![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
genetic disorders or teratogens: VSD, clenched hands, cleft palate, rounded heels, and a horseshoe kidney.
|
edwards trisomy 18
|
|
|
microcytic anemia and increased concentration of hemoglobin A2
|
beta thalassemia trait (also called -thalassemia minor)
|
|
|
noisy breathing on inspiration w/ chest retractions, flaring of the nostrils, and a barking cough. Bugs? Tx?
|
croup -> airway tends to collapse on inspiration, producing the characteristic findings this patient demonstrates;
Tx: racemic epinephrine and single dose of steroids -> reduce the length of time in the emergency room and hospitalizations. Bugs: parainfluenza types 1 and 3, influenza A and B, RSV |
|
|
small, firm, white, cold patches of skin in exposed areas. Dx?
|
Frostnip
|
|
|
prolonged exposure to cold and/or moisture-> foot is cold, numb, pale, edematous, and clammy.
|
Trench foot
|
|
|
cold exposure: initial stinging, followed by aching, culminating in numb areas. Once rewarmed, the area becomes red, blotchy, and painful.
|
frostbite
|
|
|
cold exposure: small, ulcerated lesions on exposed areas such as the ears and fingers.
|
Chilblains
|
|
|
cold exposure: area of erythematous, firm, and slightly swollen skin
|
Cold panniculitis
destruction of fat cells caused by exposure to cold weather or a cold object; in this case, the child had "Popsicle panniculitis," which is usually a benign condition that self-resolves. |
|
|
mass lesion that causes: precocious puberty or acromegaly plus paroxysms of laughter
|
Hypothalamic hamartomas - nonneoplastic
loc: neurons and glia in the region of the hypothalamus -> causes neuroendocrine functions tx: surgically. |
|
|
runny nose and coughing for 2 days now nasal flaring and wheezing. CXR: patchy infiltrates with flat diaphragms. No previous wheezing episodes and no family history of atopy. Dx? Tx? Bug?
|
bronchiolitis
TX: monitoring oxygenation and hydration status +/- a single dose beta-agonist might be tried in this patient but would be expected to be of limited benefit for a patient with bronchiolitis. Bug: respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza and adenoviruses |
|
|
1 and 3 months of age, with cough, tachypnea, and lack of fever. Examination reveals rales but not wheezing. increase in eosinophils in the peripheral blood. The chest radiograph shows hyperinflation with interstitial infiltrates. Dx?
|
15% of infants born to mothers with Chlamydia trachomatis infection develop pneumonia.
|
|
|
school-age child or young adult w/ gradual onset of headache, malaise, fever, and lower respiratory symptoms. Dx? Bug?
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
|
|
<1 year of age w/ URI for several days -> abrupt onset of fever and respiratory distress +/- Pleural effusion, empyema, and pyopneumothorax are common complications. Labs: markedly elevated WBC count with left shift. CXR: lobar pneumonia. DX? Bug?
|
Staphylococcal pneumonia is caused by S aureus.
|
|
|
Child with sudden onset of fever, cough, and chest pain +/- Pleural effusions or empyema. Bug? Tx?
|
Pneumococcal pneumonia
high-dose penicillin, cefuroxime, amoxicillin/clavulanate, or even vancomycin may be required. |
|
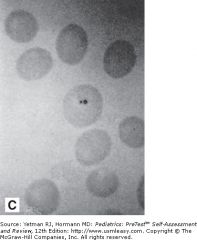
describe. What assoc w/?
|
Howell-Jolly bodies (slide C) are small, spherical, nuclear remnants seen in the reticulocytes and, rarely, erythrocytes of persons who have no spleen (because of congenital asplenia or splenectomy) or who have a poorly functioning spleen (eg, in hyposplenism associated with sickle-cell disease).
|
|
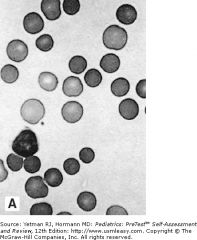
describe and assoc w/?
|
Uniformly small microspherocyte are typical of hereditary spherocytosis. Because of a decreased surface to volume ratio, these osmotically fragile RBCs have an increased density of hemoglobin. Although spherical RBCs also can appear in other hemolytic states (eg, immune hemolytic anemia, microangiography, ABO incompatibility, and hypersplenism), their cellular volume is only irregularly augmented. Patients with hereditary spherocytosis can present in the newborn period with anemia, hyperbilirubinemia, and reticulocytosis. They may remain asymptomatic until adulthood, when they develop symptoms. After infancy, hepatosplenomegaly and gallstones are common.
|
|
|
The leading causes of death in teenagers between the ages of 13 and 18 years old, in order of decreasing frequency, are
|
motor vehicle accidents,
homicide, suicide, |
|
|
CNS tumors associated with telangiectasias of the retina (von Hippel-Lindau syndrome).
|
Hemangioblastomas are vascular CNS tumors
|
|
|
CNS tumors associated with polycystic kidney disease
|
Hemangioblastomas are vascular CNS tumors
|
|
|
complex partial seizures and mild mental retardation has a birthmark consisting of deep red discoloration extending over her forehead ( facial cutaneous angiomas ) and left upper eyelid. Dx? Brain findings?
|
encephalofacial angiomatosis (Sturge-Weber syndrome)
intracranial abnormalities such as leptomeningeal angiomas. Persons with the syndrome may be mentally retarded and often exhibit hemiparesis or hemiatrophy on the side of the body opposite the port-wine nevus. |
|
|
When children can consistently identify themselves as male or female and recognize others as male or female?
|
By 2 1/2 years of age,
|
|
|
hypodense bone calcification w/ history of fractures; unresponsive vitamin supplementation. DX? serum (Ca2+)? phosphate (PO4)?
|
vitamin D–resistant rickets
Path: X-linked dominant trait -> 1. decreased renal tubular reabsorption of phosphate -> hyperphosphaturia and hypophosphatemia 2. decreased conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. 3. decreased intestinal absorption of phosphate Low PO4, normal Ca |
|
|
Vitamin _ excess slows normal growth and causes hyperostosis (excess bone growth), hepatomegaly, increased CSF pressure, and drying of skin?
|
A
|
|
|
Excess vitamin __ causes skin flushing and pruritus; long-term use can cause tachycardia, liver damage, hyper-glycemia, and hyperuricemia.
|
Nicotinic acid, a vasodilator,
|
|
|
Excessive Vitamin __ causes kidney stones, diarrhea, and cramps and increase the normal requirement for the vitamin when large doses are discontinued.
|
vitamin C
|
|
|
Excessive intake of vitamin __ can result in sensory neuropathy with altered sensation of touch, pain, and fever.
|
pyridoxine (B6)
|
|
|
excessive intake of vitamin __can cause nausea, diarrhea, weight loss, polyuria, and soft-tissue calcification of heart, kidney, blood vessels, bronchi, and stomach?
|
D
|
|
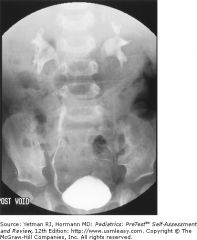
voiding cystoure-throgram finding?
|
reflux into the ureters and into the kidney, with dilation of the renal pelvis, making the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux
|
|
|
anorexia, polydipsia and polyuria, vomiting, and unexplained fevers, glucosuria w/ normal blood sugar, abnormally high urine pH and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, and albuminuria and normal serum protein and albumin. DX?
|
Fanconi syndrome (aka global proximal tubular dysfunction).
hereditary or acquired (drugs that cause acute tubular necrosis, alteration of renal blood flow, intratubular obstruction, or allergic reactions within the kidney itself). |
|
|
Testicular torsion (how long to tx before probs? Tx
|
If treated within the first 4 to 6 hours of onset of symptoms, the chance of saving the testicle is high.
Tx: rotate testicle -> orchiopexy is performed on BOTH testicles. |
|
|
Usually < 2 y/o w/ painless rectal bleeding who is afebrile, alert, and playful, and is eating well without emesis. He is slightly tachycardic, and his abdominal examination is normal? Dx tool? Dx?
|
Meckel diverticulum = failure of the embryonic duct connecting the yolk sac to the intestine to regress completely and persist as a diverticulum attached to the ileum.The lining of the Meckel diverticulum usually contains acid-secreting gastric mucosa that can produce ulcerations of the diverticulum itself or the adjacent ileum. Bleeding, perforation, or diverticulitis can occur. VOLVULUS, INTUSCICEPTION
DX: technetium scan that labels gastric mucosa, TX: surgical excision. |
|
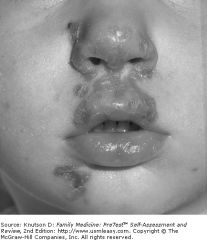
dx?
|
impetigo
|
|
|
meningitis tx drug?
|
high-dose penicillin or ceftriaxone must be given intravenously for 10 to 14 days. Tetracycline qid for 30 days should be used for patients who are allergic to the intravenous treatments.
|
|
|
the most common form of thrombocytopenic purpura.
|
Idiopathic (immune) thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
|
|
|
T/F: bulimics do no have an altered perception of body weight or shape.
|
F. They do.
|
|
|
T/F: anorexics feel a lack of control over eating during episodes of binging.
|
F: anorexics often feel a strong sense of control. Bulimics lose control.
|
|
|
Newborn is large for their gestational age and thought to have a peripheral nerve injuries such as Erb-Duchenne and phrenic nerve paralysis. What is the best dx test after a CXR?
|
An ultrasound or fluoroscopy of the chest would reveal asymmetric diaphragmatic motion in a seesaw manner.
|
|
|
Obstructive jaundice (ie, direct-reacting bilirubin greater than 20% of the total) DDX: (genetic, metabolic x 3, infectious, gross anatomic, histologic)
|
Cystic fibrosis
Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency galactosemia, tyrosinemia, urinary tract or other infections choledochal cyst - US w/ hepatic iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan histologic diagnosis (eg, hepatitis, biliary atresia), |
|
|
Age? respond to a bell,
|
1 month infants
|
|
|
Age? begin to vocalize,
|
1 month infants
|
|
|
Age? follow items to the midline,
|
1 month infants
|
|
|
Age? regard face
|
1 month infants
|
|
|
Age? lift their head from the examining table
|
1 month infants
|
|
|
age? smile
|
8-week-old child
|
|
|
age? coo when smiled at or talked to.
|
8-week-old child
|
|
|
age? follow a moving toy from side to side and also in the vertical plane.
|
3 months
|
|
|
PROM birth – then <4wks later fever. Dx? Bug?
|
Neonatal sepsis is defined as an invasive bacterial infection occurring during the first 90 days of life.
GBS - women carry this organism in their vagina – PROM increases risk by causing-> ascending infection. |
|
|
severe eczema, thrombocytopenia, and unusual infections. Immunodeficiency? Test?
|
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is unlikely if the platelet count is normal
|
|
|
frequent infections, Abnormal facies w/ Cleft palate, Hypocalcemia, and murmur. Dx? Most appropriate diagnostic laboratory test?
|
An intradermal skin test using Candida albicans will result in no response in the patient with T-cell deficiencies
|
|
|
Repeated pneumococcus and meningococcus infections. Think? Dx test?
|
Asplenia results in Howell-Jolly bodies and also an increased risk for encapsulated organisms such as pneumococcus or meningococcus; a CBC with a peripheral smear can rule out this disease.
|
|
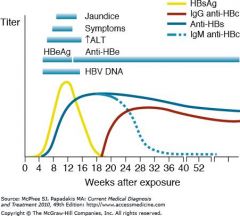
Anti-HBs positive means? neonate tx?
|
immune or
Chronic hepatitis B with heterotypic anti-HBs (about 10% of cases) tx: immunize |
|
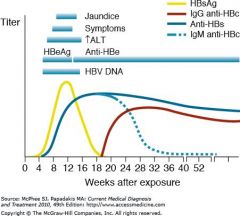
HBsAg positive means?
|
Acute hepatitis B or
Chronic hepatitis B tx:Administer hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B vaccine to the infant. |
|
|
HBeAg positive means?
|
Acute hepatitis B or
Chronic hepatitis B tx:Administer hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B vaccine to the infant. |
|
|
Anti-HBe positive means?
|
Chronic hepatitis B with low viral replication or
Recovery from hepatitis B (immunity) |
|
|
Anti-HBc IgM positive means?
|
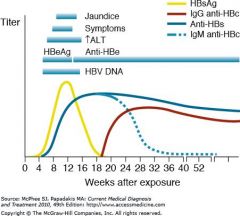
Acute hepatitis B
|
|
|
Anti-HBc IgG positive means?
|
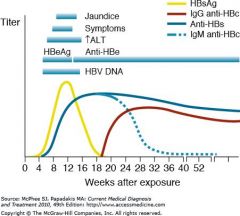
Chronic hepatitis B or
Recovery from hepatitis B (immunity) |
|
|
nausea and vomiting. His symptoms began acutely last evening, starting with malaise, headache, low-grade fever, body aches, and diarrhea. Dx? Bugs?
|
viral gastroenteritis
Norwalk virus, reoviruses, and adenoviruses |
|
|
Ulcer: Test for herpes
|
1. Examination of a Tzanck preparation of scraping from the ulcer reveals multinucleated giant cells and intranuclear inclusions.
2. Herpes simplex virus is readily cultured. 3. rapid diagnostic tests using immunofluorescence or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are available, 4. polymerase chain reaction (HSV PCR) assay. |
|
|
Painless swelling of lymph nodes in neck, armpits or groin, fever, night sweats, malaise, weight loss, and pruritus. Think? Next step?
|
Hodgkin disease – CXR =mediastinal mass
|
|
|
Pregnant mother is hyperthyroid. Fetus is at risk for? ASSOC W/ organ prob? Face issue?
|
Neonatal thyrotoxicosis secondary to high maternally-acquired thyrotropin receptor-stimulating antibody (TRSAb) falls. Unlike TRSAb, TSH does not cross the placenta.
SEVERE SX: microcephaly, hepatosplenomegaly and heart failure. |

