![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 year-old male
Difficulty walking Frequent respiratory infections High rate of radiation-induced genetic mutations in cultured cells Diagnosis Pathophys |
Ataxia-telangiectasia (AR disorder)
Cerebellar atrophy leads to ataxia in first years of life Oculocutaneous telangiectasia is another manifestations, but is usually delayed Pts with ataxia-telangiectasia also have severe immunodeficiency with REPEATED sinopulmonary infections. Risk of CANCER is elevated because of INEFFICIENT DNA REPAIR. High rate of radiation-induced genetic mutation due to DNA hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation (UV). |
|
|
What causes proptosis in Graves' Disease?
Treatment? |
Infiltrative ophthalmopathy characterized by edema and infiltration of lymphocytes and macrophages into extraocular muscles and connective tissue. Eventually inflammation becomes fibrosis, which restricts extraocular movements, causing diplopia.
Treated with high dose glucocorticoids to inhibit inflammatory infiltration. Remember that conventional antithyroid drugs do not improve ophthalmopathy. |
|
|
What Vitamin D reaction is catalyzed by exposure to sunlight?
|
7-dehydrocholesterol-->Cholecalciferol
|
|
|
Hemochromatosis:
Pathophys Risks |
Mutation of HFE gene (AR inheritance)
HFE expressed on basolateral surface of intestinal epithelium It binds to transferrin receptor to regulate endocytosis of transferrin/iron complex into cells If individual has mutatn HFE tha tis unable to detect circulating iron levels, there will be unregulated expression of iron uptake proteins This will lead to excessive amount of iron absorbed by the GI tract, causing an iron overload Liver cirrhosis and HCC are complications |
|
|
Most common cause of asceptic meningitis.
|
Enteroviruses: Coxsackie, echo, polio, entero--responsible for over 90% of cases
|
|
|
Outline the steps of the MAP-kinase signaling cascade.
|
Growth factor binds receptor tyrosine kinase
Receptor is AUTO-PHOSPHORYLATED Leads to Ras activation (a G protein that when activated is bound to GTP) Activated Ras activates kinase which active MAP kinase (MITOGEN-ACTIVATED PROTEIN) Note that mutated (permanently activated) Ras is assocd w/devt of malignant tumors. |
|
|
45 year-old male
HIV positive Bronchoscopy for cough, chest pain Mucicarmine stain reveals budding yeast forms with thick capsules Diagnosis |
Cryptococcus neoformans--commonly manifests as CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS
|
|
|
7 year-old male
Stung by a bee and developed generalized urticaria that required hospitalization Later developed a puffy face and now reports foamy urine 4.5 g protein/day lost in urine Diagnosis Pathophys Treatment |
Facial edema with massive protein loss = Nephrotic syndrome--most common cause if minimal change disease (also called lipoid nephrosis)
May be a/w resp infections, immunization, or atopic disorders Light microscopy will show normal glomeruli Immunofluorescence will NOT reveal immunoglobulin or complement deposits EM will show DIFFUSE EFFACEMENT of foot processes of podocytes ("fusion of foot processes) Important feature is RAPID response to corticosteroid treatment |
|
|
79 year-old male
Visual abnormalities, nausea, anorexia History of atrial fibrillation Receives weight-adjusted dose of digoxin Pathophys of symptoms |
Digoxin is renally cleared with a half-life of approximately 1.5 days in pts w/normal kidney fn.
As pts age, renal function decreases progressively. This decrease is often not accompanied by rise in serum Cr (since Cr is derived form muscle tissue and lean body mass also decreases with age) Thus, all elderly patients should receive reduced doses of renally cleared medications to prevent toxicity. |
|
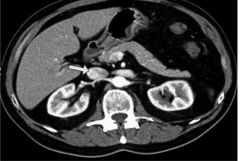
Label structures.
|
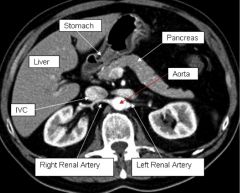
|
|
|
34 year-old male
Recently diagnosed membranous glomerulopathy Develops sudden onset flank pain and gross hematuria Left-sided varicocele Urinarlysis reveals increased proteinuria Pathophys |
Membranous glomerulopathy is a common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults
Inc'd permeability of glomerular capillary wall in nephrotic syndrome causes proteins to be peed out Loss of anticoagulant factors, esp. AT III is responsible for thrombotic and thromboembolic complications of nephrotic syndrome. Renal vein thrombosis can be a manifestation of hypercoagulable state. Sudden onset abdominal or flank pain and gross hematuria due to renal vein thrombosis on left side-->obstruction in male patients impedes venous flow from left testis, and results in left-sided varicocele |
|
|
What congenital aortic morphology results in accelerated onset of calcific stenosis?
|
Congenital bicuspid aortic valve
|
|
|
Which drug class prolongs Thrombin Time?
|
Drugs that directly inhibit thrombin (which is Factor II btw): argatroban, dabigatran
|
|
|
Describe the change induced by stimulation (cAMP/DAG/IP3 levels) of adrenergic receptors by Norepinephrine.
Include the clinical effect seen. |
Remember: NE is an adrenergic agonist that affects predominantly alpha, and beta-1, little influence on beta-2
alpha-1: inc'd IP3, peripheral vasoconstriction alpha-2: dec'd cAMP, dec'd release of NE, insulin beta-1: inc'd cAMP, inc'd contractility beta-2: inc'd cAMP, bronchodilation, vasodilation*** Note that NE's direct effect on heart rate (positive chronotropic) is counteracted by an indirect, baroreceptor-mediated reflex bradycardia that occurs following increase in peripheral resistance. Result is heart rate remains unchanged or even decreases. |
|
|
Retinoblastoma:
Hypo vs Hyperphosphorylation Associated cancers |
Hypophosphorylated = active (does not allow G1-->S progression)
Hyperphosphorylated = inactive Hyperphosphorylating mutations linked to retinioblastoma and osteosarcoma |
|
|
What vitamin is useful in treating measles?
|
Vitamin A--also reduces time to recovery from pneumonia, diarrhea
|
|
|
Burr cells are a sign of ______.
|
Mechanical trauma to RBCs
|
|
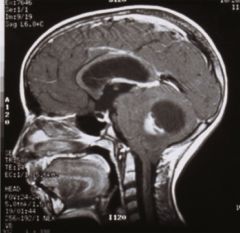
12 year-old male
|
Pilocytic astrocytoma--low grade neoplasm arising from astroycytes
(can also develop in cerebral hemispheres) Neoplasm is cystic with tumor nodule; solid mass = white, cystic component = dark gray Will see pilocytic astrocytes and Rosenthal fibers on microscopic examination |
|
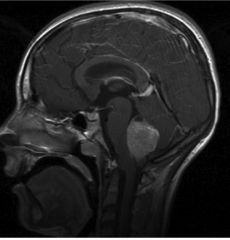
12 year-old male
|
Medulloblastoma (2nd most common brain tumor of childhood)
Malignant, poor prognosis Located exclusively in cerebellum Medulloblastoma only has SOLID component, no cystic (fluid-filled) component. So appears light grey. |
|
|
Why doesn't an infection with neisseria gonorrhoeae result in long lasting umminty?
|
Bacteria modifies outer membrane proteins via antigenic variation
Ab's generated during one infection will only be specific for that single antigenic episode Also recall that repeated Neisseria infections can be caused by terminal complement deficiencies leading to inability to form MAC |
|
|
21 year-old male
Bilateral lens opacities Urinary excretion of large amounts of galactose Diagnosis Pathophys of Syx |
Bilateral cataracts but otherwise asyx-->galactokinase deficiency
Results in elevation of galactose Excess galactose converted to GLACTITOL by ALDOSE REDUCTASE and to galactonic acid by galactose oxidase Excess galactitol in cells responsible for cataracts |
|
|
47 year-old
Homeless alcoholic Fevers, night sweats, weight loss, productive cough CXR reveals cavitary lesion in right middle lobe with air fluid levels Cause |
CXR lesion consistent with lung abscess, usually due to aspiration pneumonia--fusobacterium, peptostreptococcus, bacteroides
Also note it's in the right lobe; more likely to aspirate into right lung |
|
|
Why would a patient with COPD exhibit decreased cerebral vascular resistance?
|
Patient is likely hypercapnic (elevated pCO2); most potent cerebral vasodilator
|
|
|
What bleed values are abnormal for vWD?
|
Deficiency of vWF causes a functional Factor VIII and platelet deficiency
Thus will have prolonged bleed time (influenced by changes to PLT fn) and prolonged PTT (sensitive to Factor VIII changes) |
|
|
Why can eukaryotic DNA be replicated at a much faster rate than prokaryotic DNA?
|
Eukaryotic DNA has multiple origins of replication
Prokaryotes have 1 origin; also don't have introns (FYI) |
|
|
M. tuberculosis expresses decreased activity of intracellular catalase-peroxidase
Why would those pose a challenge to treatment? |
Isoniazid must be processed by mycobacterial catalase-peroxidase for drug to be activated within bacteria
Note: INH also requires a specific protein sequence in the enzyme target (necessary for mycolic acid)--genetic modification of the INH binding site could also result in resistance to INH |
|
|
Lab values associated with B12 deficiency (not quality of RBCs).
|
MMA
Homocysteine |
|
|
What is the effect of B12 replacement in someone with B12 deficiency anemia secondary to atrophic gastritis (on level of bone marrow)?
|
Immature erythrocytes released from BM into periphery
Peripheral count of reticulocytes will rise within one week Anemia typically takes 6 weeks to correct. |
|
|
55 year-old male
Severe, throbbing, right-sided orbitofrontal headache Diplopia Anisocoria Right pupil dilated and nonreactive to both light and accomodation Right eye is down and out with ipsilateral ptosis Location of aneurysm |
CN III palsy due to aneurysm arising from either posterior cerebral or superior cerebellar arteries.
|
|
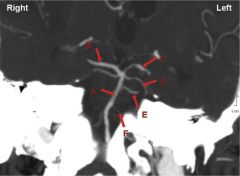
Label, include effects of aneurysms
|
A) Basilar artery
B) R Posterior Cerebral Artery C) L Posterior Cerebral Artery (would cause third nerve palsy on LEFT) D) Superior Cerebellar Artery E) Parapontine Perforating Artery (no clue) F) Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (Aneurysm can compress FACIAL and VESTIBULOCHOCHLEAR nerves) |
|
|
Most common cause of osteomyelitis in Sickle Cell.
|
SALMONELLA
followed by E. coli |
|
|
HIV positive patient
Latex agglutination positive for soluble polysaccharide antigen |
Cryptococcus: a budding yeast!
|
|
|
Why might an elderly patient with no relevant medical history experience B12 deficiency?
How would this affect delivery of supplements? |
Gastric atrophy (normal part of aging process) leads to achlorhydria, dec'd release of IF
Would require parenteral B12 administration |
|
|
Direct arteriolar vasodilators:
Examples AEs (not CN tox) |
Reflex tachycardia
Edema (often give in combination with sympatholytics and diuretics) |
|
|
Enveloped virus with partially double-stranded circular DNA
Packs its own RNA-dependent DNA polymerase |
Hepatitis B virus
|
|
|
8 year-old male
Diagnosed with acute MI Increased serum methionine Diagnosis What amino acid is likely essential? |
Homocysteinuria
Due to defective cystathionine synthetase involved in Homocysteine-->Cystathionine (precursor of cysteine) This leads to build up of homocysteine which is shunted to methionine But no cysteine formed! |
|
|
DVT:
Treatment How does this change in pregnancy? |
Warfarin is best long-term anticoagulant used for tx of DVT, however, it is contraindicated in pregnancy bc it's teratogenic (causes fetal warfarin syndrome)
Use heparin in pregnancy Note: ASA on its own is not enough for DVT tPA is not used for DVTs, it's reserved for STEMIs and ischemic stroke |
|
|
55 year-old female
Weight gain, easy fatigability Delayed relaxation of knee, ankle reflexes Skin is very dry and thick Likely diagnosis Best screening test |
Patient likely has primary hypothyroidism (dec'd release of TSH from hypothalamus)
Serum TSH is the single most important screening test in diagnosing primary hypothyroidism. Although TSH is not elevated in pts w/cetnral hypothyroidism, central hypothyroidism is UNCOMMON. (Central hypothyroidism = unresponsive pituitary) |
|
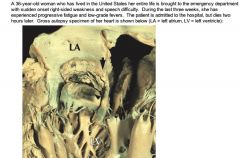
Diagnosis
Pathophys |
Patient's history is consistent with native valve bacterial endocarditis (NVBE) complicated by embolic cerebrovascular accident.
Arrow shows vegetation attached to prolapsed mitral valve leaflet (arrowhead). Vegetation is most probably source for embolus that lodged in one of patient's intracranial arteries (likely Left MCA based on presentation). In short, cause = MV prolapse (MV prolapse predisposes to infected vegetations on mitral leaflets) Rheumatic valvular dz potential, but less likely in US. |
|
|
Friedrich's ataxia:
Heart defect |
Hypertrophic CM
|
|
|
Tuberous sclerosis:
Heart defect |
Valvular obstruction due to cardiac rhabdomyomas
|
|
|
Turner's syndrome:
Heart defect |
Coarctation of the aorta
|
|
|
Down syndrome:
Heart defect |
Endocardial cushion defects resulting in ATRIAL septal defects (endocardial cushions); may also have regurgitant AV valves
|
|
|
45 year-old male
2 year history abdominal discomfort, greasy stools, weight loss Treated for joint pain with ibuprofen Intestinal biopsy shows multiple macrophages loaded with PAS-positive granules Diagnosis Significance of PAS-positive granules Treatment (General) |
Whippled disease caused by the actinomycete, Tropheryma whippelli.
Proliferates in small intestine, joints, and CNS. Appears as rod-shaped bacilli and PAS-positive granules (consist of LYSOSOMES and PARTIALLY DIGESTED BACTERIA)--this alone should clue you in on infection Treat with Abx |
|
|
List tumor promoters (proto-oncogenes) and tumor suppressors (anti-oncogenes)
|
Proto-oncogenes (tumor promoters); activating mutations lead to cancer:
ras N-myc ERB-B1/B2 TGFalpha abl Anti-oncogenes; deactivating mutations will lead to cancer: BRCA-1/2 NF-1 APC, DCC, p53 RB WT-1 |
|
|
List three different types of necrosis and which tissues exhibit them.
Exclude caseous and enzymatic fat necrosis. |
Coagulative -- all organs except CNS following lethal ischemic injury
Liquefactive - CNS infarcts Fibrinoid necrosis-- walls of BVs during immune complex vasculitis |
|
|
Essential fructosuria vs Hereditary fructose intolerance:
Presentation Enzymes affected |
Essential fructosuria: Large amounts of fructose from diet excreted in urine; due to deficient fructokinase (BENIGN)
Fructose intolerance: aldolase deficiency, results in vomiting, hypoglycemia after fructose ingestion |
|
|
6 month-old male
Recent onset vomiting, irritability, jaundice Exclusively breast fed until one week ago Began eating cereals and fruit juices Exam reveals hepatomegaly and abnormal LFTs Diagnosis Pathophys |
Hereditary fructose intolerance due to deficiency in ALDOLASE B
|
|
|
This bursitis arises in those who spend a lot of time on their knees, e.g., roofers, gardeners, prostitutes
|
Prepatellar bursitis ("housemaid's knee")
|
|
|
Korsakoff Syndrome:
What region of the brain is damaged? Presentation |
MEDIAL DORSAL NUCLEUS of thalamus (m for memory!)
Damage due to alcoholism causes memory loss and confabulation (fill in gaps of a story when can't remember something) Memory and learning impairment is usually permanent. |
|
|
Role of BRCA gene.
|
DNA repair
|
|
|
PSGN:
Glomerular light microscopy findings Immunofluorescence findings (include deposits) |
LM findings will show diffuse HYPERCELLULAR glomeruli (filled with neutrophils, monocytes)
Immunofl is "starry sky" in appearance and will have deposits of IgG, IgM and C3 in GBM |
|
|
32 year-old female
History of amenorrhea Presents with white nipple discharge FMH significant for maternal breast cancer at 50 Diagnosis |
Prolactin-secreting pituitary adenoma
Note: if you were thinking nipple discharge due to breast cancer (as in intraductal papilloma), discharge would be bloody or serosanguinous |
|
|
What's the cut off for hyperpyrexia (in ºC)?
Treatment: immediate and general |
Anything above 40ºC is hyperpyrexia and may lead to permanent brain damage if left untreated.
Body needs to be cooled immediately using cold blankets, cold water enemas, application of cool saline bags, etc. Rectal or oral administration of acetaminophen is the antipyretic of choice (in children) Dec'd PGE2 will decrease the hypothalamic set point (temperature). |
|
|
What two regions of the intestine are most susceptible to ischemic damage during hypotension/low perfusion states?
|
Splenic flexure
Distal sigmoid colon |
|
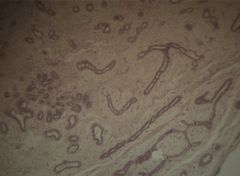
Breast biopsy:
What is it and why? |
Fibroadenoma--cellular/myxoid stroma encircling glandular and cystic spaces. Epithelium of fibroadenoma can be compressed by surrounding stroma (as seen in this patient).
This is mostly seen in women in their 20s or 30s. Usually freely movable, palpable. |

