![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many sides does an icosahedral have? How many subunits does it have?
|
-20 sided
-60 subunits |
|
|
What are some of the ways viruses are classified?
|
-Type of nucleic acid
-Number of strands of nucleic acid -Arrangement of nucleic acid -Symmetry of capsid -Presence or absence of envelope Early taxonomy based on disease they caused |
|
|
How is the taxonomy of viruses organized?
|
-Order (-virales)
-Family (-viridae) -Subfamily (-virinae) -Genus (-virus) -Species (tobacco mosaic virus) |
|
|
What are some of the ways viruses can be named?
|
-By species of origin (eg Swine flu)
-By location (eg Ebola virus) -By disease (eg influenza) |
|
|
What are the different possible types of viral genomes?
|
-dsDNA
-ssDNA (positive or negative sense) -dsRNA -ssRNA (positive or negative) All can be linear, circular, or segmented |
|
|
Where are the 3 types of symmetry found in icosahedrals?
|
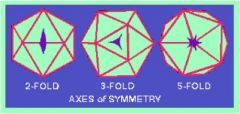
|
|
|
What are the two types of viral shapes?
|
-Helical
-Icosahedral |
|
|
Who created the virus classification scheme that is used today? What does it use to classify viruses?
|
-David Baltimore
-How a virus gets to making mRNA is how they are classified |
|
|
What are the features of Class I viruses?
|
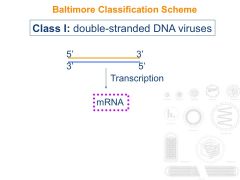
|
|
|
What are the features of Class II viruses?
|
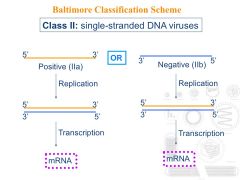
|
|
|
What are the features of Class III viruses?
|
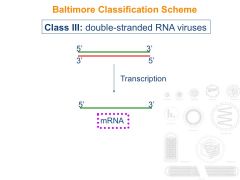
|
|
|
What are the features of Class IV viruses?
|
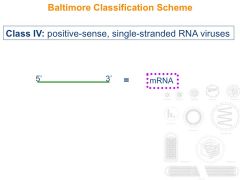
|
|
|
What are the features of a Class V virus?
|
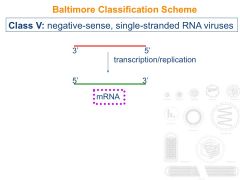
|
|
|
What are the features of a Class VI virus?
|

|
|
|
What are the features of a Class VII virus?
|
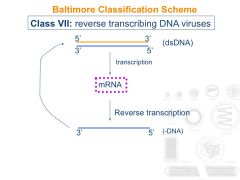
|
|
|
What is the difference between positive and negative sense RNA viruses?
|
Positive sense viruses can be used directly for translation and negative sense viruses need to make a positive sense copy of their RNA before they can translate
|
|
|
What is one feature of all ssDNA viruses?
|
They are typically small and have few genes
|
|
|
What is one feature of all dsDNA viruses?
|
They are among the largest of all viruses
|
|
|
What is one feature of positive sense RNA viruses?
|
They are very common in vertebrates and plants
|
|
|
What is one feature of negative sense RNA viruses?
|
They all have helical nucleocapsids and some have fragmented genomes
|
|
|
What is one feature of dsRNA viruses?
|
They have fragmented genomes and capsids with icosahedral symmetry
|
|
|
What are satellite viruses? What are viroids?
|
-Satellite viruses require a helper virus to replicate
-Viroids do not code for proteins and replicate independently of other viruses |
|
|
What are some classifications of viruses based on how they are spread (epidemiological criteria)?
|
-Enteric (ingestion/intestinal tract)
-Respiratory (inhalation/lungs) -Arboviruses (spread by arthropods/bites) -Oncogenic (acquired by close contact/alters host cell) |
|
|
What is the regressive theory of viral evolution?
|
Viruses came originally from cells and evolved to have capsids/viral proteins
|
|
|
What is the prebiotic RNA model of viral evolution?
|
Viruses came originally from the prebiotic soup.
|
|
|
What is the cellular constituent model of viral evolution?
|
Random mutations in a cell's DNA/RNA produced a genome that could replicate itself and give rise to capsid proteins.
|
|
|
What factors influence viral evolution?
|
-Mutation
-Recombination |
|
|
How do DNA viruses evolve?
|
Low rate of mutation (1 in 10^8-10^11) because of DNA pol's fixing of errors
High duplication (many copies made) means errors are propagated) High multiplicity of infection (MOI) leads to many copies of viral nucleic acid in cells, leads to deletions mutations and insertions Also can recombine (when 2 different viruses infect same cell) |
|
|
How do RNA viruses evolve?
|
High rate of mutation (1 in 10^4-10^5)
High duplication rate High MOI Not much recombination Reassortment with segmented RNA viruses |
|
|
What are the 3 phases in the viral replication cycle?
|
-Initiation of infection
-Replication and expression of genome -Release of virions from infected cell |
|
|
What does the virus growth curve look like?
|
1-step
|
|
|
What are the 7 steps in the virus replication cycle?
|
1. Binding to cell receptor
2. Entry and uncoating 3. Early gene expression 4. Replication of viral genome 5. Late gene expression 6. Assembly of virions 7. Exit |
|
|
What are some of the ways a virus can enter the cell?
|
1. Fusion with host cell membrane (enveloped viruses)
2. Endocytosis followed by fusion of host membrane (enveloped viruses) 3. Lysis/pore formation (non-enveloped virus) Many viruses use pH as a means of getting out of the endosome |
|
|
How do viruses get transported through the cell?
|
Virions/capsids moved via vesicles or microtubules
|
|
|
What are some of the ways viral genomes get into the nucleus?
|
-Through nuclear pores (after partial disassembly in the cytoplasm)
-They can disassemble AT the nuclear pore -Some virions can go right through the NPC |

