![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does liver failure result in gynecomastia?
What other symptoms arise as a result of this? |
Liver unable to metabolize circulating estrogens (specifically, androstenedione)-->hyperstrinism
In EtOH liver dz-->inc'd sex hormone-binding globulin (Increases T:E ratio) Also results in: -Testicular atrophy -Dec'd body hair -Spider angiomata |
|
|
What cells/regions of the brain is most sensitive to cerebral ischemia?
|
Pyramidal cells of hippocampus, neocortex
Purkinje cells of cerebellum |
|
|
alpha1-antitrypsin:
Role |
Inhibits elastase in lungs
|
|
|
What is necessary for phosphorus absorption in the gut?
|
Vitamin D
|
|
|
Patient eats more than usual
Feels guilty and depressed Vigorously exercises Has had similar episodes for 5 months BMI is 23.7 Diagnosis Why? |
Bulimia nervosa; not body dysmorphic disorder.
In body dysmorphic disorder, patients have an intense preoccupation with imagined bodily defects which leads to FUNCTIONAL IMPAIRMENT. In bulimia, there's binge-eating with either restrictive or purging compensatory behaviors. Normal BMI. This description fits the bill. |
|
|
Adenosine deaminase:
Role Effects of deficiency |
Adenosine deaminase:
-present in all cells; deminates adenosine to eliminate excss adenosine from cell -adenosine accumulation is toxic to lymphocytes -deficiency leads to widespread death of both T and B cells with resultant combined cellular and humoral immunodeficiency (SCID!) |
|
|
Patient hypotensive and bleeding from MVA
Receives blood transfusion Develops dyspnea, chills Goes into renal failure Pathophys |
Acute hemolytic reaction with blood transfusion due to ABO incompatibility.
Anti-ABO antibodies in recipient bind antigens on donor erythrocytes. Ag-Ab complexes activate COMPLEMENT, results in production of C3a and C5a (ANAPHYLATOXINS) as well as MAC (C5-C9_-->SHOCK THIS IS A HYPERSENSITIVITY TYPE II REACTION |
|
|
Stroke
Sensory loss on right side of body Unsteady gait Diagnosis |
Thalamic syndrome--infarct of left thalamus (CONTRALATERAL)
|
|
|
s/p MI
5mm cavities in deep brain filled with clear fluid Diagnosis Pathophys |
Lacunar infarctions (within basal ganglia, pons, cerebellum, ~5mm)
Result of small vessel lipohyalinosis (destructive vessel lesion) and atherosclerosis; most common in setting of uncont'd HTN and DM. |
|

Label
|
|
|
|
KOH test
Positive whiff test |
Bacterial vaginosis
|
|
|
Somatomedin C:
Role |
AKA IGF-1
Inc'd when GH released from pituitary; causes differentiation and proliferation of chondrocytes in epiphyseal growth plate (increase in linear growth) Unlike, estrogen, does NOT accelerate epiphyseal closure. |
|
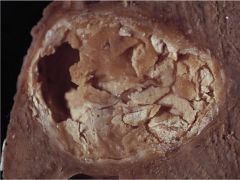
Diagnosis
Epidemiology Pathophys Surgical Considerations Treatment |
Hydatid cyst formed by tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus
Occurs in Mediterranean, South Amera, Middle East, Australia/New Zealand, Southern Africa Dog = part of tapeworm lifecycle (can affect Americans that work with sheep dogs) Tx with albendazole or mebendazole DO NOT ASPIRATE--spilling of cyst contents within peritoneum can cause anaphylaxis |
|
|
What do schistocytes suggest?
|
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (TTP, HUS, DIC) or mechanical damage)
|
|
|
Bloody diarrhea
Anemia Thrombocytopenia Normal PT/PTT Schistocytes Diagnosis Pathophys |
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (a form of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia)
Undercooked ground beef-->Enterohemorrhagic E. coli-->Shiga toxin-->bloody diarrhea Endothelial cell injury-->activation of platelets and formation of microthrombi While passing by, RBCs are damaged by microthrombi and appear as schistocytes. Unlike in DIC, coagulation system is not active, so PT and PTT normal. (not sure why shiga toxin is necessary, but bloody diarrhea usually precedes childhood HUS) |
|
|
How does hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) differ from thrombotic thrombocytic purpura (TTP)?
|
HUS and TTP both present with:
-fever, neurologic syx renal failure, thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia Usually, TTP occurs in adults with predominant neurologic syx HUS, in children with primarily renal involvement (renal failure) |
|
|
What is radial traction?
|
Outward pulling
|
|
|
Restrictive lung disease:
Examples Lung Test Values Effect on recoil, radial traction |
Restrictive lung disease = pulmonary fibrosis
Dec'd TLC, VC, Inspiratory capacity Dec'd FEV1, FVC Inc'd FEV1/FVC bc FEV1 dec'd less than FVC Relatively high expiratory rate due to dec'd lung compliance (inc'd elastic recoil) and inc'd radial traction (outward pulling) exerted on conducting airways by fibrotic lung |
|
|
Where is the majority of total frictional airway resistance localized?
How does this change as air progresses through the respiratory airways? |
Majority of resistance at medium and small-sized bronchi greater than 2mm in diameter.
Regional airway resistance is maximal in 2nd-5th generation of airways (there are 23 generations of branching total). Airway resistance is minimal in bronchioles. |
|
|
Aldolase B participates in _______ metabolism.
|
Fructose
|
|
|
Maltose is broken down into ______.
|
Glucose and Glucose
|
|
|
Lactose is broken down into ______.
|
Galactose and Glucose
|
|
|
Sucrose is broken down into ______.
|
Fructose and Glucose
|
|
|
The majority of cervical cancers are _______.
|
Squamous cell carcinomas
|
|
|
Overexpression of viral proteins E6, E7:
Viral association Effects |
HPV-16,18 (HIGH RISK)
E6: binds p53 and decreases its degradation E7: binds Rb and displaces transcription factors normally bound to it |
|
|
Stop codons
|
UAG
UAA UGA You're a goat You're an ass You're a goat's ass |
|
|
Causes of left/right shifts of oxygen-dissociation curve.
|
Left shift:
Increased affinity for oxygen, caused by: -Dec'd H+ (inc'd pH) -Dec'd 2,3-DPG -Dec'd temp Right shift: Dec'd affinity for oxygen caused by: -Inc'd H+ (dec'd pH) -inc'd 2,3-DPG -Inc'd Temp |
|
|
What is the effect of strenuous exercise on the oxygen-dissociation curve?
|
Exercise-->inc'd CO2-->dec'd pH (inc'd H+)
Right shift (dec'd affinity for O2) |
|
|
Exhibits IgA protease
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
Hemolysin:
Effects Associated bacteria |
Staph--secreted factor, not bound fo cell wall
Effects: produces hemolysis and destruction of nphils, macs, PLTs |
|
|
Protein A:
Effects Associated bacteria |
Protein A = characteristic of Staph aureus
Binds Fc portion of IgG and prevents activation of complement Results in dec'd production of C3b-->impaired opsonization |
|
|
D-alanine-D-alanine analog that prevents bacterial peptidoglycan cross-linking
|
Cell wall inhibitor!!
D-ala-D-ala = substrate of PCN binding protein (bacterial enzyme targeted by PCNs) |
|
|
Why is penicillin not effective against mycoplasma?
What agents are effective? |
Mycoplasma lack peptidoglycan walls so cell wall inhibitors like PCN, cephalosprins, vanco, etc. won't work.
Mycoplasma has a single phospholipid bilayer with cholesterol; just like human cells. Need to use anti-ribosomal agents like macrolides and tetracyclines. |
|
|
These bacteria lack peptidoglycan walls and are similar in structure to human cells.
|
Mycoplasma
Ureaplasma |
|
|
Inferior wall infarct appears in these EKG leads.
Artery affected? |
II, III, aVF
Occlusion of RCA |
|
|
Anteroseptal infarct appears in these EKG leads.
Artery affected? |
V1-V4
Proximal LAD |
|
|
Lateral wall infarct of left ventricle appears in these EKG leads.
Artery affected? |
V5, V6
Left Circumflex |
|
|
Draw a ventricular muscle action potential.
Label and describe what happens during every phase. |
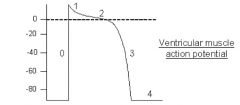
Phase 4: Resting potential (diastole)--permeability to K+ ions in resting state.
Phase 0: Rapid depolarization: Voltage-gated Na+ channels open and Na+ ions rush into cell Phase 1: Initial rapid repolarization: rapid closure of Na+ channels Phase 2: Plateau: L-type dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels open, some K+ channels close (membrane becomes highly permeable to Ca2+, minimally permeable to K+) Phase 3: Late phase repolarization: Closure of Ca2+ channels; opening of K+ channels. Efflux of K+ from cell restores membrane resting potential. |
|
|
Which clotting factors are vitamin K dependent?
|
II, VII, IX, X
|
|
|
Rodenticide ingestion:
Effect Treatment |
Rodenticides contain brodifacoum, a 4-hydroxycoumarin derivative, i.e., A VITAMIN K ANTAGONIST
This depletes patients of vitamin K dependent clotting factors, causing acquired coagulopathy. RISK OF GI BLEEDING (POTENTIALLY FATAL) Must replenish factors through IV fresh frozen plasma. Vitamin K1 also. |
|
|
Heparin OD:
Treatment |
Protamine
|
|
|
Patient taking amphotericin B
EKG reveals PVCs Pathophys |
Amphotericin B is nephrotoxic
Causes dec'd GFR, has direct toxic effects on tubular epithelium Causes hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia (due to inc'd memnbrane permeability of distal tubule) These metabolic disturbances can result in arrhythmias (hypokalemia = T wave flattening, PACs, PVCs; if profound-->Vfib/Vtach) |
|
|
Infection with delta agent:
Pathophys |
delta agent = Hepatitis D
By itself, HDAg is replication-defective; must be COATED by HBsAg of HBV before it can infect hepatocytes and multiply. HDV can either arise as acute coinfection with HBV or as superinfection of chronic HBV carrier. |
|
|
GABA-a vs GABA-b vs GABA-c:
Functions Associated drugs |
GABA-a: ion channel (bound by benzodiazepines, barbiturates, EtOH)
GABA-b: linked to G-protein GABA-c: ion channel |
|
|
What vitamin must be supplemented with INH use?
Why? |
Pyridoxine (B6)
INH is structurally similar to pyridoxine. As a result, increases urinary excretion of pyridoxine and competes for its binding sites, leading to defective synthesis of GABA. Can induce NEUROPATHY. |
|
|
Mifepristone:
MOA Use AEs |
"Anti-progestin"
Progesterone antagonist (has 5 times the affinity for PG receptor than natural PG) PG necesary for implanatation and maintenance of pregnancy. When antagonized by mifepristone-->decidual necrosis and expulsion of products of conception. Anti-progestin effects induce release of endogenous Prostaglandins-->abdominal cramps, nausea, vaginal bleeding |
|
|
Spatial vs Temporal Summation:
General |
Spatial: impulses from several different neurons
Temporal: sequential impulses from same neuron over time |
|
|
What is the space constant?
What increases it? Decreases it? |
Measure of how far along an axon an electrical impulse will travel.
Increased by myelin, decreased by demyelination (MS) |
|
|
Describe the following presentations of 21-OHase deficiency:
Non-classic Classic, non-salt wasting Classic, salt-wasting |
Non-classic, delayed:
Mild degree of 21-OHase deficiency Present with premature pubarche or sexual precocity Young women can present with acne, hirsutism, menstrual irregularity Classic, non-salt-wasting: Moderate degree of 21-OHase deficiency Females present at birth with ambiguous genitalia Males present at 2 to 4 years with signs of early virilization Classic, salt-wasting: Females present at birth with ambiguous genitalia Males present at 1-2 weeks with failure to thrive, dehydration, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia |
|
|
68 year-old female
Rash involving a single dermatome on chest Diagnosis Symptom likely to suffer from within 6 months? |
Herpes Zoster--arises when latent varicella zoster virus reactivated within a single dorsal root sensory ganglion
Rash does not usually recur in immunocompetent host. Post-herpetic neuralgia is most common complication --described as stabbing, localized pain that lasts for several months. |
|
|
Why do oral contraceptives reduce the risk of non-hereditary ovarian cancer?
|
Risk of ovarian cancer is associated with irregularities of reparative processes of ovarian surface (repeated aberrant repair is thought to induce dysplasia and neoplasia).
OCPs reduce the risk of non-hereditary ovarian cancer by decreasing the total number of times a woman ovulates in her lifetime. With fewer ovulatory cycles, there is less need for repair at the ovarian surface. |
|
|
What can decrease the risk of ovarian cancer?
|
Multiparity
Breast-feeding OCPs |
|
|
Warfarin-induced skin necrosis:
Pathophys |
Protein C and S are natural anticoagulants.
Following warfarin administration, there's a rapid drop in Factor VII and Protein C. If protein C deficiency present, procoagulant/anticoagulant imbalance is exaggerated, causing hypercoagulable state with thrombotic occlusion of microvasculature and skin necrosis. |
|
|
3-month old male
Right-sided white pupillary reflex Diagnosis |
Retinoblastoma
|
|
|
Sporadic vs Familial Retinoblastoma:
Prognostic differences |
Sporadic: unlikely to develop other malignancies
Familial: most likely to develop osteosarcomas (or other sarcoma, but mostly osteosarcoma) |
|
|
What proteins are able to directly bind DNA?
|
Transcription Factors
Steroids Thyroid Proteins Vitamin D Receptors Retinoic Acid Receptors DNA transcription and replication proteins |
|
|
N-myc:
Role |
Transcription factor--CAPABLE OF BINDING DNA
|
|
|
First line treatment of hypertriglyceridemia.
|
Fibrates
|
|
|
22 year-old male
Serum triglyceride of 1500 mg/dL (normal <200) Treatment? |
Niacin and fibrate (ex:gemfibrozil)
|
|
|
Ezetimibe:
MOA |
Selectively inhibits intestinal absorption of cholesterol.
|
|
|
What is projection?
|
Transplanting unacceptable impulses or affect onto another person or situation.
Ex: When MD hears of patient's drug abuse, he transplants unacceptable impulses towards his daughter on the patient's mother (bc she does drugs too apparently). |

