![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for glycolysis?
|
Phosphofructokinase-1
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for gluconeogenesis?
|
Fructose-1,6-biphosphate
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for the TCA cycle?
|
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for glycogen synthesis?
|
Glycogen synthase
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for glycogenolysis?
|
Glycogen phosphorylase
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for the HMP shunt?
|
G6PD
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for de novo pyrimidine synthesis?
|
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for de novo purine synthesis?
|
Glutamine-PRPP-amidotransferase
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for the urea cycle?
|
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for fatty acid synthesis?
|
Acetyl-CoA-carboxylase
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for fatty acid oxidation?
|
Carnitine acyltransferase I
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for ketogenesis?
|
HMG CoA synthase
|
|
|
Which enzyme is the rate limiting step for cholesterol synthesis?
|
HMG-CoA reductase
|
|
|
What is the mnemonic for the gycogen storage diseases?
|
Very Poor Carbohydrate Metabolism
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in Von Gierke's disease (type I)?
|
Glucose-6-phosphotase; severe fasting hypoglycemia, increased glycogen in the liver, increased blood lactate and hepatomegaly.
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in Pompe's disease (type II)?
|
Lysosomal a-1,4-glucosidase; cardiomegaly and systemic findings
Pompe's trashes the Pump (heart liver and muscle) |
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in Cori's disease (type III)?
|
Debranching enzyme (a-1,6-glucosidase); milder form of type I with normal blood lactate levels; gluconeogenesis is intact
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in McArdle's disease (type V)?
|
Skeletal muscle glycogen phosphorylase; increased glycogen in muscle, but cannot break it down, leading to painful muscle cramps and myoglobinuria with exercise.
McArdles = Muscle |
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in the lysosomal storage disorder Fabry's disease?
|
a-galactosidase A; peripheral neuropathy of hands/feet, cardiovascular and renal disease, X-recessive.
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in the lysosomal storage disorder Gaucher's disease?
|
Glucocerebrosidase; hepatosplenomegaly, aseptic necrosis of femur, Gaucher's cells (look like crumpled tissue paper). A-recessive
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in the lysosomal storage disorder Neimann-Pick disease?
|
Sphinomyelinase; neurodegeneration, cherry red spot on macula, foam cells, A-recessive.
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in the lysosomal storage disorder Tay-Sachs disease?
|
Hexosaminidase A; neurodegeneration, cherry red spot on macula, onion-skinned lysosomes, NO hepatosplenomegaly, A-recessive
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in the lysosomal storage disorder Krabbe's disease?
|
B-galacocerebrosidase; peripheral neuropathy, optic atrophy, globoid cells, A-recessive
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in the lysosomal storage disorder Metachromatic Leukodystrophy?
|
Arylsulfatase A; central and peripheral demyelination with ataxia and dementia; A-recessive.
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in the lysosomal storage disorder Hurlers' syndrome?
|
a-L-iduronidase (accumulates heparin.dermatan sulfate); gargoylism, airway obstruction, corneal clouding, hepatosplenomegaly, A-recessive
|
|
|
Which enzyme is deficient in the lysosomal storage disorder Hunter's syndrome?
|
Iduronate sulfatase; Mild Hurler's + aggressive behavior, no corneal clouding, X-recessive
|
|
|
Mnemonic for Neiman-Pick, Tay-Sachs and Hunters:
|
No man picks (Neimann-Pick) his nose with his sphinger (sphingomyelinase).
Tay-SaX (tay-sachs) lacks heXosaminidase. Hunters see clearly (no corneal clouding) and aim for the X (X-recessive). |
|
|
At what stage are primary oocytes held until ovulation?
|
Prophase of meiosis I.
|
|
|
At what stage of meiosis II is an egg released during ovulation?
|
Metaphase
|
|
|
Complete mole:
|
Normal 46XX karyotype; results from fertilization of an empty egg with a haploid 23X sperm. Complete moles are characterized by generalized edema of chorionic villi forming grape-like transparent vesicles and an absence of a fetus.
Partial moles are usually triploid (69XXX or 69XXY) due to fertilization of an egg with two sperm. * Preeclampsia during first trimester, MASSIVELY elevated hCG levels. |
|
|
Derivatives of pharyngeal arch 1:
|
Cranial nerve V
Muscles of mastication Maxilla, Mandible, Malleus, Incus |
|
|
Derivatives of pharyngeal arch 2:
|
Cranial nerve VII
Muscles of facial expression. Stapes. |
|
|
Derivatives of pharyngeal arch 3:
|
Cranial nerve IX
Common carotid and internal carotid arteries. |
|
|
Derivatives of pharyngeal arch 4:
|
Cranial nerve X
Muscles of soft palate, muscles of the pharynx, right subclavian artery, arch of aorta. |
|
|
Derivatives of pharyngeal arch 6:
|
Cranial nerve X (recurrent part).
Muscles of larynx, upper muscles of esophagus, pulmonary arteries, ductus arteriosus. |
|
|
Derivatives of the pharyngeal pouches:
|
1 - epithelial lining of auditory tube and middle ear cavity.
2 - epithelial lining of palatine tonsil crypts 3 - inferior parathyroid glands, thymus 4 - superior parathyroid gland |
|
|
Differences between a direct and an indirect inguinal hernia:
|
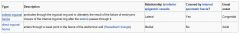
|
|
|
What is the difference between Erb's and Klumpke's palsy?
|
Erb's palsy is an adduction injury to the upper brachial plexus, whereas Klumpke's palsy is an abduction injury to the lower brachial plexus that may involve the sympathetic chain at T1 producing Horner's syndrome.
|

