![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the smallest group of DNA viruses?
|
Circoviridae
|
|
|
What 3 diseases do Circoviridae viruses cause?
|
PCV2
PBFDV CAV |
|
|
Is the icosahedron of circoviridae naked or enveloped? What kind of genome does it have?
|
Naked iscosahedral nucleocapsid
Circular, single-stranded DNA genome |
|
|
What are the ORFs of Circovirus?
|
ORF1: replication-associated (Rep) protein
ORF2: capsid protein ORF3: Genes associated with immune evasion |
|
|
- main highway for ascending and descending fiber tracts that connect the brain to the spinal nerves
- mediates reflexes |
Spinal Cord
|
|
|
What are PCV1 and PCV2? Where are they geographically located?
|
Porcine circovirus 1 (PCV 1)
All over the world in swine Non-clinical disease Porcine circovirus 2 (PCV 2) All over the world in swine Porcine multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS) |
|
|
What is PMWS?
What are the morbidity and mortality rates? |
It was first recognized in 1991
Worldwide Morbidity is about 100% Mortality ranges 5-50% It affects pigs at 4-12 week old (why?). Because the virus needs to replicate within growing/dividing cells. |
|
|
How Is PCV transmitted?
|
Horizontally
Oral and nasal Vertically- Transplacental infection often leads to abortion weak neonates mummified fetuses |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of PCV?
|
Porcine circoviruses
Replication in macrophages/ monocytes and dendritic cells (why?) Persistent Apoptosis Immunosuppression Replication in kidney, liver, lung in young animals Pathology: -Lymphocyte depletion in secondary lymphoid tissues -Granulomatous inflammation in numerous organs -Interstitial pneumonia -Often seen basophilic cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in macrophages |
|
|
What are the clinical signs and gross lesions of PCV?
|
Wasting, slowed growth,
Enlargement of inguinal lymph nodes Frequently dyspnea Noncollapsed and mottled lungs Occasionally jaundice |
|
|
What causes immunosuppression in PCV?
|
Virus attacks monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose PCV2?
|
Demonstration of PCV2 within lymphoid tissue lesions by
IHC PCR in situ hybridization Virus isolation |
|
|
How do you prevent PCV2? Can you vaccinate against them?
|
Disinfection of premises
Acid It is resistant to detergents Removal of affected animals Vaccination: SuvaxynTM PCV2 One Dose Circovac (Merial) |
|
|
What birds are effected by beak and feather disease virus?
Via what routes is it spread? |
Affects many species of psittacine birds
Cockatoos are very susceptible Spread via alimentary and respiratory routes |
|
|
What is the pathology of BFDV?
|
Beak and feather disease virus
Infect the immune cells and progenitor cells for feathers and beak Abnormal feather and beaks |
|
|
What happens when erythrocytes and other cells are replaced by fat cells in the bone marrow?
|
Anemia
|
|
|
What are the common features of circovirus infection?
|
Infect young animals
Persistent infection Prone to secondary infections |
|
|
Which side is the healthy secondary lymphoid tissue?
|
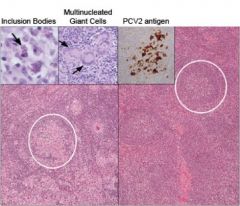
The one on the left is unhealthy because the germinal centers have been depleted.
|

