![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Etruscan Civilization
|
modern name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio
|
|
|
|
Enology
|
the study of wine and winemaking
|
|
|
|
Tenuta
|
vast farm estate, often controlled by a noble family
|
|
|
|
Mezzadria System
|
prevailed throughout central and northern Italy up until the 1950s, was a culture in which the sharecropper made a little wine for himself and turned over the rest of his grapes (and portions of all his other produce) to the landowner as rent.
|
debt
|
|
|
Mezzadri (English meaning)
|
Sharecroppers
|
|
|
|
Fattoria
|
Central winery
|
|
|
|
Latifondo System
|
oppressive southern Italy - peasants had no vested interests in the large landed estates.
|
|
|
|
What governmental change occurred in Italy after WW2?
|
Italy transformed itself from a monarchy to a republic
|
|
|
|
By the early sixties Italy was among the world’s largest producers of what?
|
washing machines, refrigerators, and cars
|
|
|
|
Rural Exodus
|
migration pattern of people from rural areas to urban areas
|
|
|
|
Rural Exodus promoted what?
|
new class of entrepreneurs, most of them businesspeople and many of them foreigners, who snapped up these distressed or abandoned properties for weekend getaways. Eventually, these nonfarmers helped reshape the Italian wine business into a real business.
|
|
|
|
What did the Italian gov't enact in 1963?
|
the Denominazione di Origine Controllata (DOC) laws, which created legally defined production zones and production formulas for what were once simple farmhouse wines.
|
|
|
|
What year was Italian DOC created?
|
1963
|
|
|
|
What were the "Green Plans"?
|
financing of massive plantings of various crops throughout Italy; 1961 & 1966
|
|
|
|
What is "cantina sociale"
|
Italian cooperative winery
|
|
|
|
What was the main function of a "Cantine"
|
to be a sponge for a lot of excess juice, and to produce lots of (often excess) wine.
|
|
|
|
Is a DOC a guarantee of quality?
|
No
|
|
|
|
The EU gives subsidies to vitners who?
|
restructure their existing vineyards to produce better-quality grapes
|
|
|
|
What is a"DOC Production Formula"?
|
the recipes vintners must follow in order to label their wines with a DOC designation
|
|
|
|
What's the most famous Italian example of a "DOC Production Formula" Revision?
|
Chianti Classico DOC, which was extensively rewritten in both 1984 and 1996
|
Classic Italian DOC
|
|
|
"DOC Production Formula s" have been revised in recent times to reflect a greater emphasis on what?
|
wine quality
|
|
|
|
Important native red grape of Sicily?
|
nero d’avola
|
|
|
|
The climate of Sicily?
|
intensely hot and dry
|
|
|
|
Sicily produces wines which are what profile?
|
soft, fruity, with decidedly New World sensibility.
|
|
|
|
What's a native red grape of Puglia?
|
primitivo
|
|
|
|
Primativo from Puglia has what tasting profile?
|
soft & plush
|
|
|
|
What's Friuli's rare dessert wine that rivals Sauternes?
|
Picolit
|
|
|
|
Where is “Salice Salentino" produced?
|
Puglia
|
|
|
|
What grape is used in "Salice Salentino"?
|
negroamaro
|
|
|
|
What grape is used for "Montepulciano d’Abruzzo"?
|
Montepulciano
|
|
|
|
What grape is used for "Vermentino di Gallura"?
|
Vermentino
|
|
|
|
What does "nomi di fantasial" mean?
|
Fantasy names
|
|
|
|
What are the four official classifications of Italian wine?
|
1. Vino da Tavola, or VdT (the most generic of the group)
2. Indicazione Geografica Tipica, or IGT (Typical Geographic Indication, meant to be a step up from table wine 3. Denominazione di Origine Controllata, or DOC 4. Denominazione di Origine Controllata e Garantita, or DOCG (Denomination of Controlled and Guaranteed Origin, reserved for a handful of wines considered of exceptional pedigree) |
|
|
|
Most VdT wine is sold in bulk as what?
|
SFUSO
(the stuff that’s poured on tap in local restaurants) or Blending Wine |
|
|
|
When was IGT classification created?
|
1992
|
|
|
|
What does IGT designate?
|
that the wine is from a particular geographic area.
|
|
|
|
Most important thing to remember about DOC and DOCG designation?
|
it is both a place-name and a production formula
EXAMPLE: The designation “Collio,”for example, refers not only to wine from the hills of Friuli–Venezia Giulia but to a specific set of things that must be done in order for the wine to carry the designation. |
|
|
|
What does a DOC discipline outline?
|
where exactly the grapes are grown, which grapes are to be used, and how long some wines must be aged before release.
|
|
|
|
When was DOC law created?
|
1963
|
|
|
|
What and when was the first declared DOC zone?
|
1966 - Vernaccia di San Gimignano, in Tuscany
|
|
|

Label 1-7 with designation
|
1.Producer
2.Vintage 3.DOC Designation, as indicated by the term Denominazione di Origine Controllata (DOC). 4.Grape variety or DOC name 5.Type of wine 6.Size and alcohol content 7. Proprietary Name (Not an official designation) |
|
|

Label 8-10 label distinctions
|
8.Importer name
9.Sulfite and Government Warnings 10. Producer Name. In most instances, it is the same as the name on the front label, but not always. The front label may carry a brand name, rather than an actual winery name, making this back label listing useful in determining exactly what the winery name is. |
|
|
|
When was DOCG created?
|
1963
|
|
|
|
What and when was the first classified DOCG?
|
Brunello di Montalcino, in Tuscany not until 1980
|
|
|
|
What are the 8 Piedmont DOCGs?
|
Asti
Barbaresco Barolo Brachetto d’Acqui/ Acqui Gattinara Gavi Ghemme Roero |
|
|
|
What are the 6 Tuscany DOCGs?
|
Brunello di Montalcino
Carmignano Chianti Chianti Classico Vernaccia di San Gimignano Vino Nobile di Montepulciano |
|
|
|
What are the 3 DOCGs of Campania?
|
Fiano di Avellino
Greco di Tufo Taurasi |
|
|
|
What are the 3 DOCGs of Lombardia?
|
Franciacorta
Sforzato di Valtellina Valtellina Superiore |
|
|
|
What are the 3 DOCGs of Veneto?
|
Bardolino Superiore
Recioto di Soave Soave Superiore |
|
|
|
What are the 2 DOCGs of Marche?
|
Rosso Cònero Riserva
Vernaccia di Serrapetrona |
|
|
|
What are the 2 DOCGs from Umbria?
|
Montefalco Sagrantino
Torgiano Rosso Riserva |
|
|
|
What is the 1 DOCG of Abruzzo?
|
Montepulciano d’Abruzzo Colline Teramane
|
|
|
|
What is the 1 DOCG from Emilia-Romagna?
|
Albana di Romagna
|
|
|
|
What is the 1 DOCG from Friuli?
|
Ramandolo
|
|
|
|
What is the 1 DOCG from Sardegna?
|
Vermentino di Gallura
|
|
|
|
3 Central Italy highlighted wines using sangiovese?
|
Chianti
Brunello di Montalcino Vino Nobile di Montepulciano |
|
|
|
What 2 southern Italy wines are highlighted using Aglianico?
|
Taurasi
Aglianico del Vulture |
|
|
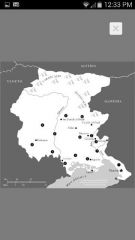
Friuli - Venezia Giulia DOC/DOCG zones
|
1 Carso
2 Colli Orientali del Friuli 3 Collio Goriziano/ Collio 4 Friuli Annia 5 Friuli Aquileia 6 Friuli Grave 7 Friuli Isonzo 8 Friuli Latisana 9 Lison-Pramaggiore 10 Ramandolo DOCG (Added in 2000-2001) |
|
|
|
Friuli has influences from which 2 countries?
|
Austria and France
|
|
|
|
What are the native grapes of Friuli?
|
Tocai friulano
malvasia istriana ribolla gialla picolit (once a Hapsburg favorite for the sweet, Sauternes-like wine it produces). |
|
|
|
What are the international varieties of Friuli?
|
So-called “French” varieties such as: chardonnay
sauvignon blanc riesling gewürztraminer “the pinots”—bianco (blanc) and grigio (gris) |
|
|
|
What is the typical Friulian prototype wine?
|
crisp, bright wine with pure varietal character.
|
|
|
|
What is the name of the northern mountains in Friuli?
|
Carnic Alps
|
|
|
|
What is the name of the eastern mountains in Friuli?
|
Julian Alps
|
|
|
|
What geographical occurrences are key to Friulis white wine production?
|
cool Alpine breezes and warm Adriatic currents
|
|
|
|
3 wines in Northern Italy that are highlighted by the Nebbiolo grape?
|
BaroloBarbarescoLombardy’s Valtellina
|
|

