![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the genome of the hepatitis B viruses?
|
All RNA EXCEPT for hepatitis B
|
|
|
What are the acute viral hepatisies?
|
A
E |
|
|
What are the more chronic hepatitis viruses?
|
B
C D |
|
|
What's the transmission of the chronic hepatitis viruses?
|
Parenterally
|
|
|
What's the transmission of the acute viral hepattitises?
|
Fecal-oral
|
|
|
What types of hepatitis are able to be prevented by vaccine?
|
A
B E D (as it is dependent on B) |
|
|
What type of hepatitis is most common in the US?
|
C
|
|
|
What population is at high risk from hepatitis E?
|
Pregnant women in the 3rd trimester
|
|
|
What's the presentation of hepatitis A in kids? Older adults?
|
Kids: not serious at all - they just stop being as active
Older adults: very bad! risk of mortality |
|
|
How do you diagnose the different kinds of hepatitis?
|
IgM against the viruse during the acute phase
In Hepatitis C, you need the RNA |
|
|
What determines if Hepatitis B will be chronic?
|
Age
Immune status |
|
|
Who gets chronic hepatitis E?
|
Immunosuppressed
|
|
|
What's the presentation of hepatitis A in kid? Adults?
|
Kids: no symptoms
Adults: symptoms of acute hepatitis: -Anorexia -Constitutional symptoms -Fagtigue -Serum-sickness |
|
|
What increases the intensity of a hep A infection?
|
Underlying liver disease
|
|
|
What are indications for hep A vaccination?
|
Kids > 1 year
Travelers to endemic areas MSM Illegal drug users Hemophiliacs People with chronic liver disease |
|
|
What are the forms of the hepatitis A vaccine?
|
Hep A vaccine: 2 doses
Combined A and B: 3 doses; 0, 1 6 months |
|
|
Where is hepatitis B commonly found
|
Asia
Africa Centrla, south America |
|
|
What population is hepatitis B most common in?
|
Immigrants from endemic areas
|
|
|
What are the recommendations for HBV screening?
|
People from 3rd world countries
People not vaccinated as infants, kids of immigrants TIssue/blood donors Pregnant women High risk groups: MSM, dialysis, partners of carriers People who will be immunosuppressed |
|
|
What is the most dangerous complication of HBV infection?
|
Fulminant hepatitis
|
|
|
Why should we screen pregnant women for hepatitis B infection?
|
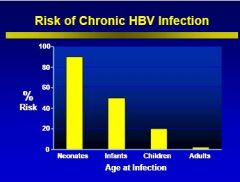
Due to the fact that their kids are at high risk of a chronic HBV infection if they get the disease1
|
|
|
What are the outcomes of a chronic hepatitis B infection?
|
Altering through an inactive carrier state and chronic hepatitis
|
|
|
What are the possible outcomes of HBV-caused chronic hepatitis?
|
Cirrhosis
HCC |
|
|
What antibody is used to test for acute HBV infection?
|
Anti-HBc IgM
Antibody against the core |
|
|
How do you test for immunity to HBV?
|
Anti-HBs
|
|
|
How do you test for a high infectivity in HBV?
|
HBeAg
|
|
|
What are the interpretations of HBV serology?
|
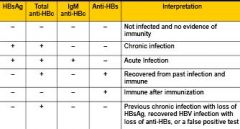
Total anti-HBc: marker of infection
Anti-HBs: immunity HBsAg: infection |
|
|
What gives you the measurement of infectivity for Hepatitis B?
|
Serum HBV DNA levels
|
|
|
What's the relationship between HBV levels and ALT levels?
|
Not correlated, always
|
|
|
What complications are present due to persistently high HBV serum levels/
|
Cirrhosis
HCC |
|
|
What's the family of the HBV?
|
Enterovirus
Gets rid of coat upon entry to the cell |
|
|
What is the structure of the DNA within HBV?
|
Complete strand
Incomplete strand After repair, you get two complete strands which twist around each other and stick to histones |
|
|
What process occurs inside HBV that doesn't occur in human cells?
|
Reverse transcription
|
|
|
What are the stages of chronic HBV infection?
|
1. Immune tolerance phase (early)
2. Immune clearance phase: vius goes away! 3. Seroconversion 4. Reactivation |
|
|
What are risk factors for HCC in HBV?
|
Viral:
Persistently high DNA load Core promoter variant HBV genotype: C>B Host factors: Age M>F Asians Coinfection, etc External: Alcohol Aflatoxin Smoking |
|
|
What are the goals for HBV treatment?
|
Suppression of HBV replication
Decrease hepatic complications Prevent progression to cirrhosis, liver failure, etc. |
|
|
How do we know if treatment to HBV is successful?
|
Decrease in serum HBV DNA
Undetectable viral load: surface antigen negative. Normalization of liver function |
|
|
What are indications for treatment of HBV?
|
Likelihood of adverse outcomes: cirrhosis/HCC
Likelihood of long-term benefit with treatmnet High ALT Fibrosis on biopsy |
|
|
What are treatments for HBV?
|
Interferon alpha 2a, b
|
|
|
What's the effect of INF-alpha on HBV infection?
|
Stimulation of host immune response
Antiviral activity |
|
|
How long is someone on interferon for HBV? Nucleoside/tide analogues?
|
Interferon: 12 months
Nucleoside/tide analogues: life! |
|
|
What are the side effects of interferon? Nucleoside/tide analogues?
|
Interferon: Many
Nucleoside/tide: rare; adefovir/tenofovir have nephrotoxicity |
|
|
What are the first-line drugs for HBV?
|
Adefovir
Tenofovir |
|
|
What protein is in the HBV vaccine?
|
HBs
|
|
|
What is the dosing for HBV vaccine?
|
3 doses
Months: 0, 1, 6 |
|
|
What are factors that lend to a poor response to the HBV vaccine?
|
Old age
Chronic illness Decreased immune response Obesity Genetics |
|
|
What are indications for HBV vaccine?
|
All infants
All kids and adolescents who weren't vacinated at birth Adults at risk of infection |
|
|
What is the impact of HBV vaccine on HCC?
|
Decreases it!
The vaccine prevents cancer! |
|
|
Who should we screen for hepatitis C?
|
Transfusions before 1990
Drug users Needlesticks Sex related stuff Offspring of infected mothers Dialysis patients |
|
|
How do you go about diagnosing HCV?
|
Hepatitis C antibody: indicator of exposure
Hepatitis C virus RNA: mark of presence of the virus/ongoing infection |
|
|
What's the correlation between HCV RNA levels and severity of disease?
|
No correlation
|
|
|
What are the most common genotypes of Hepatitis C?
|
Genotype 1
Genotype 2, 3 |
|
|
Which HCV genome responds best to treatment? Worst?
|
2, 3 respond best
1 responds not well |
|
|
What are the symptoms of an acute hepatitis C infection?
|
Nothing!
|
|
|
What is the most common symptom of chronic hepatitis C infection?
|
Fatigue!
|
|
|
When do HCV symptoms manifest?
|
Late stage!
It's a silent killer. |
|
|
What are the common symptoms of hepatitis C infection?
|
Fatigue
Anorexia RUQ discomfort Extrahepatic: renal, skin, neurologic |
|
|
What are the factors affecting progression of HCV?
|
Age at infection
Alcohol consumption Gender Immune function Obesity |
|
|
What are the labs that you order up for HCV?
|
HCV RNA< Genotype
LFTs CBC+P PT Look for HBV, HIV Look for HCC Abdominal US +/- biopsy |
|
|
Is HCV curable?
|
YES!
|
|
|
What is the effect of IL28B muttions to HCV treatment? Who has this?
|
You get a worse response to HCV therapy
Black patients |
|
|
What are the side-effects of interferon?
|
Flu
Fatigue Mood changes Sleep disturbances Hair loss Decreased whic, platelet counts Retinal hemorrhage |
|
|
What are the side effects of ribavirin?
|
ANEMIA!
TERATOGENIC! Dry cough Puritis Decreased appetitie |
|
|
What should you give someone who has HCV?
|
INF
Protease inhibitors Ribavirin |
|
|
What are the side effects of telaprevir and boceprevir?
|
Anemia
Just telaprevir: skin rash, anorectal discomfort |
|
|
Who with HCV should be treated?
|
Advanced fibrosis
Early stage liver disease Relapsers and partial responders |
|
|
When can someone get hepatitis D?
|
Coinfection with D
Superinfection with B, then they get exposed to D |
|
|
Who should be tested for hepatitis D?
|
People with acute hepatitis:
-Anti HBsAg+ and IgM anti HBc+ -Severe course -Risk factors Chronic liver disease -HBsAg+ -Active liver disease despite low HBV DNA -Risk factors |
|
|
What are the sequelae of acute HDV infection? Superinfection?
|
Acute:
-Recovery -Fulminant hepatitis -Chronic hepatitis Superinfection: -Chronic hepatitis -Fulminant hepatitis |
|
|
What's the treatment for HDV?
|
Interferon is the only one that works
|
|
|
How do you prevent HDV infection?
|
Vaccine for HBV
|
|
|
What is hepatitis E similar to?
|
Hepatitis A
|
|
|
What are risk factors for HEV?
|
Endemic areas: asia, mexido
Pigs Ingestion of raw meat |

