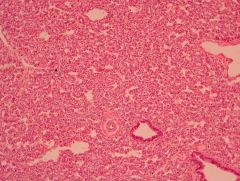
Who does this occur in?
|
Hyaline membrane disease (NRDS)
- Preterm infants <34 weeks of gestational age |
|
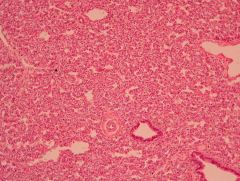
Histologically, what is happening here?
|
Hyaline membrane disease (NRDS)
Immaturity of Type II Pneumocytes resulting in inadequate surfactant production |
|
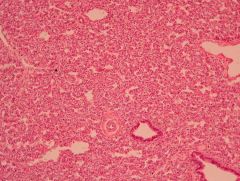
How is this evaluated?
|
Hyaline membrane disease (NRDS)
Amniocentesis |
|
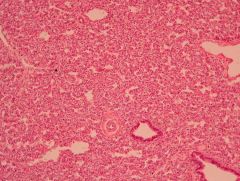
Clinical features?
|
Hyaline membrane disease (NRDS)
- Flaring nostrils - Grunting - Strained, or abnormal breathing |
|
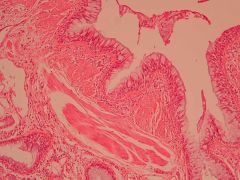
What is this? Define.
|
Bronchial asthma
Chronic inflammatory, reversible disorder of the airways |
|
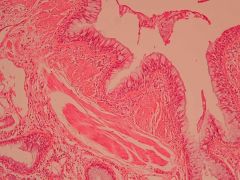
Histological features?
|
Bronchial asthma
- Glands become bigger (hyperplastic hypertrophy) which are secreting a lot of mucus (lots of sputum production) - Increase in goblet cells (hyperplastic goblet cells) which are also secreting mucus - Inflammatory cells such as: lymphocytes and plasma cells - Eosinophils |
|
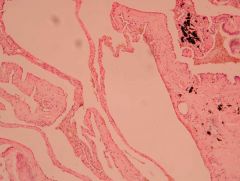
What is this? Define.
|
Emphysema
Enlargement of the alveoli DISTAL to the terminal bronchioles with destruction of interalveolar septum |
|
Etiology?
|
Emphysema
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency |
|
Clinical features?
|
Emphysema
- Patients present with a prolonged history of exertional dyspnea and a minimal non-productive cough |
|
What are the (2) kinds of this?
- This was NOT a Seva Question - |
Emphysema
1. Centriacinar 2. Panacinar |
|
What are the (2) kinds of this?
- This was NOT a Seva Question - |
Emphysema
1. Centriacinar 2. Panacinar |
|
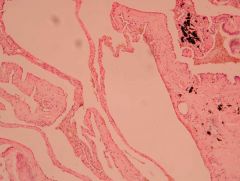
Histological features?
|
Emphysema
- In those big pink spaces we should really have lots of alveoli - The IV septum is broken so the alveoli have become "bigger" - There is a lack of gas exchange |
|
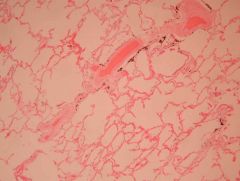
What is this? What is increased?
|
Pulmonary hypertension
- Increase in thickness of tunica media - Increase in pulmonary vasculature pressure |
|
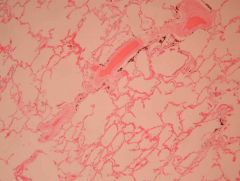
Etiology if this is secondary?
|
Pulmonary hypertension
Secondary = R - L shunt, Mitral Stenosis, COPD |
|
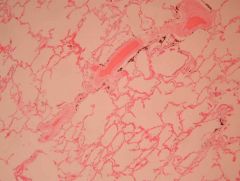
Etiology if this is primary?
|
Pulmonary hypertension
Primary = IDIOPATHIC |
|
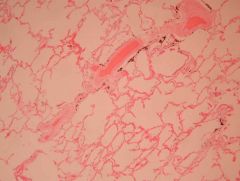
Clinical features?
|
Pulmonary hypertension
- DYSPNEA - Weakness - Recurrent syncope |
|
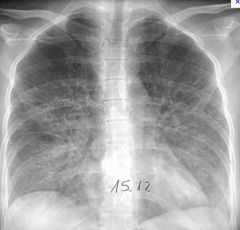
What is this? What is another name for it?
|
Viral pneumonia (Interstitial pneumonia)
|
|
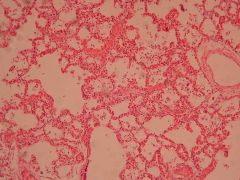
What is this? What is another name for it?
|
Viral pneumonia (interstitial pneumonia)
|
|
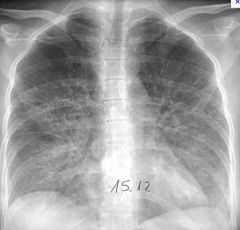
Etiology?
|
Viral pneumonia
Cytomegalovirus |
|
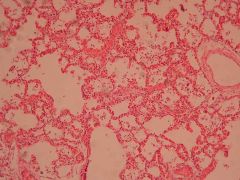
Etiology?
|
Viral pneumonia
Cytomegalovirus |
|
Clinical features?
|
Viral pneumonia
- Low grade fever - Dry cough - Headache, malaise |
|
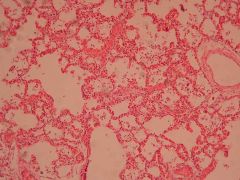
Clinical features?
|
Viral pneumonia
- Low grade fever - Dry cough - Headache, malaise |
|
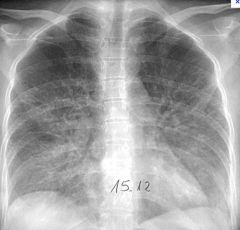
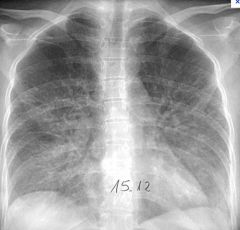
Radiological criteria of lobar pneumonia?
|
Viral pneumonia
LOBAR: consolidation of an entire lobe or segment of a lung |
|
Radiological criteria of lobar pneumonia?
|
Viral pneumonia
LOBAR: consolidation of an entire lobe or segment of a lung |
|
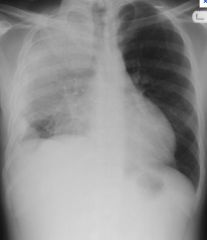
Radiological criteria of bronchopneumonia
|
Viral pneumonia
BRONCHO: dispersed bilateral, focal, patchy area of consolidation |
|
Radiological criteria of viral pneumonia?
|
Bat wing apperance
|
|
Radiological criteria of viral pneumonia?
|
Bat wing appearance
|
|
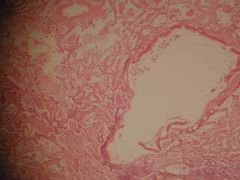
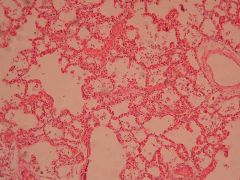
What is this?
|
Bronchopneumonia
|
|
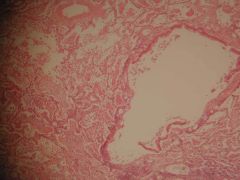
Clinical features?
|
Bronchopneumonia
- Abrupt onset of high fever (with rigor and chills) - Malaise - Productive cough (same as lobar) |
|
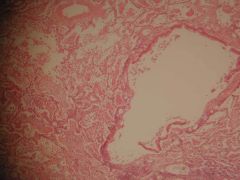
What does this typically involve?
|
Bronchopneumonia
Typically involves a small airway and surrounding alveolar spaces; relatively small area of involvement |
|
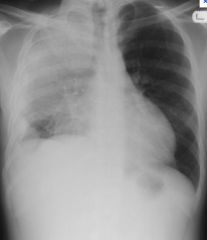
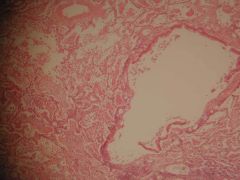
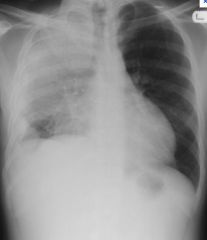
What is this?
|
Lobar pneumonia
|
|
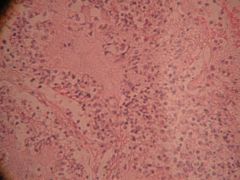
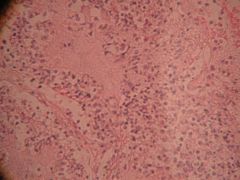
What is this?
|
Lobar pneumonia
|
|
What are pre-disposing factors?
|
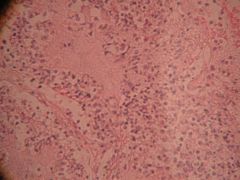
Lobar pneumonia
- Decrease cough reflex - Injury to cilia (smokers) - Decrease function of the alveolar macrophages - Edema or congestion - Retention of secretions |
|
Routes of infection?
|
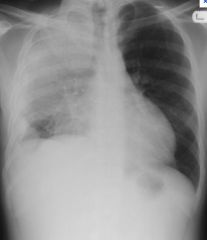
Lobar pneumonia
- Aspiration - Inhalation - Bacteremia - Direct extension |
|
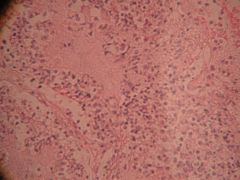
Clinical features
|
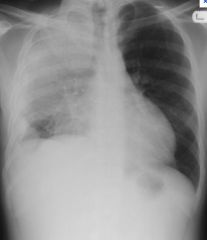
Lobar pneumonia
- Abrupt onset of high fever (with rigor and chills) - Malaise - Productive cough (same as bronchopneumonia) |
|
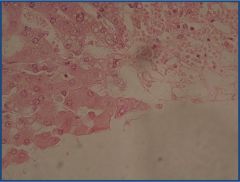
Identify the central vein.
|
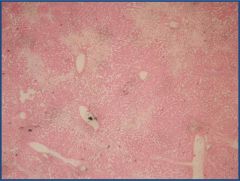
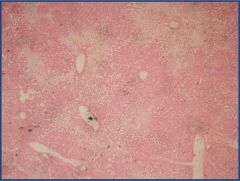
Liver passive congestion
Identify the central vein |
|
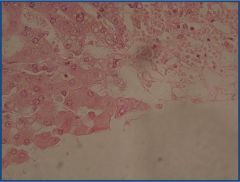
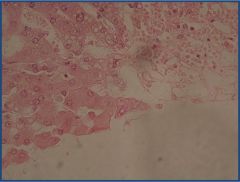
Look for the congested central zone with atrophic hepatocytes
|
Liver passive congestion
Look for the congested central zone with atrophic hepatocytes |
|
Etiology?
|
Liver passive congestion
?? |
|
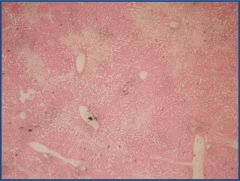
Etiology?
|
Liver passive congestion
?? |
|
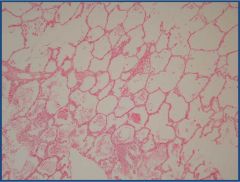
Histologically, what are we looking for?
|
Pulmonary edema
- Alveoli - Fibrin crystals - RBCs - Macrophages - Heart failure cells |
|
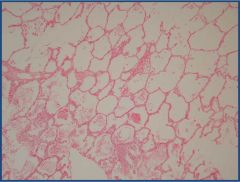
Etiology?
|
Pulmonary edema
- Left ventricular failure - Mitral stenosis - ARDS - Sepsis |
|
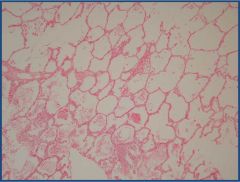
What is in the alveoli?
|
Pulmonary edema- FLUID
|
|
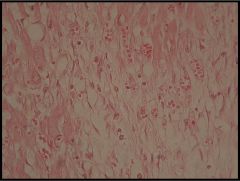
What kinds of cells should we see here?
|
MI Granulation tissue
- Capillaries - Fibroblasts - Residual inflammatory cells |
|
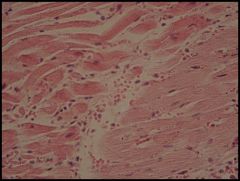
What is this?
|
Myocardial infarction
|
|
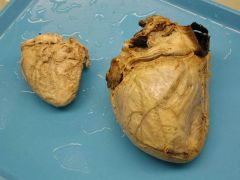
What is this? Define.
|
Cardiomegaly
- Increase in weight or size of the heart |
|
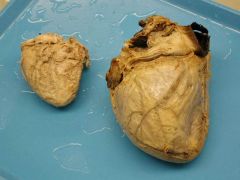
Etiologies? (LOTS)
|
Cardiomegaly
- Hypertension (LV) - Valvular disease (MS, MR, AS, AR) - Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy - Congenital heart disorders - Alcohol - Sarcoidosis - Amyloidosis - Acromegaly |
|
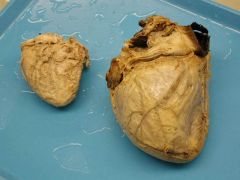
What is this
|
Biological heart valve
|
|
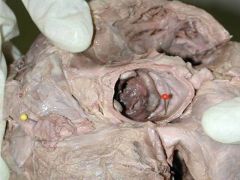
What is this made of
|
Bio prostheses
Mechanical frame with the porcine aortic valve cusp or bovine pericardial pieces |
|
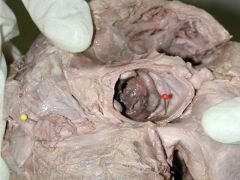
Characteristics
|
Bio prostheses
Good hemodynamic function, with little obstruction and resists thromboembolic complications |
|
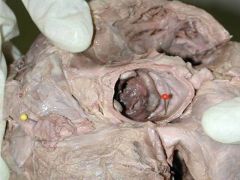
Complications
|
Bio prostheses
- Tissue degeneration with calcification and fragmentation. Indicated in females of reproductive age group |
|

What is this?
|
Mechanical valve
|
|

This kind of valve requires what
|
Mechanical valve
- Life long anti-coagulants |
|

Complications
|
Mechanical valve
|
|
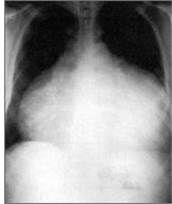
What is this?
|
Cardiac
|
|
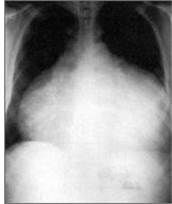
How is this described radiologically?
|
Cardiac tamponade
Water bottle appearance |
|
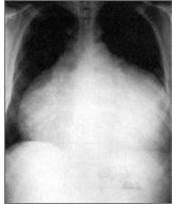
Is this a medical emergency or a chronic condition?
|
Cardiac tamponade
Medical EMERGENCY! |
|
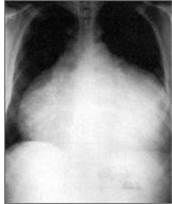
Name the features of Becks Triad
|
Cardiac tamponade
- Hypotension - Increased jugular venous pressure - Muffled heart sounds |
|
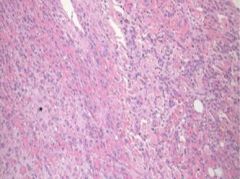
Etiology?
|
Acute pericarditis
- Common coxsachie virus (young adult male will suddenly have a fever) - Myocardial infarction (Dressler's syndrome) - Rheumatic fever |
|
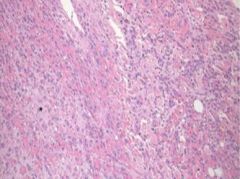
Clinical features?
|
Acute pericarditis
Pericardial friction rub on auscultation (scratching sound) is the cardinal sign, and a fever |
|
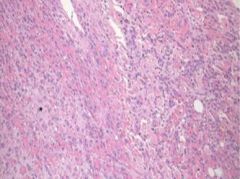
How is this chest pain different from MI angina?
|
Acute pericarditis
- Relieved by sitting forward - Increased by lying down and respiration - Pericardial friction rub sound |
|
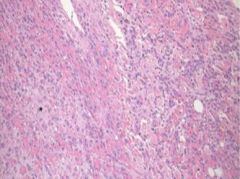
Define the terminology
|
Acute pericarditis
SUDDEN, sharp, substernal chest pain that can refer to the neck or shoulder |
|

What is this?
|
Rhabdomyoma
|
|

Benign or malignant
|
Benign
|

