![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diabetic Retinopathy
|
Cotton-wool spots -nonspecific, but common in DM. With progression, neovascularization --> vitreous hemorrhage --> retinal detachement. NOTE - AV nicking is more common in HTN, but often co-morbid in diabetics
|
|
|
Congenital Hypothyroid Features
|
Feeding problems, jaundiced mottled skin, hypotonia, course face, protruding tongue, hoarse cry.
|
|
|
Galactosemia
|
Jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, seizures, hypoglycemia, cataracts, vomiting after milk consumption; GIVE galactose-free foods.
|
|
|
Phenylketonuria
|
AR, light hair, mousy odor, seizures, vomiting, dermatitis, growth retardation.
|
|
|
Cerebral Edema
|
Presents with abdominal pain, n/v/polyuria, lethargy. Usually precipitated by cessation of insulin intake, or surgery, or DKA. TREAT with mannitol acutely, then correct electrolyte imbalance.
|
|
|
DKA --> Cerebral Edema
|
TREAT initially with insulin + saline or LR. As glucose and potassium fall, they must be replaced.
If glucose drops too fast, Cerebral edema develops. Lower serum glucose at rate of 50-100mg/dl/hour. |
|
|
Adrenal Insuff
|
Presents with hypotension, confusion. May occur in minor urinary or respiratory tract infections. (e.g. recent cough/fever) other findings may include loss of mineralocorticoid action: high/normal potassium, low/normal sodium, increased creatinine.)
|
|
|
Acromegaly
|
Adult with elevated IGF-1 level, acral enlargement, course facial features, protuberant jaw. DIAGNOSE with MRI of pituitary. TREAT with transphenoidal resection
|
|
|
Thyroid nodule
|
if Euthyroid, male --> suspect malignancy. Other risk factors include - firm, fixed nodule; MANAGE suspected malignancy with FNA.
|
|
|
Thyroid workup
|
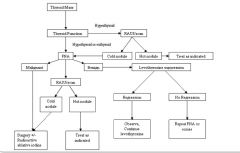
|
|
|
Prolactinoma
|
Bitemporal hemianopsia, erectile dysfunction, loss of libido, elevations of prolactin. Often, medication induced. If truly a macroadenoma, get MRI pituitary and bromocriptine may be used temporarily.
|
|
|
Grave's disease -
|
aka thyroid ophtalmopathy. Cigarette smoking has been linked to disease severity. Diplopia results frominfiltration of extraocular muscles. Exophtalmos may be unilateral
|
|
|
1' Hyperparathyroidism
|
Results from parathyroid producing too much PTH --> hypercalcemia, maybe hypophosphatemia; TREAT with surgical evaluation; "STONES, BONES, and ABDOMINAL GROANS"
|
|
|
2' Hyperparathyroidism
|
Results from renal disease and hypocalcemia/phosphatemia, leading to secondary hyperparathyroidism. TREAT underlying disease, maybe vitamin D.
|

