![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Trace the bloody supply of the kidney from renal artery to nephrons |
Renal arteries -> Segmental arteries -> Interlobar arteries -> Arcuate arteries -> Cortical Radiate arteries -> Afferent arterioles RSI ACA |
|
|
Trace the blood supply of the kidney within the nephron. |
Glomerus -> Efferent arteriole -> Pertubular capillaries |
|
|
Trace the blood supply of the kidney from the nephrons to the renal vein. |
Pertubular capillaries -> Venules -> Cortical radiate veins -> Arcuate Veins -> Interlobar veins -> Renal vein PVC AIR |
|
|
What type of epithelial tissue covers the proximal tube? |
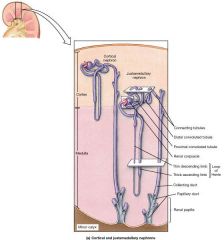
Simple Cubodial cells with microvilli |
|
|
What type of epithelial tissue covers the descending loop of Henle? |
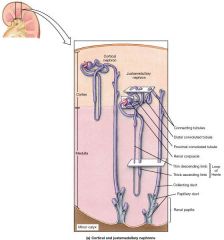
Simple Squamous or Low cuboidal cells |
|
|
What type of epithelial tissue covers the ascending loop of Henle? |
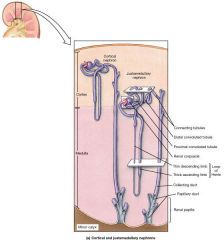
Simple Squamous or Low cuboidal cells |
|
|
What type of epithelial tissue covers the distal tubule? |
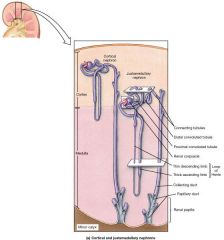
Cuboidal cells with few microvilli |
|
|
What type of epithelial tissue covers the collecting duct? |
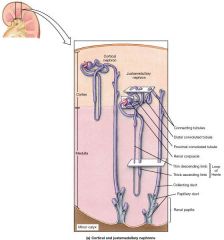
Cuboidal to columnar cells |
|
|
What type of epithelial tissue covers the papillary duct? |
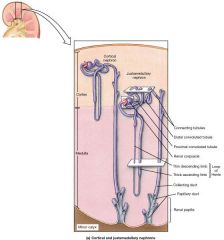
Columnar cells |
|
|
What forces filtrates to move across the filtration membrane? |
Pressure difference |
|
|
Where does 80% of reabsorption happen? |
It happens in the proximal tubules and the descending loop of henle |
|
|
In what part of the nephron is reabsorption regulated? |
In the distal tubules and collecting ducts. |
|
|
What is the filtration membrane? |
The filtration membrane is a barrier. It prevents blood cells and proteins from entering lumen of Bowman's capsule, but is many times more permeable than typical capillary. |
|
|
How do you calculate filtration pressure? |
Filtration pressure = GCP (Glomerular Capillary Pressure) - CP (Capsule Pressure) - BCOP (Clood Colloid Osmotic Pressure) |
|
|
What is glomerular capillary pressure (GCP)? |
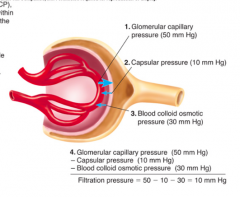
Blood pressure inside capillary tend to move fluid out of capillary into Bowman's capsule. |
|
|
What capsule pressure (CP)? |
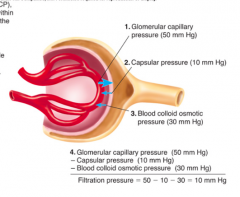
Pressure of filtrate already in the lumen |
|
|
What is blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP)? |
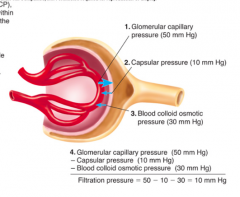
Osmotic pressure caused by proteins in blood. Favors fluid movement into the capillary from the lumen. BCOP is greater at the end of glomerular capillary than at beginning because of fluid leaving capillary and entering lumen. |
|
|
Where does tubule secretion occur? |
Secretion only takes place at the proximal and distal tubules. |
|
|
What is ADH? |
ADH, also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), increases the permeability of distal tubules and collecting ducts to water (water is reabsorbed resulting in low urine volume). |
|
|
What secretes ADH? |
ADH is secreted by the posterior pituitary gland. |
|
|
What would happen if ADH was not secreted? |
Insufficient ADH secretion results in diabetes insipidus |
|
|
If there is too much ADH secreted, what happens? |
High blood pressure. |
|
|
What is aldosterone? |
Aldosterone stimulates the conservation of sodium ions and the elimination of potassium ions. Aldosterone secretion occurs in response to a drop in blood Na+content, blood volume, or blood pressure, or to a rise in blood K+ concentration. |
|
|
What is atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH)? |
Hormones released by specialized cardiocytes when they are stretched by an abnormally large venous return; promotesfluid loss and reductions in blood pressure and invenous return. Includes atrial natriuretic peptide(ANP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP). |
|
|
What is the epithelium lining of the ureters? |
It is lined by transitional epithelium. |
|
|
Decreased blood colloid osmotic pressure affects renal function by |
Increasing net filtration rate |

