![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Initial stroke management?
|
1. check if > or < 3 - 4.5 hours
2. CT scan to look for bleeding, infarcts, etc 3. if < 3 hours: fibrinolytic therapy 4. if > 3 hours: ASA and permissive HTN 5. If patient has difficulty speaking, must do swallow study before giving anything oral ==> then can give oral ASA, statin 6. NO indication for mannitol in acute setting 7. patient should receive full-dose heparin b/c 2-10% will get DVT |
|
|
what is permissive BP in ischemic stroke? In hemorrhagic stroke?
|
- ischemic stroke: up to 220/120
- hemorrhagic: ~140; can use Nicardipine (CCB) given IV to control BP |
|
|
If pt undergoes TPA, next step?
|
- don't give heparin, ASA, until 24-48 hours after for DVT ppx
- control BP ~180/105 with IV labetalol, nicardicpine, sodium nitroprusside |
|
|
MMSE dementia cut off?
|
- less than 24 points is 82% specific for dementia
|
|
|
initial presentation of dementia workup?
|
- 20% have reversible cause thus academy of neurology recommends following tests: CBC, Chem7, glucose, B12, depression screen, B12, LFTs
- only test for syphilis in those that have RF, prior hx, or live in high risk area |
|
|
dementia sx due to hypoTH?
|
- macrocytosis (nl=80-100), hyponatremia, bradypsyche (slowed thought process), slowed speech, delayed ankle reflex
|
|
|
Medial medullary syndrome?
|
- occlusion of vertebral artery or branch ==> contralateral paralysis of arm and leg, contralateral tactile, vibrating position sense, tongue deviation to injured side
- tongue deviation: each half of tongue pushes to other side, so weak left side means tongue is pushed to left |
|
|
Right Lateral midpontine syndrome?
|
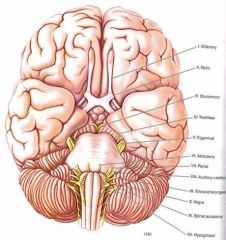
The loss of pain and temperature sensation on the right side of his face and left side of his body suggest injury to the spinothalamic tract on the right and the sensory division of CN 5 on the right side. The lack of a direct and consensual corneal response from stimulation of the eye on the right is also consistent with a 5th nerve sensory loss on the right. Motor weakness of the muscles of mastication, diminished jaw jerk and the pointing of the jaw to the right is consistent with injury to the motor fibers of the 5th nerve on the right; hence, both motor and sensory divisions of CN 5.
Motor examination indicated weakness and incoordination of the right arm and leg which is consistent with injury to the right cerebellar hemisphere or in this case the right middle cerebellar peduncle. The short circumferential branches of the basilar artery at mid-pontine levels serve the middle cerebellar peduncle and in the tegmentum the motor and sensory root of the trigeminal nerve and the nearby spinothalamic tract. |
|
|
Wallenberg syndrome?
|
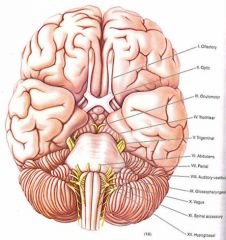
- lesion of lateral medulla ==> ipsilateral Horner syndrome, loss of pain and temperature sensation of face, weakness of palate, pharynx, vocal cords, cerebellar ataxia,
- loss of pain and temperature on contralateral side of body http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lateral_medullary_syndrome |
|
|
Lesion of central midbrain?
|
- many different syndromes are possible: Weber's, Benedikt's, Calude's, Nothragel, Parindaud
- common in all: oculomotor paresis, CN III fx abnormalities - may happen: cerebellar ataxia, contralateral hemiplegia |
|
|
Sx of hypoCa2+
|
- muscle spasms, hand contractures ==> repetitive tonic-clonic sz
|
|
|
who's at risk for hypoCa2+
|
- pts with renal or hepatic failure, hypothermia, shock who receives blood transfusion ==> unable to metabolize citrate to lactate ==> citrate binds to calcium
- NOTE: serum Ca2+ levels may be normal b/c deficit is of ionized calcium - thus give ppx of 10cc of 10% calcium gluconate for 500ml of pRBC |
|
|
When to give sodium bicarb?
|
- if levels are extremely low (5mEq/ml or less)
|
|
|
C/I to tPA?
|
- presence of internal bleeding, bleeding diathesis (plt <100,000), recent extracranial surgery or trauma in past 14d, hypodensity in > 33% of arterial territory of CT, intracranial hemorrhage on CT, intracranial surgery in last 3 mo, BP >185/110
|
|
|
After acute stroke tx, what evaluation is done to determine etiology?
|
- carotid duplex U/S or MRA or CTA
- ECG - TTE or TEE |
|
|
CSF of traumatic LP?
|
- RBC > 6,000
- very telling: if 1 WBC per 750-1000 RBCs - elevated protein, elevated glucose - WBC/RBC ratio not exceeding 0.01 has 100% NPV for meningitis - ddx SAH by xanthochromia |
|
|
work up of suspected SAH?
|
- sx: headache, neck pain, vomiting
- CT scan ==> may be neg in 5-10% pts ==> then do lumbar puncture ==> presence of xanthochromia |
|
|
features of opioid withdrawal?
|
- GI sx: cramps, diarrhea, vomiting
- dilated pupils, myalgias, autonomic disturbances - HTN, tachy - lacrimination/rhinorrhea, sweating - piloerection, insomnia |
|
|
pt with chronic warfarin use now with trauma? How to reverse quickly?
|
- fresh frozen plasma
- don't use vit K because it's too slow: liver has to use it to synthesize clotting factors |
|
|
Wenicke's triad? Tx?
|
- confusion, ataxia, nystagmus
- 2/2 thiamine deficiency ==> injury of mamillary bodies - give thiamine; giving glucose only will worsen sx |
|
|
sx that precipitates delirium?
|
- nystagmus
|
|
|
Korsakoff's psychosis?
|
- characteristic feature: confabulation
- antegrade amnesia is more common, psychosis, skin crawling - sequel of Wernicke's |
|
|
superior sagittal sinus thrombus?
|
- associated with trauma, infx, hypercoagulation, vasculitis, nephrotic syndrome, severe hydration, pregnancy
- sx: HA, hemiparesis, papilledema, seizures - MRI, MRV- hemorrhage in hemisphere white matter thrombus in superior sagittal sinus - tx: HEPARIN- even if there is hemorrhage on CT b/c bleeding is secondary to venous HTN |
|
|
Lesion of dominant parietal?
|
- usually left hemisphere
- Gertsmann syndrome: acalculia (can't perform simple arithmetic tasks); finger agnosia (inability to name individual fingers), agraphia (impaired writing); right/left confusion- can't distinguish left versus right |
|
|
Lesion of non-dominant parietal?
|
- construction apraxia (can't copy simple drawings)
- dressing apraxia (can't dress self) - confusion |
|
|
Lesion of dominant temporal lobe
|
- homonymous upper quadrantanopia
- LANGUAGE aphasia - wernicke's aphasia: incomprehension of spoken or written language |
|
|
Lesion of nondominant temporal lobe
|
- VISUAL disorder, homonymous upper quadrantaopia
- auditory agnosia |
|
|
pt with hx of HA/migraine who now presents with acute HA different from previous?
|
- CT/lumbar puncture to r/o SAH
- don't just treat as another migraine |
|
|
cardinal features of Parkinson's disease?
|
- 2 of 3: tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity
- often asymmetric presentation |
|
|
ddx Parkinson's
|
- look for Parkinson plus syndrome: falls early in course, dysautonomia, poor response to DA therapy
|
|
|
MS CSF
|
- oligoclonal bands
|
|
|
tx Parkinson's?
|
- start with pramipexole: DA agonist medication
- once sx worsen, use levodopa- save for later b/c of dyskinesia and other side effects - COMT inhibitor: prolongs effect of levodopa |
|
|
Tx essential tremor?
|
- benzos, primidone (anticonvulsants), propranolol
|
|
|
Best way to dx MS?
|
- MRI- demyelination in white matter especially periventricular and subpial white matter of cerebrum, optic nerves, brain stem, spinal cord
- CSF: elevated IgG index but nonspecific, oligoclonal bands don't confirm dx b/c high false positive |
|
|
Tx of MS?
|
- acute: IV methylprednisone-- doesn't prevent future relapses
- prevention of relapse or progression: immunosuppressive drugs (cyclophosphamide, beta interferon, glatiramer acetate) - plasmapheresis - repeat MRI in 3 months to monitor - advise contraception b/c teratogenic |
|
|
MS and pregnancy
|
- decreases relapse during pregnancy but increase in relapse post partum
|
|
|
prognostic sx in MS pts
|
- good: early age of onset, female, relapsing form
- initial presentation that are good: sensory sx or CN involvement (esp optic neuritis) - poor: cerebellum, brainstem, pyramidal sx, internuclear ophthalmoplegia, nystagmus, hemiparesis |
|
|
different gaits
|
- shuffling gait: barely picking up feet = parkinson's
- senile gait: "walking on ice;" feet wide apart, knees and hips flexed, arms wide as if expecting to fall - scissoring gait: circular leg movements, no flexion of knees = spastic paraparesis - drunken sailor gait- zigzag course = cerebellar ataxia - steppage gait - excessive elevation of legs, toes touch before heals = distal lower motor neuron dz |
|
|
vasovagal syncope
|
- aka common faint
- 2/2 strong emotional situation - do upright tilt table test |
|
|
ALS pathology
|
- involves LMN (anterior horn cells, brainstem neurons innervating bulbar muscles), and upper or corticospinal motor neurons
|
|
|
ALS sx?
|
- insidious asymmetric weakness in distal limb; cramping with volitional movements that occur early in AM
- weakness: wasting, atrophy of muscles, spontaneous twitching, fasciculation of motor units - bulbar muscles: difficulty with chewing, swallowing, fasciculations of face and tongue - preserved: ocular motility, sensory, bowel, bladder, cog fx |
|
|
Binswanger dz?
|
- vascular dementia of white matter ==> apathy, agitation, bilateral corticospinal or bulbar sx
|
|
|
tx of ALS
|
riluzole: glutamate inhibitor - prolong survival and delay need for tracheostomy
|
|
|
cluster HA sx?
|
- occurs 1-3x daily lasting 30min to 1 hour x 4-8wks
- severe retroorbital pan, lacrimation, conjunctival injection, rhinorrhea, sweating, pallor - can present as Horner's syndrome - ddx chronic migraines- migraines have no eye and nasal sx |
|
|
tx of cluster HA?
|
- preventative: verapamil, check ECG
- if verapamil fails, try Li - acute cluster: sumatriptan; avoid in CAD - very severe: 100% O2 |
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis?
|
- 2/2 Ab to ACh receptor
- fluctuating muscle weakness that worsens throughout day - usually have double vision 2/2 EOM weakness; also dysphagia and dysarthria - do CT- check for thymoma |
|
|
Meralgia paresthetics?
|
- very common syndrome 2/2 lateral femoral cutaneous nerve entrapment
- decrease sensation over anterolateral thigh - 2/2 obesity and tight garmets |
|
|
Creutzfeldt Jakob disease
|
- periodic sharp wave complexes observed on EEG
- 14-3-3 protein in CSF |
|
|
Alzheimer's pathology
|
- decrease ACh 2/2 degeneration of basal nucleus of Meynert and deficiency of acetyltransferase
|
|
|
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
|
- tacrine, donepezil
- increase behaviors and cog domains in Alz |
|
|
Benign essential tremor genetics?
|
- autosomal dominant inheritance
|
|
|
Tx of TIA
|
- tx RF like DM, HTN
- carotid etiology: clopidogrel or ASA but not BOTH- no extra benefit - warfarin if cardiogenic source |
|
|
tx of carotid stenosis?
|
- 70-99 stenosis: carotid endarterectomy; sometimes 50% even
- else antithrombic meds: ASA or Clopidogrel but not both |
|
|
Pick's disease
|
- frontal lobe dementia
- speech abnormalities: logorrhea, echolia, aphasia, mutism - impaired executive fx; hyperoral, irritable, disinhibtion - gliosis, neuronal loss, Pick bodies - silver staining cytoplasmic inclusions |
|
|
Lewy Body dementia?
|
- second most common dementia
- visual hallucinations, parkinsonism, falls are very common - cytoplasmic inclusions = lewy bodies |
|
|
explain hyperbili in B12 deficiency
|
- intense erythroid hyperplasia ==> erythroid precursors don't mature normally ==> die in bone marrow ==> anemia and indirect hyperbilirubinemia
- see increase LDH = hemolysis |
|
|
subarachnoid hemorrhage symptoms
|
- headache, neck pain, vomiting, hx HTN and presents with HTN
- get CT head - if CT head neg, get LP |
|
|
ascending paralysis after camping?
|
- neurotoxin secreting tick
- do a skin exam - ddx with GBS with normal CSF |
|
|
sx of GBS, etiology, tx
|
- flaccid paralysis and absence of DTRs
- etiology: campy, CMV, EBV, herpes - plasmapheresis or IVIG if severe disease (e.g. respiratory sx) - no role for steroids |
|
|
traumatic LP
|
- WBC to RBC is (1:750-1000)
- elevated protein and glucose |
|
|
Wallenberg syndrome
|
- Horner, loss of pain and temp of face, weakness of palate, pharynx, vocal cords, cerebellar ataxia
- LATERAL medulla |
|
|
medial medullary syndrome
|
- vertebral artery --> contralateral paralysis of arm and leg, loss of tactile, vibratory and position sense, tongue deviation to injured side
|
|
|
lateral midpontine syndrome
|
- impaired sensory and motor function of CNV w/ limb ataxia
|
|
|
medial pontine syndrome
|
- ipsilateral limb ataxia and contralateral eye deviation and paralysis of face, arm, and leg
- variable impairment of touch and position sense |
|
|
central midbrain lesion
|
- many syndromes: weber's, benedikt's, claude, nothnagel, parinaud
- all share oculomotor paresis and other CNIII dysfx and cerebellar ataxia and contralateral hemiplegia |
|
|
delirium with increased MCV
|
- b12
|
|
|
pt with bell's palsy, next step?
|
- check ears for HSV
- don't do lyme titers-- lyme doesn't cause bell's, it can cause facial palsy, but see other signs of lyme as well - just give eye patch and artificial tears - can give CS and acyclovir |
|
|
impaired balance, impaired upward gaze, which tumor?
|
- pineal --> Parinaud's syndrome: loss of pupillary reaction, vertical gaze paralysis, loss of optokinetic nystagmus, ataxia, headache
- ddx craniopharyngioma where headache and other sx of anterior pit tumor vs pit tumor causing bitemporal hemianopsia but see hormonal dysfx |
|
|
tx of MS prevention
|
- beta-interferon or glatiramer acetate
- need contraception - relapses reduced in pregnancy but occurred in first 6months postpartum - get MRI in 3 months to follow course |
|
|
MS good prognosis
|
- early age, female, relapsing form
- initial sx: sensory, CN involvement esp optic neuritis - bad: cerebellum, brainstem, pyramidal, internuclear ophthalmoplegia, nystagmus, hemiparesis, brainstem, cerebellum, pyramidal system |
|
|
signs of hypoTH
|
- macrocytosis, hyponatremia, bradypsyche, slowed speech
|
|
|
AEDs safe for kids
|
- barbiturates, benzos, phenytoin, fosphenytoin
|
|
|
dementia with CT showing enlarged ventricles
|
- VP shunt
- look for wide based gaits, loss of urine |
|
|
meralgia paresthetica- which nerve
|
- lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
|
|
|
entrapment: femoral nerve, L5 and S1, obturator
|
- femoral: anterior and anteromedial thigh with quadriceps muscle weakness, decreased knee jerk
- L5 and S1: back pain down lateral or posterior aspect of leg, weakness of muscle - obturator: sensory loss over medial thigh and weakness in leg adduction |
|
|
pt with TIA
|
- tx with clopidogrel > aspirin
|
|
|
elevated LDH
|
- marker of hemolysis
|
|
|
toddler with suspected CP?
|
- get head CT
|
|
|
brain death findings
|
- absence of cerebral and brainstem function
- comatose, absent motor response, absent pupillary light reflex, absent gag, absent rooting, absent corneal and oculovestibular reflexes, absent apnea |
|
|
medications associated with pseudotumor cerebri?
|
- isotretinoin, all trans-retinoic acid, minocycline, tetracycline, cimetidine, CS, danazol, tamoxifen, levo, Li, nitrofurantoin
|
|
|
Lewy body dementai vs Alzheimers?
|
- lew body: dementia + 2 of 3: cognitive fluctuation ("mom has good days and bad days"), visual hallucinations, parkinsonism
- bad response to dopamine agonists! - tx with dopa and ACh-I |
|
|
psychogenic coma
|
- do ear canal cold water irrigation-- normal response: transient, conjugate, slow deviation of gaze to the side of the stimulus followed by saccadic correction to midline
|
|
|
vertebrobasilar insufficiency
|
- reduced blood flow to brain secondary to emboli, thrombi or dissection
- vertigo, dizziness, dysarthria, diplopia, numbness - resolves |

