![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
203 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
reversible loss of contractile function and works afterrevascularization
|
Myocardial stunning <30mins of ischemia,
hibernating myocardium is chronic or repeatitive stunning- sufficient ATP prevents contracture. There may be increased gene expression of TNF-alpha, NOS, decreased beta adrenergic receptor density, ca and excitation coupling defects might be the cause resulting from low perfusion. |
|
|
where do you see Pulsusparadoxus and what is it?
|
difference of > 10mmHg during inspiration and expiration= pericarditis, COPD, cardiac tamponade, restrictive cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
Funnysensation
|
1. palpitation=AF=absence P-wave (holiday heart syndrome-alcohol consumption) |
|
|
what controls ventricular rate in AF-RVR and what is the cause? |
1. AF-RVR,caused by pulmonary veins, lead to re-entrant pulses. Ventricles contractsbased on the AV nodal refractory period based on pulses that get toit…ventricular rate = 90-170 in AF |
|
|
treatment of AF-RVRwith PEA-no Pulse, ECG normal or Abnormal |
cardiaccompression30*1 breath
|
|
|
12 Causes of AF-RVR with PEA
|
Hypovolemia,hypoxia, hydrogen ions, hyperkalemia, hypokalemia, hypothermia Tabletsor toxins, tamponade, tension pneumothorax, trauma-hypovolemia,thrombosis-myocardial and pulmonary emboli
|
|
|
treatment of Afibwith WPW |
Class 1a=quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide or Class 3-reverseuse-dependent-slower HR, the more prolonged QT Digoxin and CCB-decresase A-V, are CI,lidocaine is not used except in digoxin induced Arrythmia |
|
|
Afibwith hemodynamic instability (unstable tachyarrhythmia >100) or stable of more than 48hrs and no anticoagulant therapy?
|
cardioversion- echocardiography first to rule out thrombus then 120-200J is the appropriate voltage
Initial recommended doses:-narrow regular: 50-100 J-Narrow irregular: 120-200 J biphasic or 200 J monophasic-Wide regular: 100 J-Wide irregular: defibrillation dose (not synchronized) |
|
|
CHF+ Afib
|
ACEI+ Digoxin (hyperkalemia=dose), or with carvedilol, metoprolol
|
|
|
Afib-RVRalone-ratecontrol
|
BB,CCB
|
|
|
SVT
|
Adenosine,flecainide-rate-use-dependent-inc HR, inc NAblocking, prolong QRS
|
|
|
SE of Nitrate vs niacin |
1. Nitrates SEheadache and flushing, Niacin flushing and hyperglycemia |
|
|
1. Isolatedsystolic HTN treatment= |
dihydropyridine CaB…amlodipine SE flushing and peripheral edema. Together with thiazides are first line for this treatment but ACE is first line if DM
|
|
|
MCC of death in MI
|
left ventricular cardiogenicshock
|
|
|
cause of death in hospitalised pateints with MI with 7 days |
hypovolemic(due to cardiac temponade after 3- 7days of transmural MI)
|
|
|
why are newer drugs for MI made to use glucose oxidation? |
1. Chronicstable angina requires that oxygen consumption should be equal to demand.Usually, myocardiocytes use fatty oxidation which produces more ATP but usesmore oxygen for energy. Newer drugsunder investigation is to shut off fatty oxidation and switch to glucoseoxidation. |
|
|
heardbetween the closure of aortic (S2)valve and opening snap of mitral (S1)valve.
|
Mitral stenosis
Prior Rh. Carditis is MCC |
|
|
Ergonovine
|
causesvasospasm, when given in low dose,it provokes prinzmental angina(nocturnal pain at rest, episodic andtransient). Best test for prinzmental.
|
|
|
usedas stent eluding drug to preventintimal hyperplasia after percutenous coronary intervention.
|
Paclitaxel and sirolimus are antineoplastic at M phase that prevent microtubulebreakdown.
|
|
|
contractilityand conduction
|
Beta-blockers
|
|
|
afterload(arterioles) = dihydropyridines DecreaseHR = verapamil
|
Cachannel
|
|
|
preloadand afterload-at high dose
|
Nitrates
|
|
|
blood flow equilibrium Duringexercise,
|
theheart tries to supply enough blood to muscles and brain. Increase preload and decreaseafter load (TPR is decreased, therefore end systolic volume is decreased-all blood is out at end systole). Increase HR and CO (HR and SV=preload andafterload)
|
|
|
Suddentearing chest pain with wide aorticcontour on x-ray
|
aortic dissection or aneurysm ifpatient history include HTN and marfan syndrome, EDS-cystic mediadegeneration (ascending aorta) decending aorta-artherosclerosis…ddx pneumothoraxby absent lung markings
|
|
|
Rectalblood supply
|
superior rectal artery from inferior mesenteric artery and same vein to portal vein (metastasisto liver ) middle – internal iliac and common iliac vein, inferior – internal pudendal artry andvein to internal iliac ( metastasis to lungs)
|
|
|
P wave-PRQRSSTTwave |
1. P wave- atrialdepolarization Na influx, PR is AV node conductance, QRS-ventriculardepolarization NA influx and Ca, ST is plateau phase of Ca influx, Twave is K efflux and ventricularrepolarization |
|
|
Tet spells - CASTS
|
Cyanosis, agitation, syncope, tachycardia, seizures and possibly death) is hypercyanotic episodes in TOf-failure of neural crest migration in primitive arteriosus and bulbus cordis-harshsystolic murmur.
Rx squatting/ knee chest prone position, O2 & morphine and IV infusion |
|
|
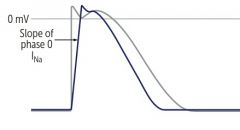
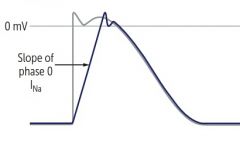
Differencebetween SA and Ventricular AP
|
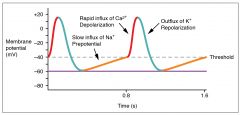
SA isdepolarized at phase 0 by influx of Ca,while Ventricular is influx of Na…having 4 phases
|
|
|
pathology leading to ASDVSDTOF, great vessles, persistent t arteriosus. |
1. ASD-foramensecundum. VSD-membranous septum,malrotation of Truncus arteriosus-TOF, great vessles, persistent t arteriosus.Valve-A/P-outflow tract, T/M fused endocardial cushion of AV canal-ebstein anomaly by Li |
|
|
hematopietic organs from embryology |
1. Young Liver Synthesizes Blood=yolk sac,liver-till birth, spleen-28wks, bone marrow-adult |
|
|
fetal circulation |
1. DuctusV-bypasshepatic circulation, IVC highest o2,PDA-open(low O2, inc pulm VRes) closed-breath& placenta separation-decprostaglandin E1 &E2 (KEEP PDA open) end with endomethacin |
|
|
Umbilical A and Umb vain-becomes |
1. Umbilical A-medial umb Lig, Umb vain-teres hepatis in falciform lig. |
|
|
most posterior,
Most ant, most lateral |
most posterior=LA,
Mostant=RV most lat=LV |
|
|
CO=
|
1. CO=HR (SA action potential) * SV (ventricularAP) |
|
|
NormalEDV(LO)=
|
120-140…increaseof this shows diastolic heart failure
|
|
|
DigoxinMOA is by
|
blocking Na/K pump, inhibits the passive influx of Na at Na/Capump which prevent secondary active transport efflux of Ca, increasingCa accumulation in cell, binds to troponin and release troponinmyosin bond,allowing actin to bind to myosin and cause contraction.
|
|
|
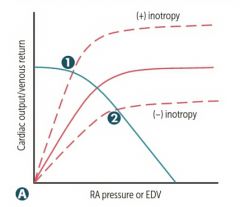
Positiveinotrophs increases
|
diastolicinterval (coronary flow increases) which also increase filling of heart, narrowsystolic interval(decrease O2 demand), increase contraction pressure and peak
|
|
|

1 |
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
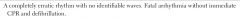
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
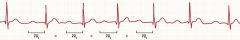
|
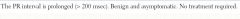
|
|

|

|
|
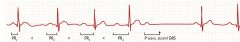
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
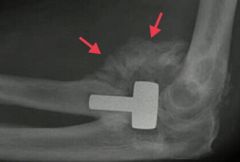
|

|
|
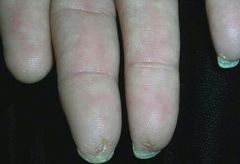
|
|
|
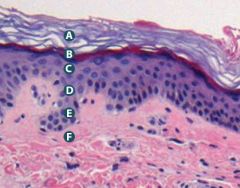
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CO is determined mostly by
|
stroke volume SV.
|
|
|
Diastolicdysfunction-
|
Diastolic dysfunction-concentric hypertrophy -decrease filling & venous return-syncope hypertrophic cardiomyopathy S4 Hereditary hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, African America, AD with multifactorial cause, mutation in beta myosin heavy chain protein leading to defect in the myofilament protiens and disordered arrangement. Friedrick ataxia-hypertrophy of heart mutationof frataxin gene, GAA Genetic AtaxiA Decrease preload or afterload due to LV wall rigidity, sudden standing, valsava, nitroglycerin, decrease chamber and separation b/w septum and mitral valve (systolic ant motion) ->increase intensity of murmur at left sternal boarder of mcburny point…decrescendo-cresendo after S1 increase total peripheral resistance, supine, squatting, handgrip, leg raising, phenylephrine, increase preload and afterload (HTN), obstruction (Aortic stenosis) -> decrease murmur Restrictive cardiomyopathy- decrease ventricular compliance
|
|
|
Systolicdysfunction
|
leadto increase volume overload, eccentric hypertrophy-Dilated cardiomyopathyS3-increase EDV -ABCCCDHemochromatosisPreg Mitral and Aortic regurgitation
|
|
|
Bruit in costovertebral angle, right renl artery most affected. Resistant toACE/ARB, with inc creatinine
|
Fibromusculardysplasia
MCC of HTN inchildren & premenopause female |
|
|
Nobruits, only episodic headache, palpitation & sweating
|
pheochro
|
|
|
HTNof upper limb, Late systolic murmur heard at the back, rib notching, weak lower pulse, occurs distal to subclavian
|
Coarctation
|
|
|
Segmental proximal artery, bruit at left renal, old patients
|
Renalartery sclera
|
|
|
Aldosterone-secretingadenoma, bilateral adrenal hyperplasia,old patient. HTN & hypokalemia
|
Conn’ssydrome
|
|
|
Stridorwith Barky cough, MC-6months-6 yrs, fever, rhinorrhea and congestion
|
Croup-laryngotracheo-bronchitis
|
|
|
Severestridor at 4-8months-worsens in supine and improves onprone/upright position
|
Laryngomalacia-laxityof supraglottic structures that collapse on inspiration
|
|
|
Stridor, acute onset, resp distress
|
Foreignbody-cough with monophonic wheezing
|
|
|
StridorBefore one year improves only with neck extension, cardiacanormalies.
|
Vascularring or slings-complete circling of trac. Or esophagus or both, common in rightsided or double aortic arch, pulmonary sling, anomalous left carotid orinnominate artery
|
|
|
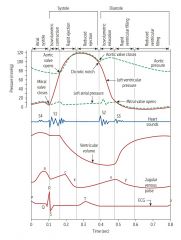
1. (depolarization and contraction ofventricles) |
P wave coincides with ventricular filling diastole, while QRS coincides with systole
|
|
|
1. Valvular event…R wave=, Twave= |
R wave=mitral valve closure, T wave=Aortic valve closure
|
|
|
EKG Event Valvular event Sound P Atrial depo PR AVN conduction
QRS Vent depo QT or ST Ejection phase
T Vent repolarization |
EKG Event Valvular event Sound P Atrial depo MO S3, S4 PR AVN conduction
QRS Vent depo MC, S1 QT or ST Ejection phase AO
T Vent repolarization AC S2 |
|
|
Fixed splitting is
|
1. ASD…L-R shunt…FiSD |
|
|
Widening of the split
|
1. - RBBB, pulmonic stenosis-WilliM-V1=W,V6=M |
|
|
PARadoxical split
|
1. – LBBB, Aortic stenosis-MorroM |
|
|
S3
|
1. early diastole normal in pregnant women,children and young adult |
|
|
S4
|
1. in late diastole before S1…stiffening and infarction |
|
|
awave
|
atrialcontraction (Pwave),
|
|
|
cwave
|
a. bulging of TR valve which is abnormal in somepeople( during ventricular contraction) |
|
|
xdescent
|
initialfilling of atrium, (absent in Atrial Fibrilation, and TR stenosis though X ispresent but less)
|
|
|
Vwave
|
atrial filling with vent systole…close of TRvalve (elevated in TR regurgitation |
|
|
Ywave
|
ventricular filling |
|
|
Highest work of heart is at
|
1. ejection with high pressure and volume |
|
|
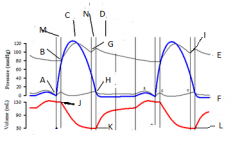
A-V shunting
|
1. increase preload…curve shiftsoutward, increase EDV |
|
|
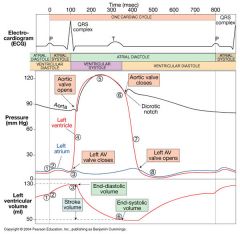
|
|
|
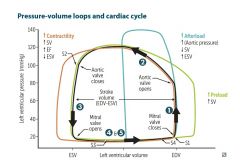
gradient difference between aortic and ventricular curves= |
ventricular aortic 80-120 120 If ventricular peak pressure increases, it is aortic pathology. If there is gradient difference between the aortic and ventricle, it is AORTIC STENOSIS...Cresendo-decresendo murmur of S2, if there is no gradient, it is AORTIC INSUFFICIENCY….decrecendo murmur |
|
|
what to suspect if ventricular curve is normal? |
atrial 15 If no increase in ventricular pressure, check atrial pressure…if more than 15, check where the increase is, in diastoles?…it is MITRAL STENOSIS….late diastole mid to late murmur, heard best at lateral decubitis position, hemoptysis from LVF, MCC is RF, if at systole, INSUFFICIENCY at systole |
|
|
Crescendo-decresendo, ASD- angina, syncope, dyspnea. Calcification Wear & tear, systolic ejection click, MHA |
AS
|
|
|
Opening Snap, RF, AF, lateral decubitis position louder, Hemoptysis Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia-schistiocytes |
MS
RX dec preload-diuretics and nitrates |
|
|
Decrescendo blowing-highpitch murmur, widenedpulse pressure (systolic-diastolic)-head bobbing,-RF, BiValv,endocarditis
|
AR
|
|
|
Holosystolic-high pitch-blowing, post MI, MVP, LV dilationat mitral area or tri area RV dilation
|
MR/TR
|
|
|
Harsh-holosystolicat Tr area
|
VSD
|
|
|
Crescendomidsystolic click-chordaetendinae-at apex-marfan, EDS, RF,myxomatous deg, endocarditis
|
MVP
|
|
|
Machine-like-S2, rubella, congenital
|
PDA
|
|
|
pre-excitationof ventricles-delta wave, widened QRS-> SVT
|
WPWsyndrome
|
|
|
drugs that cause torsades |
1. Some Risky Med Can Prolong QT-sotalol, risperidone, macrolide, chloroquine, proteaseinhibitors, quinidine, thiazides-or ABCDE–antiArrhythmics-(class 1A, 3), antiBiotics-(macrolides), antiCychotics-(haloperidol), antiDepressents-(TCA) antiEmetics-(ondansetron) treat with Mg |
|
|
cause of sudden cardiac death by torsades in infant before 1 year |
congenitaltorsades de pointes-romano ward syndrome (no deafness)jarvell&lange-nielsen syndrome-sensorineural deafness
|
|
|
cause of sudden cardiac death by RBBB |
1. Brugadasynd- Asian SCD by RBBB-ST elevation |
|
|
AFib most important causes
|
1. holiday heart-binge drinking, CAD, HTN Vfib-fatal, 3rdBB-lime disease |
|
|
goodNPV for dx HF |
ANP-atrial. BNP-ventricles-goodNPV for dx HF, Nesiritide=BNP |
|
|
jawclaudication>50yrs
|
Giant cell-Temporal arteritis
|
|
|
(jointand proximal muscle pain), blindness..treatwith steroids….ESR increase,
|
POLYmyalgia rheumatica
|
|
|
Asianfemale with pulsless artries, weakupper extremities due to granulomatousthickening of mediaof aortic arch-coronary, renal…treat withsteroids…ESR increase, 40yrs <
|
Takayasu
|
|
|
PAN-polyarteritis nodosa
|
all organs except lung vs Wegener(granulomatous polyangitis), PAN is associated with IV drug abuser, Hep B, melena due to GI bleed, fibrinoid necrosis is Type 3 hypersensitivity…steroids
|
|
|
children less than 4yrs, strawberry tongue with lymphadenitis, fever and conjunctival injection…coronary artery aneurysm with MI and rupture…treat…immunoglobulin, aspirin
|
Kawasaki…
|
|
|
smokers,Raynaud phenomenon, segmental thrombosing vasculitis…treat…stop smoking…segmentalvasculitis extending to veins, artriesand nerves
|
Buerger (thromboangitis obliterans)---
|
|
|
RPGNinvolves kidney and lungs, P-anca, sinusitis, treat cyclophosphamide.
|
Granulomatous polyangiitis (wegener)-
microscopic polyangitis-without nasopharyngeal involvemnt |
|
|
Focal necrotizing granulomas due to HCV and complements, drusen deposits…
|
crecent kidney-MPGN-tram track
|
|
|
without nasopharyngealinvolvement…no granulomas, P-anca, MPO-anca…treat cyclophosphamide
|
Microscopic polyangiitis
|
|
|
1. asthma,sinusitis, palpable purpura…increase igE…P-anca, MPO-anca |
Churg-strausssyndrome
|
|
|
secondaryto igA complex, URI, palpable purpura on buttocks, multiple lesions on legs
|
Henoch-schonleinpurpura
lesions buttocks down is schonlein! |
|
|
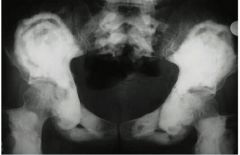
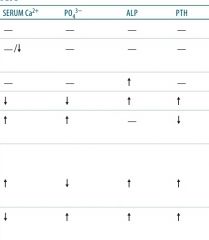
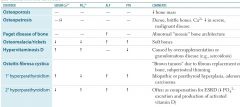
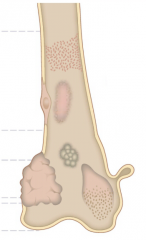
symptom of mockenberg medial calcification
|
1. mockenberg medial calcification, is without symptom. seen accidentally on x-ray |
|
|
Arteriosclerosiswith is hyalization of arterioles, lead to stenonsis…in
|
DMor benign HTN
|
|
|
steps in atherosclerosis |
2. Injury, then macrophage and oxLDL accumulate,then foam cell, fatty streak, smooth muscle by PDGF, FGF, extracellular metrix,then fibrous capsule and complex plaque Atherosclerosis, oxLDL and lipid in intima of blood vessel, diet and exercise can reverse it….once you get fibrosis, with the appearance of cap, it becomes permanent |
|
|
morethan 120mm/hg. Onion skin( due to hyperplasia of endothelium), flea bittenkidney due to compression and ischemia..papiledema…
|
MalignantHTN
|
|
|
below renal artries for AAA-intimal streak atherosclerosis =abdo, coro, popli, carotid
|
Abdominalaortic Aneurysm
|
|
|
cysticmedial degeneration, marfansyndrome and elderly with HTN, back pain, complicated by tamponade, enlarge mediastinum,
|
ThoracicAortic aneurysm
|
|
|
atroot of aorta, tree barking, obliterativeendarteritis, vasa-vasorum,stenosis of coronary artery, cor bovinus…due to enlarged heart, aortic dilation
|
Syphiliticaneurysm-thoracic
|
|
|
1. treatment of Aortic dissection(diff. BP in arms) typeA=ascending-, type B=descending- |
type A=ascending-surgery
type B=descending-venodilators,BB |
|
|
high output cardiac failure in A-V malformation is due to |
1. A-V malformation associated with padgetdisease…high output cardiac failure due to new blood vessel formation |
|
|
problem with Varicoseveins
|
Weak valves and stasis leading to ulceration of skin. superficial location, no Pulmonary emboli.
|
|
|
triad ofhip, thigh and buttock claudication,symmetric atrophy of bilateral lowerlimb, and impotence due to ischemic-smoking
|
Aortoiliac occlucion-leriche syndrome-
|
|
|
postsurgical pus accumulation in mediastinum. Rx-drainage, surgical debridement andantibiotics
|
Acutemediastinitis
|
|
|
Hemangiomas usually in infants and regress, occur on skins and internal organs
|
strawberry for children, cherry for adult
|
|
|
Glomustumor
|
forthermoregulation under nails
|
|
|
Hemagioblastoma associated with
|
VHL…cerebral and retina and RCC
|
|
|
Kaposisarcoma HHV8 can lead to what on RBC
|
extravasation of RBC
|
|
|
vinylchloride
|
1. Angiosarcoma of liver…vinyl chloride(hemangiosarcoma) |
|
|
Bacillaryangiomatosis
|
1. Bacillary angiomatosis (Bartonella hensae) |
|
|
ECG of MI
|
transmuralis st elevation q wave no R, endocardial is st depression
|
|
|
Lab for MI |
1. LDH enzymes peaks late…if elevated, MI is morethan a week, Troponin is within 4hrs to 7 days, best for diagnosis, CK-MB returns to normalearliest by 2 days if seen at next lab, then a recurance might have occured |
|
|
stages of cardiac repair due to ischemia |
1. Wavy and contraction band—4 hrs, coagulation- 1day, neutrophil –days, macrophage-7days, granulation tissue-28days, scar-months |
|
|
Sudden cardiac death is due to
|
1. Sudden cardiac death is due to Ventricularfibrillation
|
|
|
differentiation of acute and chronic heart failure with pleural fluid |
1. acute is only transudate Left heart congestive heart failure…hemosiderin–laden macrophages (heart failure cells) may lead to cardiogenic shock |
|
|
MCC of Rightheart failure
|
isLHF, pulmonary HTN, TR stenosis…lead to nutmeg liver(passive congestion inliver) ascites, pleura and peritoneal transudate
|
|
|
Aorticcalcification
|
stenosis,syncope, Bicuspid valve,…treat by valve replacement, old
|
|
|
Mitralvalve prolapse
|
Marfan syndrome…weak valve the parachutes are balloons into LA…Myxomatous degeneration…complication rupture of chordae tendinea. Palpitation
|
|
|
nonbacterialthrombotic bacteria…steril vegetation due to hypercoagulable state as a result of a cancer somewhere,. the vegetations line up at the closure of thevalve. SLE both surface of valve
|
Maranticendocarditis
|
|
|
Staph auraus –acute (highvegetations), subacute- strept viridans(small vegetations-fibrin platelets),bacteria FROM JANE fever, Roth spots,osler nodes,murmur, janeway lesions, anemia, nail-splincter hemorrhage, emboli,PE, papillary rupture
|
Infectiveendocarditis
|
|
|
RhFever
|
GAS-Mprotein IgM-mimicry type 2 hyperS, aschoff bodies-granuloma-anittschkow-macrophagewith rod-like nucleus with worst prognosis…fish mouth appearance of chronicRF in adult, JONES fever- joints( migratory polyarthritis), Oardaitis subcutaneous nodules, erythema marginatum, valvulardamage…thin vegetation, ESR, red and Sydenhamchorea….increase Antistrptolysin O….PX benzathine penicillin G IMevery 4 weeks for 5yrs/21yrs-if without carditis, 10/21 with carditis but nosymp, 10/40 with carditis and symptoms
|
|
|
Cholesterolemboli-
|
cardiac catheterization/DM-2/HTN/hypercholesterolemia-stroke, amaurosisfugax, hollenhorst plaques, intestinal ischemia and pancreatitis, livedoreticularis-blanches on pressure and blue toes, kidney injury. Dx-eosinphilia/eosinophiluria, elevatedserum creatinine, dec complement
|
|
|
HTNin pregnancy
|
1. HTN in pregnancy-Methyldopa, labetalol, hydralazine,nifedipine. Thiazides and clonidine as 2nd line. CI ACE, ARB, aldosterone blockers, direct renin blockers,furosemide. Volume depletion should be avoided in pregnancy |
|
|
causes of Congenitalheart diseas
|
Rubella,alcohol, drugs, idiopathic
|
|
|
Dilatedcardiomyopathy
|
1. Dilated cardiomyopathy…systolic dysfunction a. ABCCCD…alcohol, Ber1Ber1wet, Coxsakie B,Cocaine, Chagas, Doxorubicin. b. Ejection fraction is less than 50 |
|
|
Hypertrophycardiomyopathy
|
1. Hypertrophy cardiomyopathy… sudden death…dytolic dysfunction-obstruction by septal and forward motion of mitralvalve a. B-myosinheavy-chain mutation, Myofibrillar disarray b. Friedreich ataxia
|
|
|
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
|
1. dystolic dysfunction-deposits-amyloid,hemochromatosis, sarcoidosis,Loffler-eosinophilia with fibrosis |
|
|
Carcinoid tumor
|
1. …right side of theheart….flushing of face |
|
|
Multiple syncopies with esophageal obstruction
|
1. Cardiac myxoma…Adult a. Ball valve from lymphoma or melanoma b. LA, can obstructesophagus c. Multiple syncopies
|
|
|
Rhabdomyoma in children
|
1. ….spider shape,associated with tuberous sclerosis |
|
|
. B1 is SAN, M2 is PANS in the heart…
|
1 a. B1 is GS---activates cAMP, PKa andphosphorylates NA,K,Ca, opening NA, Ca and closing K…this increase rate ofdepolarization and HR, b. while M2 is Gi, decrease cAMP, opens K andcloses Na and Ca…bradycardia |
|
|
fast vs slow response fibers in CVS |
1. Fast response fibers are ventricular cell and nodalcells are slow response |
|
|
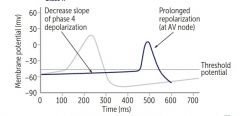
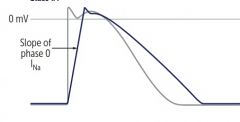
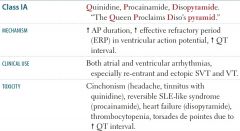
a. Quinidine |
i. Has antimuscarinic effect like atropine-increaseHR…Torsades ii. Alpha blocker cause hypotension iii. Cinnconism due to both effect…GI, Tinnitus,Ocular dysfunction,QRS and QT prolongation…Tosardes, when all wave look likeQRS iv. Give digitalis to slow AV and avoid arrhythmia before givingquinidine
|
|
|
a. Procainamide
|
i. ismetabolized by N-acetyltransferase ii. SLE due to being a hapten and in slowacetylators iii. Hematotoxicity…monitor CBC |
|
|
Disopyramide SE
|
heartfailure
|
|
|
1. Class 1B |
Lidocaine and mexiletine phenytoin Decrease conduction at hypoxic tissue, APD dueto blocking slow Na conduction b. Used in Ventricular fibrillation PostMI and digoxin toxicity |
|
|
Flecanide
|
1. Class 1C has no effect on APD prolong ERP on AV node but not purkinje and ventricular cells a. Flecanide…proarrythmic |
|
|
site of action of class 2 drugs |
1. Class 2…Beta blocker…acts on phase 4 nodal cell not ventricular,increase PR and effect of PANS, bradycardia….nonselective ispropranolol….selective…esmolol and atenolol a. Metoprolol; decrease mortality, but cause dyslipidemia
|
|
|
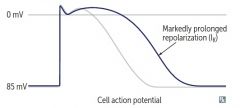
MOA of Class 3 |
1. Class 3…blocks K on vent AP……Amiodarone andSoltalol a. Increase APD and ERF, QT b. Amiodaroneis 40% iodine, binds with other protein, accumulates in lungs lead to pulmonaryfibrosis and decrease TLC, with normalor increased FEV1/FVC ratio in restrictive lung disease c. Thyroiddysfunction…could be hyper or hypo d. Corneal deposit and skin (blue pigmentation smurf skin)due to accumulation e. Soltalol…ventricular arrhythmia…excess Bblocking lead to Torsades |
|
|
site of action of Class4
|
1. block Ca channel in SA and AV node not ventricle, increase PRand ERP a. Verapamil and diltiazem SE-constipation, flushing, edema, cardiovascular effects-HF, AV block, sinus node depression |
|
|
Adenosine
|
1. Adenosinevasodilation -acts on Gi-coupleddecrease in cAMP, increase K efflux like M2 receptors a. DOC for SVT since it acts on AV node b. SE…flushing and sedation, Dyspnea (Gq coupledbronchospasm) c. Shorthalflife of less than 10sec..DOC for paroxysmalSVT d. When patient have COPD, theophylline (can causeVTach with other xathines like caffeine cause palpitation) will antagonizeAdenosine |
|
|
Magnesium is used for
|
1. Tosardes
|
|
|
Any drug that decrease K efflux will cause
|
1. Tosardes…antimuscarinic, B1 agonist, TCAs, antipsychotics thioridazine,potassium-channel blockers |
|
|
noreflex tachycardia with drugs working in SANS…like
|
1. no reflex tachycardia with drugs working inSANS…like Beta blockers a. but they may have orthostatic hypotension(change by 20mmhg systolic, or 10mmhg diastolic can be due to decbaroreceptor firing, dec NE, or arterial stiffness inold age or dec sensitivity of myocardium to SANs) due to SANS alphaactivity i. dopaminehydroxylase deficiency can lead to same clinical picture due to the factthat NE will not be produced…remember that phenylalanine hydroxylase togetherwith tetradihydrobiopterin( deficient in PKU) convert pHe to tyrosine which isin turn hydrolysed ( tyrosine hydroxylase) to DOPA then converted by dopamine decarboxylase( inhibited bycarbidopa) with pyridoxine to dopamine then by dopamine hydroxylase to NEwith vit C from which PNMT converts NE to epinephrine b. increase PANS, leading to increase secretion andGI motility |
|
|
alpha2 MOA
|
1. alpha2 stimulate Gi, inhibiting presynaptic NE,which inhibit alpha1 and B1 a. clonidine and methyldopa b. decrease TPR and HR c. methyldopa high protein binding leads to positive coombs test d. methyldopa cannotcross BBB or PB due its high proteinbinding e. they both cause Edema due to RAA (renin angiotensinaldosterone) f. both cause CNS depression g. remember TCAinhibit reuptake of NE therefore decrease antihypertensive effect of alpha 2agonists
|
|
|
Effect of reserpine |
1. Riserpine destroys neurotransmitters, DA,NE, etcand lead to severe depression |
|
|
can Guanethidine be given with TCA? |
1. Guanethidinecannot be given with TCAs because it blocks the site of reuptake of NE anddestroys the NE vesicles… |
|
|
Selective Alpha1 blockers
|
1. SelectiveAlpha1 blockers….zosin…prazosin, doxazosin, terazosin a. Will cause reflextachycardia and orthostatic hypotension b. First dose syncope c. Used in BPH to dilate the bladder sphincter…symptomatictreatment |
|
|
common side effect of |
1. Sexual dysfunction is seen in all SANs inhibitors or NEinhibitors due to the rousing effect
|
|
|
B blockers do not cause reflexive tachycardia, it also decrease
|
1. RAA by inhibitingrenin production, |
|
|
1. Hydralazine increase cGMP through |
NO, vasodilates arteries, has SLE effect used in pregnancy
|
|
|
1. Nitroprussidedilates |
both arteries and venules, a. DOC in HTN emergencies b. Co-administer with nitrates which has high affinity for hb, forming Met hb, while thiosulfate will bind cyanide and elimante it |
|
|
1. ATP dependent K channels opening… |
will dilate arterioles, and drug induced diabetes a. Minoxidil (hypertrichosis) and diazoxide ( hyperglycemia to reduce insulin tumor) |
|
|
Fenoldopam MOA
|
1. DA1 agonist decrease BP andincrease Natiuresis
|
|
|
Dihydropyridine L-type Ca blockers
|
1. ..nifedipineand all the pines, cause vasodilation |
|
|
Aliskiren
|
1. is anti-Renin and B blockers don’t block the enzyme but decrease secretion |
|
|
1. Inotropes are beneficial for acute CHF…thecontractile effect through RAS kinase pathway may lead to cardiac remodeling…what drugs are under this group and can prevent remodelling |
drugs like spironolactone, carvedilol, labetalol, metoprolol, acei, arbs
|
|
|
Use Bosetan for
|
1. pulmonary hypertension which inhibit ETA in endothelium that cause vasoconstriction on pulmonary vessels, |

