![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two types of strokes? (% of each?)
|
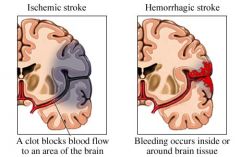
Bleeds (30%)
Blocks (70%) |
|
|
Blocks are caused by:
|
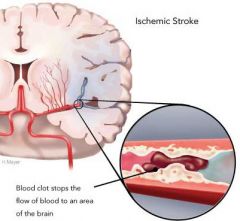
Slow: Arteriosclerosis leading to thrombus (clot)
Fast: Embolus - blood clot, fat particule |
|
|
Bleeds are caused by:
|
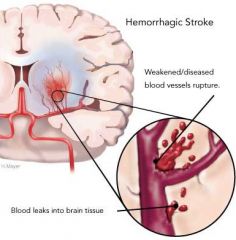
Aneurysm - weakened wall of blood vessel
|
|
|
What % of each type of stroke are fatal?
|
Blocks: 20% are fatal
Bleeds: 80% are fatal |
|
|
What affect foes the loss of ATP have on the brain? (Due to Cardiac Arrest)
|
1. Shutdown of Na-K Pumps
2. Edema |
|
|
Cardiac arrest causes loss of consciousness in approximately ___ seconds.
|
10 seconds!
|
|
|
What are the two catagories of hypoperfusion and what are the signs?
|
Signs:
1. TIA: Transient Ischemic Attacks - focal retinal or cerebral deficits 2.TGA: Transient Global Amnesia - Memory disturbance |
|
|
What would be the result of an infarct of the Anterior Spinal Artery?
|
ASA infarct = Inferior Alternating Hemiplegia
Symptoms include: Contralateral hemiplegia with babinski, ipsilateral tongue atrophy and deviation to the side of lesion (CNXII GSE damage) |
|
|
Occulsion of the PICA or bulbar branches of the vertebral artery can cause:
|
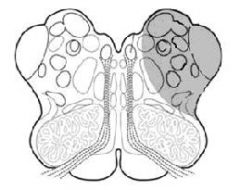
Lateral Medullary Syndrome (Wallenburg)
-Loss of pain and thermal sense on ipsilateral face and contralateral body -Ipsilateral Horner's Syndrome -Dysphagia and Disphonia -Cerebellar ataxi |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Lateral Medullary Syndrome (Wallenburg)?
|
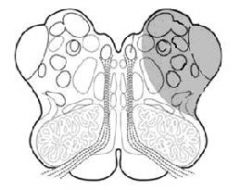
1. Loss of pain and thermal sense on ipsilateral face and contralateral body
2. Ipsilateral Horner's Syndrome 3. Dysphagia and Disphonia 4. Cerebellar ataxia |
|
|
The Brain is supplied by two pairs of arterial trunks:
|
1. Vertebral Arteries (Vertebral basilar system)
2. Internal Carotid Arteries |
|
|
Branches of the Vertebral Basilar System
|
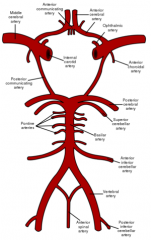
A. Major Vertebral Artery Branches
- Anterior Spinal Artery - Bulbar Branches - PICA - Basilar Artery B. Basilar Artery Branches -AICA -Labyrinthine Artery -Pontine Arteries -Superior Cerebellar Arteries -Posterior Cerebellar Arteries |
|
|
What are the two types of lower brain stem infarcts?
|
1. Paramedian infarcts
2. Lateral infarcts |
|
|
What are the symptoms of a Paramedian infarct?
|
1. Contralateral loss of tactile, vibration and kinesthesis due to loss of MEDIAL LEMNISCUS
2. CONTRALATERAL HEMIPLEGIA due to loss of corticospinal tract. 3. Ipsilateral involvement of the GSE cranial nerves: 3, 6, or 8 |
|
|
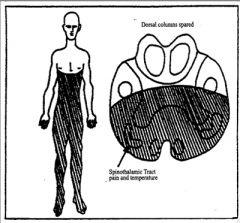
What are the symptoms of a lateral infarct?
|
1. Contralateral Spinothalamic defictis
2. Ipsilateral trigeminal Deficits 3. Ipsilateral SVE cranial nerve deficits 4. Ipsilateral Horner's |
|
|
What are the (4) pats of the Internal Carotid Artery?
|
1. Cervical
2. Petrous 3. Carvernous/Sigmoid 4. Supraclinoid |
|
|
Branches of the ICA?
|
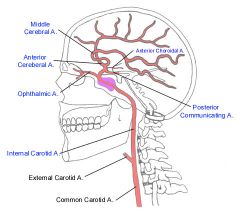
1. Ophthalamic
2. Posterior Communicating Artery 3. Anterior Choroidal Artery 4. Anterior Cerebral Artery 5. Middle Cerebral Artery |
|
|
What arteries comprise the circle of willis?
|
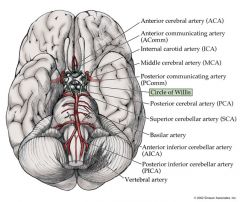
Ant./Post. Cerebral
Ant./Post. Communicating Arteries |
|
|
Functions of the Circle of Willis?
|
It is an anatomosis that equalizes blood flow to various parts of the brain.
|
|
|
Area of the Brain supplied by the Anterior Cerebral Artery:
|
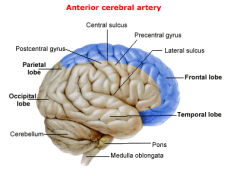
|
|
|
What would an occlusion of the Anterior cerebral artery cause?
|
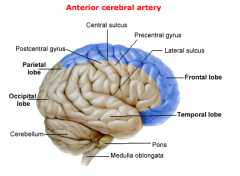
1. UMN and sensory deficits in the CONTRALATERAL LOWER extremity.
(Paracentral lobule) 2. Personality change. (Prefrontal cortex) |
|
|
Areas supplied by the Posterior Cerebral Artery:
|
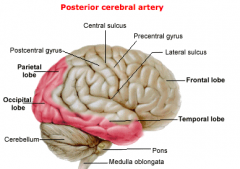
|
|
|
Branches of the Post.Cerebral.A:
|
1. Anterior Branches: Inf. surface of temporal lobe
2. Calcarine Artery: Supplies primary visual cortex |
|
|
Infarcts of the Post.Cerebral.A cause:
|
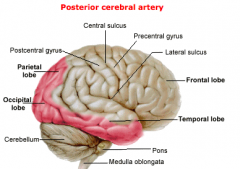
Contralateral homonymous hemianopsia (visual field deficit)
|
|
|
Area supplied by the Middle Cerebral Artery:
|
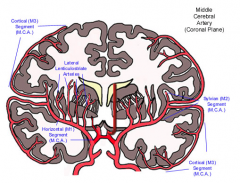
|
|
|
What would be the effect of an occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Artery vessels supplying Head and arm areas of pre-/post- central gyri?
|
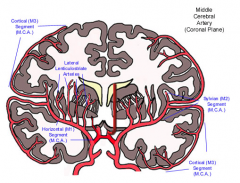
Hemiplegia and sensory deficits in the contralateral face and upper extremity.
|
|
|
What would be the effect of an occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Artery vessels supplying Left Side Broca's or Wernicke's Areas?
|
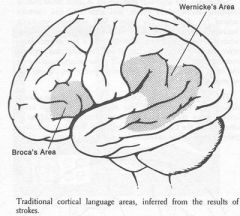
Aphagia!
-Difficulty with motor planning of speech (Broca's) -Sensory processing areas of speech (Wernicke's) |
|
|
MCA infarct: frontal eye fields and auditory cortex
|
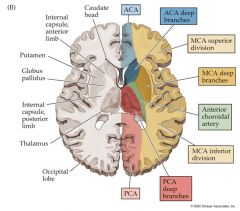
May cause disturbances of voluntary eye movement and some diminution of hearing, respectively
|
|
|
What is the Sylvian triangle?
|
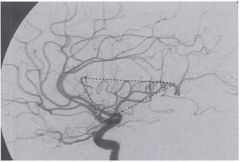
A course of branches of the MCA in the insular region.
MCA branches lying on insula form an imaginary triangle |
|
|
Why is the Sylvian triangle clincally important?
|
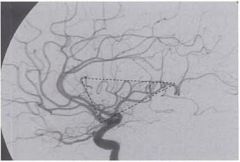
Displacement of the Sylvian triangle in an angiogram provides the location of a space-occupying lesion.
|
|
|
What are lacunar infarcts?
(Circle of Willis) |
Lacunar infarcts are caused by occlusions of central branches of the Circle of Willis that are END arteries, which do not anastomose effectively.
|
|
|
What is a capsular infarct?
|
A capsular infarct results from an occlusion or hemorrhage of vessels supplying the internal capsule
(i.e internal carotid, MCA, Medial and Lateral striate, and of anterior choroidal) |
|
|
What would be the area affected by a capsular infarct of the CORTICOSTRIATE FIBERS?
|
CORTICOSTRIATE:
-Dyskinesia (abnormal involuntary movements) |
|
|
What would be the area affected by a capsular infarct of the CORTICOBULBAR FIBERS?
|
CORTICOBULBAR:
-Central voluntary facial palsy |
|
|
What would be the area affected by a capsular infarct of the CORTICOSPINAL and SOMATOSENSORY Radiations?
|
CORTICOSPINAL and SOMATOSENSORY Radiations:
-Contralateral Hemiplegia -Loss of sensory in contralateral body |
|
|
What would be the area affected by a capsular infarct of the OPTIC and AUDITORY Radiations?
|
OPTIC and AUDITORY Radiations:
-Contralateral Homonymous Hemianopsia -Contralateral Diminution in Hearing |

