![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A 3 week old newborn presents with vomitting.
What is your ddx? |
Newborn
OBSTRUCTIVE : Esophageal or intestinal stenosis/atresia, Pyloric stenosis, malrotation+/- volvulus, incarcerated hernia, meconium ileus/plug, Hirschprung, imperforated anus, enteric duplications NEURO: ICH/ICmass, hydrocephalus, cerebral edema, kernicterus RENAL : UTI, Obstructive uropathy, RI INFECTIOUS: Viral illness, Gastro, meningitis, sepsis METABOLIC : Inborn errors of metabolism, CAH MISC: Ileus, GERD, NEC, milk allergy, GI perforation. |
|
|
Name 5 causes of diarrhea in children that may result in significant morbidity
|
Infection : Salmonella gastroenteritis, Shigella, C. difficile (pseudomembranous colitis)
Anatomic abnormalities : Intussusception, Hirschsprung disease w toxic megacolon, partial obstruction, appendicits IBD w toxic megacolon HUS |
|
|
What triad caracterizes HUS?
|
Hemolytic microangiopathic anemia
Thrombocytopenia Renal Insufficiency |
|
|
What three clinical signs have been found to have significant positive LR for 5% dehydration?
Name 5 other signs which may be evaluated for dehydration in children? |
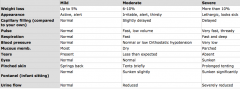
Prolonged capillary refill time
Abnormal skin turgor Abnormal respiratory pattern |
|
|
What are the indications for measuring serum electrolytes and glucose in chidren with gastroenteritis?
|
Moderately dehydrated children whose history and PE findings are incnsistent with acute gastroenteritis
All severely dehydrated chidren All children requiring IV rehydration, or those with potential hyper-or hyponatremia |
|
|
How does ORT (oral rehydration therapy) work?
Recette maison? What do we aim for ORT? |
ORT is based on the coupled transport of Na and glucose molecules at the brush border of intestinal epithelial cells, which provides a gradient for the passive absorption of water.
1 L eau + 4 c. à thé de sucre + 1/2 c. à thé de sel aim for about 30 cc / kg / h |
|
|
Is vomitting a contraindications to ORT?
|
NO.
Odansetron (serotonin R antagonist) may be used as an adjunct. 0.15 mg/kg / dose IV or PO Dopamine R agonists (metoclopramide) should not be used in children. |
|
|
When should antibiotc therapy should be considered for acute gastroenteritis?
What antibio? |
In patients with sx of invasive (inflammatory) infection : acute onset of bloody diarrhea w mucus and high fever.
Most common bacterial causes of this presentation : Shigella, Campylobacter, S. enterica Azithromycin is an appropriate 1st line agent (salmonelle, campylobacter). Ceftriaxone is the treatment of choice for parenteral therapy. |
|
|
For which bacterial causes of diarrhea are antibiotics not indicated?
|
Shiga-toxin-producing E.coli
- do not affect clinical course - possible increased risk of HUS Salmonella unless specific RF (underlying immune deficiencies, sickle cell, immunosuppressive, IBD, less 3 months old) Indicated : V. cholera, campylobacter, shigella |
|
|
Which probiotics strain have proven to be somewhat effictive in diarrheal illnesses?
|
Lactobacillus GG and Saccharomyces boulardii
Couteux. Doses importantes (donc yaourt n'est pas efficace). Contre indications : immunocompromis Diminution durée diarrhée de 24 heures. |
|
|
What antibiotics are most associated with C.difficile diarrhea?
|
Clindamycin
Cephalosporine Penicillins |
|
|
What is the leading cause of acute intestinal obstruction in infants?
|
Intussusception
Present 3 m - 12 months of age most commonly. (Pyloric stenosis appears 2wks - 8 wks of life and malrotation can present at an age but nearly all present in 1st wk of life, 2/3 within first months) |
|
|
Nommer 4 pathogènes de diarrhée sanglante et leur traitement
|
(SECSY)
Salmonella poulet mal cuit, produits laitiers non pasteurisés, mayonnaise, reptile (tortue) Shigella Day care, condition de mauvaise hygiène E. Coli Eau/bouffe contaminé par selles Campylobacter poulet, l'eau non traité, lait non pasteurisé Yersinia porc mal cuit, lait non pasteurisé, eau non |
|
|
Indications pour traitement de diarrhée
|
Indications pour traitement :
Majorité des patients non traités Patients immunocomprimés (sickle cell, immunosuppressive therapy, IBD, infants less 3 months old) Salmonella Typhi Patient malade +++ Jeune enfants Si rappelés une fois résultats obtenus et sx persistant |
|
|
Effet secondaires connu Zofran
|
Augmentation du QT
Si considère donner maintes doses : attention aux patients à risques Majorité des patients avec arythmies rapportés : patients sous chimie (plusieurs doses de zofran) |
|
|
Trois indications de traiter le RGO chez le nourrisson
|
''Failure to thrive''
Pneumonie d'aspiration, wheezing, ALTE Oesophagite Traitement : prokinétique (césaride) |
|
|
Pathophysiologie du volvulus, âge de présentation et la présentation clinique
|
At the 4 wk of gestation, the GI system is a straight tube centrally located in the abdomen. During the ensuing 8 wks, the midgut rotates and becomes fixed to the posterior abdominal wall. Arrest of development at any stage narrows the mesenteric base and impairs fixation, leaving the bowel at high risk for volvulus
âge = majorité dans le premier mois de vie Présentation = vomissement bileux (obstruction secondaire à volvulus ou bandes fibreuses) |
|
|
À quoi réfère le ''double bubble'' à la PSA?
|
Volvulus
Atrésie duodénale |
|
|
Réhydratation de maintenance?
Nouveau né vs plus âgé? |
moins qu'un mois
1/2 NS avec D5 Plus qu'un mois NS avec D5 |
|
|
What is the composition of different Crystalloids?normal saline (0.9% NS) =
½ normal saline (0.45% NS) = ⅔⅓ (⅔ D5W with ⅓ NS) = 0.2 normal saline (0.2% NS) = D5W = 5% dextrose sol’n = D10W = 10% dextrose sol’n = ⅔⅓ has ⅔ D5W = |
based on sodium concentration
normal saline (0.9% NS) = 154 mEq/L ½ normal saline (0.45% NS) = 77 mEq/L ⅔⅓ (⅔ D5W with ⅓ NS) = 51 mEq/L 0.2 normal saline (0.2% NS) = 34 mEq/L we can also add sugar to solutions D5W = 5% dextrose sol’n = 50 g/L D10W = 10% dextrose sol’n = 100 g/L ⅔⅓ has ⅔ D5W = 33 g/L |
|
|
A patient presents with characteristic purpura associated with HSP. What is the basic laboratory tests?
|
FSC
Coag Urine Analysis |

