![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood is a Transport System and carries? |
O2, CO2, Nutrients, Hormones |
|
|
What part of the RBC carries the O2? |
Hemoglobin |
|
|
What part of blood carries components other than O2? |
Plasma |
|
|
What is the liquid portion of blood, including platelets and proteins, called? |
Plasma |
|
|
What is the liquid portion of blood, without platelets or proteins, called? |
Serum |
|
|
What are red blood cells called? |
Erythrocytes
|
|
|
What are white blood cells called?
|
Leukocytes
|
|
|
What are platelets called?
|
Thrombocytes
|
|
|
What is a sample that contains plasma and all other components?
|
Whole Blood
|
|
|
What is the main contributor to clotting? |
Platelets |
|
|
From top to bottom label the HCT Tube
|
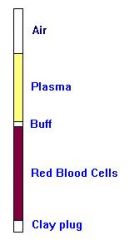
HCT Tube
|
|
|
What is Hematopoiesis and where does it occur? |
Production of all blood cells |
|
|
What is the process of RBC (Red Blood Cell) production called? |
Erythropoiesis |
|
|
When levels of O2 are low in the blood (Hypoxia) what hormone is produced to signal the bone marrow to produce RBCs? |
EPO - Erythropoietin
(Hormone) |
|
|
What is the shape of RBC - Erythrocytes? And Why?
|
Round, non-nucleated, biconcave disks. |
|
|
How many O2s can one hemoglobin carry? |
Each hemoglobin can carry 4 molecules of O2. |
|
|
What does most of the destruction of old or damaged cells? |
Macrophages
|
|
|
What is the color of blood? |
Normal hemoglobin is red in color.
|
|
|
What is the color of plasma?
|
Plasma is normally yellow.
|
|
|
What is a low number of circulating red blood cells called?
|
Anemia
|
|
|
What is an above normal increase in RBC concentration within blood called?
|
Polycythemia
|
|
|
What is the word used for the production of platelets?
|
Thrombopoiesis
|
|
|
Any nucleated cell normally found in blood is a?
|
WBC (White Blood Cell) |
|
|
What are the two main subtypes of white blood cells (leukocytes)?
|
Granulocytes |
|
|
What is the most common WBC in most mammals (infantry)? They have multi-lobed nuclei and the cytoplasm stains neutral color. |
Neutrophils |
|
|
What white blood cell type uses phagocytosis to engulf and digest bacteria that they come in contact with? |
Neutrophils, Monocytes/Macrophages |
|
|
This white blood cells are less than 5% of total WBC count. Associated with allergic reactions and parasite infections. They have a two-lobed nucleus and the cytoplasm stains pink. |
Eosinophils |
|
|
This WBC is the least common, contains histamine and heparin granules and is involved in allergic reactions. It has an irregular "blob" nucleus and the cytoplasm stains dark. |
Basophil |
|
|
What are the largest in size of WBCs and are a major phagocytic cell? They have a horseshoe shaped nucleus.
What do they become in the tissues? |
Monocytes
In the tissues they turn into macrophages
|
|
|
What is the one WBC that has no phagocytic capabilities, and has a large, circular nucleus?
What are the two types and what does each class do? |
Lymphocytes
B cells produce antibodies T cells fight pathogens by releasing chemicals
|
|
|
Different terms:
|
-cytosis - increased number of cell type. |

